The BIS task force has developed five scenarios which highlight how Fintech disruption might play out, in a 50 page report “Implications of fintech developments for banks and bank supervisors.” Bankers will find it uncomfortable reading!
 Under the The Bank For International Settlements (BIS) five scenarios, the scope and pace of potential disruption varies significantly, but ALL scenarios show that banks will find it increasingly difficult to maintain their current operating models, given technological change and customer expectations.
Under the The Bank For International Settlements (BIS) five scenarios, the scope and pace of potential disruption varies significantly, but ALL scenarios show that banks will find it increasingly difficult to maintain their current operating models, given technological change and customer expectations.
The fast pace of change in fintech makes assessing the potential impact on banks and their business models challenging. While some market observers estimate that a significant portion of banks’ revenues, especially in retail banking, is at risk over the next 10 years, others claim that banks will be able to absorb or outcompete the new competitors, while improving their own efficiency and capabilities.
The task force used a categorisation of fintech innovations. Graph 1 depicts three product sectors, as well as market support services. The three sectors relate directly to core banking services, while the market support services relate to innovations and new technologies that are not specific to the financial sector but also play a significant role in fintech developments.
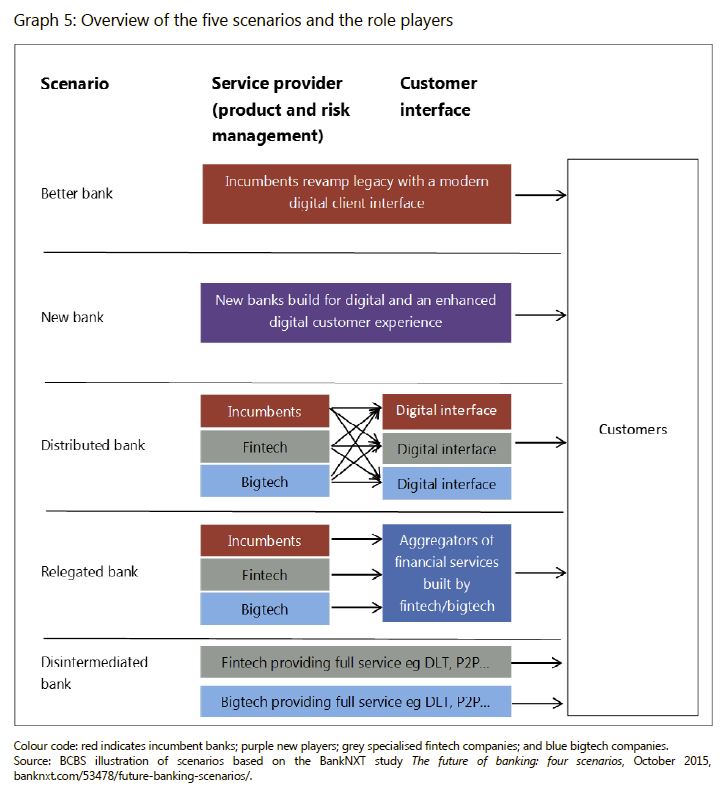
The analysis presented in this paper considered several scenarios and assessed their potential future impact on the banking industry. A common theme across the various scenarios is that banks will find it increasingly difficult to maintain their current operating models, given technological change and customer expectations. Industry experts opine that the future of banking will increasingly involve a battle for the customer relationship. To what extent incumbent banks or new fintech entrants will own the customer relationship varies across each scenario. However, the current position of incumbent banks will be challenged in almost every scenario.
1. The better bank: modernisation and digitisation of incumbent players
In this scenario the incumbent banks digitise and modernise themselves to retain the customer relationship and core banking services, leveraging enabling technologies to change their current business models.
Incumbent banks are generally under pressure to simultaneously improve cost efficiency and the customer relationship. However, because of their market knowledge and higher investment capacities, a potential outcome is that incumbent banks get better at providing services and products by adopting new technologies or improving existing ones. Enabling technologies such as cloud computing, big data, AI and DLT are being adopted or actively considered as a means of enhancing banks’ current products, services and operations.
Banks use new technologies to develop value propositions that cannot be effectively provided with their current infrastructure. The same technologies and processes utilised by non-bank innovators can also be implemented by incumbent banks, and examples may include:
- New technologies such as biometry, video, chatbots or AI may help banks to create sophisticated capacities for maintaining a value-added remote customer relationship, while securing transactions and mitigating fraud and AML/CFT risks. Many innovations seek to set up convenient but secure customer identification processes.
- Innovative payment services would also support the better bank scenario. Most banks have already developed branded mobile payments services or leveraged payment services provided by third parties that integrate with bank-operated legacy platforms. Customers may believe that their bank can provide a more secure mobile payments service than do non-bank alternatives.
- Banks may also be prone to offer partially or totally automated robo-advisor services, digital wealth management tools and even add-on services for customers with the intention of maintaining a competitive position in the retail banking market, retaining customers and attracting new ones.
- In this scenario, digitising the lending processes is becoming increasingly important to meet the consumer’s demands regarding speed, convenience and the cost of credit decision-making. Digitisation requires more efficient interfaces, processing tools, integration with legacy systems and document management systems, as well as sophisticated customer identification and fraud prevention tools. These can be achieved by the incumbent by developing its own lending platform, purchasing an existing one, white labelling or outsourcing to third-party service providers. This scenario assumes that current lending platforms will remain niche players.
While there are early signs that incumbents have added investment in digitisation and modernisation to their strategic planning, it remains to be seen to what extent this scenario will be dominant.2. The new bank: replacement of incumbents by challenger banks
In the future, according to the new bank scenario, incumbents cannot survive the wave of technology-enabled disruption and are replaced by new technology-driven banks, such as neo-banks, or banks instituted by bigtech companies, with full service “built-for-digital” banking platforms. The new banks apply advanced technology to provide banking services in a more cost-effective and innovative way. The new players may obtain banking licences under existing regulatory regimes and own the customer relationship, or they may have traditional banking partners.
Neo-banks seek a foothold in the banking sector with a modernised and digitised relationship model, moving away from the branch-centred customer relationship model. Neo-banks are unencumbered by legacy infrastructure and may be able to leverage new technology at a lower cost, more rapidly and in a more modern format.
Elements of this scenario are reflected in the emergence of neo- and challenger banks, such as Atom Bank and Monzo Bank in the United Kingdom, Bunq in the Netherlands, WeBank in China, Simple and Varo Money in the United States, N26 in Germany, Fidor in both the United Kingdom and Germany, and Wanap in Argentina. That said, no evidence has emerged to suggest that the current group of challenger banks has gained enough traction for the new bank scenario to become predominant.
Neo-banks make extensive use of technology in order to offer retail banking services predominantly through a smartphone app and internet-based platform. This may enable the neo-bank to provide banking services at a lower cost than could incumbent banks, which may become relatively less profitable due to their higher costs. Neo-banks target individuals, entrepreneurs and small to medium-sized enterprises. They offer a range of services from current accounts and overdrafts to a more extended range of services, including current, deposit and business accounts, credit cards, financial advice and loans. They leverage scalable infrastructure through cloud providers or API-based systems to better interact through online, mobile and social media-based platforms. The earnings model is predominantly based on fees and, to a lesser extent, on interest income, together with lower operating costs and a different approach to marketing their products, as neo-banks may adopt big data technologies and advanced data analytics. Incumbent banks, on the other hand, may be impeded by the scale and complexity of their current technology and data architecture, determined by factors such as legacy systems, organisational complexity and historical acquisitions. However, the customer acquisitions costs may be high in competitive banking systems and neo-banks’ revenues may be offset by their aggressive pricing strategies and their less-diverse revenue streams.
3. The distributed bank: fragmentation of financial services among specialised fintech firms and incumbent banks
In the distributed bank scenario, financial services become increasingly modularised, but incumbents can carve out enough of a niche to survive. Financial services may be provided by the incumbents or other financial service providers, whether fintech or bigtech, who can “plug and play” on the digital customer interface, which itself may be owned by any of the players in the market. Large numbers of new businesses emerge to provide specialised services without attempting to be universal or integrated retail banks – focusing rather on providing specific (niche) services. These businesses may choose not to compete for ownership of the entire customer relationship. Banks and other players compete to own the customer relationship as well as to provide core banking services.
In the distributed bank scenario, banks and fintech companies operate as joint ventures, partners or other structures where delivery of services is shared across parties. So as to retain the customer, whose expectations in terms of transparency and quality have increased, banks are also more apt to offer products and services from third-party suppliers. Consumers may use multiple financial service providers instead of remaining with a single financial partner.
Elements of this scenario are playing out, as evidenced by the increasing use of open APIs in some markets. Other examples that point towards the relevance of this scenario are:
- Lending platforms partner and share with banks the marketing of credit products, as well as the approval process, funding and compliance management. Lending platforms might also acquire licences, allowing them to do business without the need to cooperate with banks.
- Innovative payment services are emerging with joint ventures between banks and fintech firms offering innovative payment services. Consortiums supported by banks are currently seeking to establish mobile payments solutions as well as business cases based on DLT for enhancing transfer processes between participating banks (see Box 4 for details of mobile wallets).
- Robo-advisor or automated investment advisory services are provided by fintech firms through a bank or as part of a joint venture with a bank.
Innovative payment services are one of the most prominent and widespread fintech developments across regions. Payments processing is a fundamental banking operation with many different operational models and players. These models and structures have evolved over time, and recent advances in technological capabilities, such as in the area of instant payment, have accelerated this evolution. Differences in types of model, technology employed, product feature and regulatory frameworks in different jurisdictions pose different risks.
The adoption by consumers and banks of mobile wallets developed by third–party technology companies – for example, Apple Pay, Samsung Pay,12 and Android Pay – is an example of the distributed bank scenario. Whereas some banks have developed mobile wallets in-house, others offer third-party wallets, given widespread customer adoption of these formats. While the bank continues to own the financial element of the customer relationship, it cedes control over the digital wallet experience and, in some cases, must share a portion of the transaction revenue facilitated through the third-party wallets.
Innovation in payment services has resulted in both opportunities and challenges for financial institutions. Many of the technologies allow incumbents to offer new products, gain new revenue streams and improve efficiencies. These technologies also let non-bank firms compete with banks in payments markets, especially in regions where such services are open to non-bank players (eg the Payment Service Directives in the European Union and the Payment Schemes or Payment Institutions Regulation in Brazil).
4. The relegated bank: incumbent banks become commoditised service providers and customer relationships are owned by new intermediaries
In the relegated bank scenario, incumbent banks become commoditised service providers and cede the direct customer relationship to other financial services providers, such as fintech and bigtech companies. The fintech and bigtech companies use front-end customer platforms to offer a variety of financial services from a diverse group of providers. They use incumbent banks for their banking licences to provide core commoditised banking services such as lending, deposit-taking and other banking activities. The relegated bank may or may not keep the balance sheet risk of these activities, depending on the contractual relationship with the fintech company.
In the relegated bank scenario, big data, cloud computing and AI are fully exploited through various configurations by front-end platforms that make innovative and extensive use of connectivity and data to improve the customer experience. The operators of such platforms have more scope to compete directly with banks for ownership of the customer relationship. For example, many data aggregators allow customers to manage diverse financial accounts on a single platform. In many jurisdictions consumers become increasingly comfortable with aggregators as the customer interface. Banks are relegated to being providers of commoditised functions such as operational processes and risk management, as service providers to the platforms that manage customer relationships.
Although the relegated bank scenario may seem unlikely at first, below are some examples of a modularised financial services industry where banks are relegated to providing only specific services to another player who owns the customer relationship:
- Growth of payment platforms has resulted in banks providing back office operations support in such areas as treasury and compliance functions. Fintech firms will directly engage with the customer and manage the product relationship. However, the licensed bank would still need to authenticate the customer to access funds from enrolled payment cards and accounts.
- Online lending platforms become the public-facing financial service provider and may extend the range of services provided beyond lending to become a new intermediary between customers and banks/funds/other financial institutions to intermediate all types of banking service (marketplace of financial services). Such lending platforms would organise the competition between financial institutions (bid solicitations) and protect the interests of consumers (eg by offering quality products at the lowest price). Incumbent banks would exist only to provide the operational and funding mechanisms.
- Banks become just one of many financial vehicles to which the robo-advisor directs customer investments and financial needs.
- Social media such as the instant messaging application WeChat13 in China leverage customer data to offer its customers tailored financial products and services from third parties, including banks. The Tencent group has launched WeBank, a licensed banking platform linked to the messaging application WeChat, to offer the products and services of third parties. WeBank/WeChat focuses on the customer relationship and exploits its data innovatively, while third parties such as banks are relegated to product and risk management.
5. The disintermediated bank: Banks have become irrelevant as customers interact directly with individual financial services providers.
Incumbent banks are no longer a significant player in the disintermediated bank scenario, because the need for balance sheet intermediation or for a trusted third party is removed. Banks are displaced from customer financial transactions by more agile platforms and technologies, which ensure a direct matching of final consumers depending on their financial needs (borrowing, making a payment, raising capital etc).
In this scenario, customers may have a more direct say in choosing the services and the provider, rather than sourcing such services via an intermediary bank. However, they also may assume more direct responsibility in transactions, increasing the risks they are exposed to. In the realm of peer-to-peer (P2P) lending for instance, the individual customers could be deemed to be the lenders (who potentially take on credit risk) and the borrowers (who may face increased conduct risk from potentially unregulated lenders and may lack financial advice or support in case of financial distress).
At the moment, this scenario seems far-fetched, but some limited examples of elements of the disintermediation scenario are already visible:
- P2P lending platforms could manage to attract a significant number of potential retail investors so as to address all funding needs of selected credit requests. P2P lending platforms have recourse to innovative credit scoring and approval processes, which are trusted by retail investors. That said, at present, the market share of P2P lenders is small in most jurisdictions. Additionally, it is worth noting that, in many jurisdictions, P2P lending platforms have switched to, or have incorporated elements of, a more diversified marketplace lending platform business model, which relies more on the funding provided by institutional investors (including banks) and funds than on retail investors.
- Cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin, effect value transfer and payments without the involvement of incumbent banks, using public DLT. But their widespread adoption for general transactional purposes has been constrained by a variety of factors, including price volatility, transaction anonymity – raising AML/CFT issues – and lack of scalability.
In practice the report highlights that a blend of scenarios is most likely.
The scenarios presented are extremes and there will likely be degrees of realisation and blends of different scenarios across business lines. Future evolutions may likely be a combination of the different scenarios with both fintech companies and banks owning aspects of the customer relationship while at the same time providing modular financial services for back office operations.
For example, Lending Club, a publicly traded US marketplace lending company, arguably exhibits elements of three of the five banking scenarios described. An incumbent bank that uses a “private label” solution based on Lending Club’s platform to originate and price consumer loans for its own balance sheet could be characterised as a “distributed bank”, in that the incumbent continues to own the customer relationship but shares the process and revenues with Lending Club.
Lending Club also matches some consumer loans with retail or institutional investors via a relationship with a regulated bank that does not own the customer relationship and is included in the transaction to facilitate the loan. In these transactions, the bank’s role can be described as a “relegated bank” scenario. Other marketplace lenders reflect the “disintermediated” bank scenario by facilitating direct P2P lending without the involvement of a bank at any stage.