Continued increases in shadow-banking regulation should be a net positive for system-wide stability and liquidity if maintained over the medium term, says Fitch Ratings.
Overall shadow-banking asset levels have remained manageable. However, more rapid growth in certain regions and activities is expected to attract additional regulatory scrutiny, given the potential indirect effects of market interconnectedness and/or asset price volatility on the overall financial system.
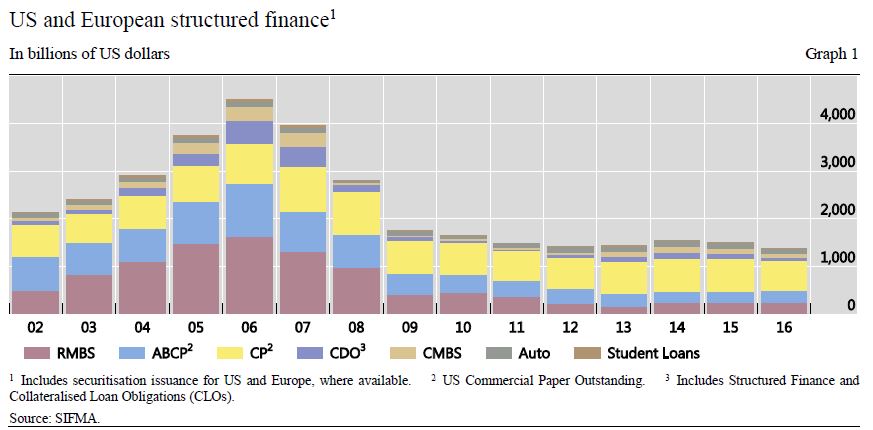
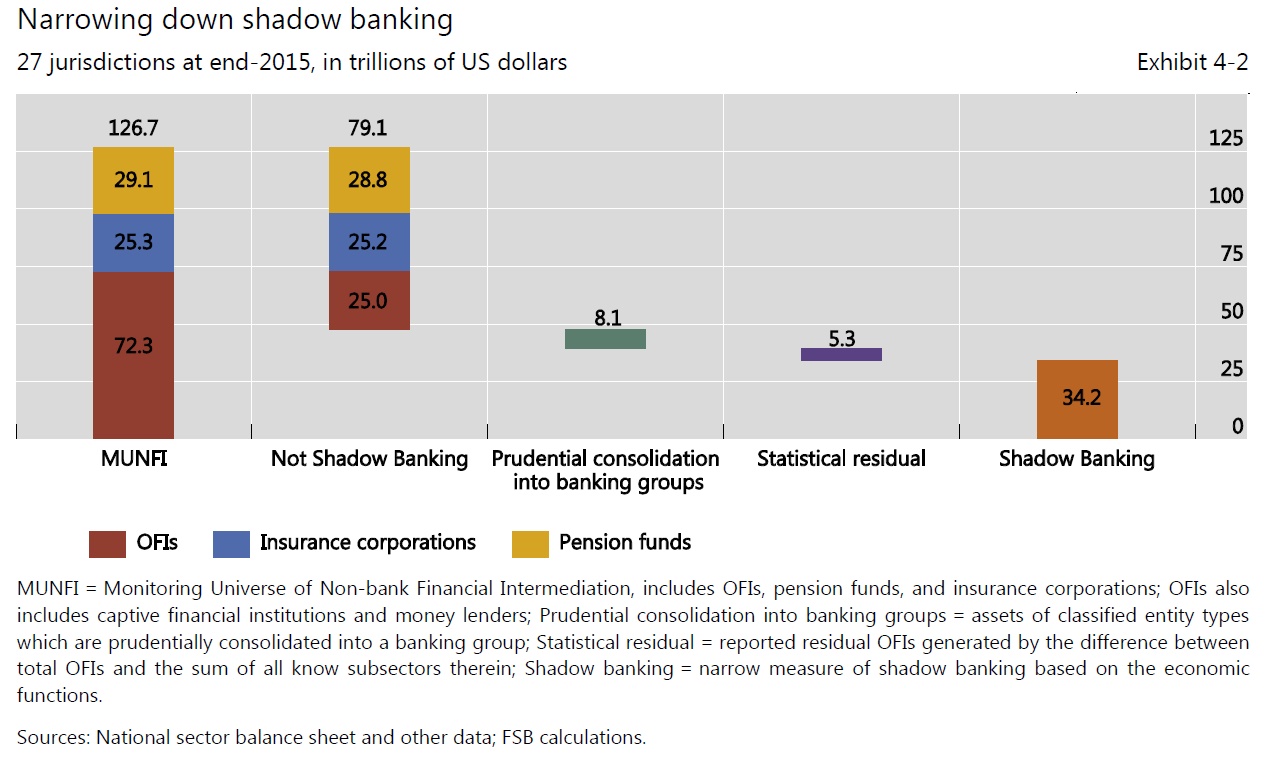
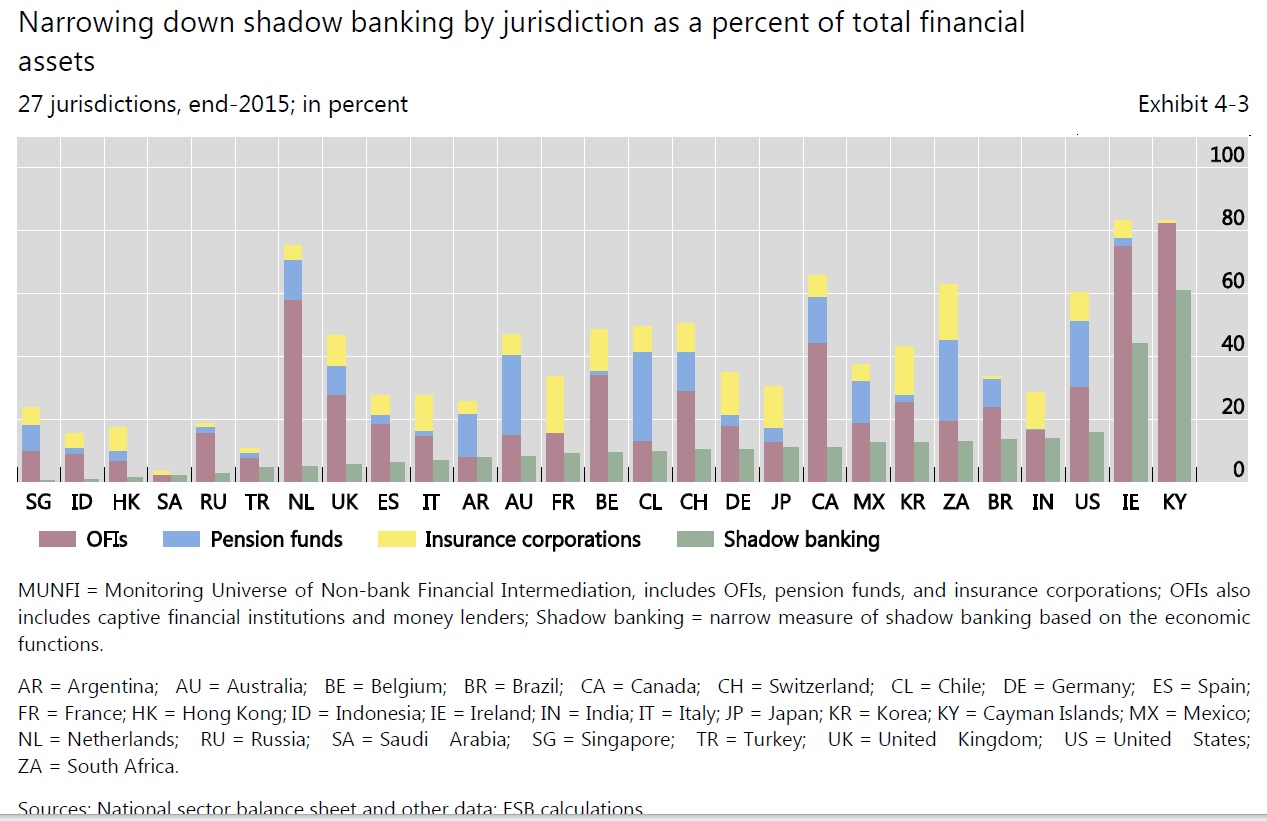
Shadow-banking assets were $45 trillion, as of YE16, or 13.2% of total global financial assets, according to the Financial Stability Board (FSB). This marked an increase of 7.6% over the previous year. In the US, shadow-banking assets remained relatively stable at $14.1 trillion, as of YE16, or 31.6% of total global shadow-banking assets. Conversely, China’s shadow-banking assets increased to $7 trillion, rising from 1.4% of total global shadow-banking assets in 2010 to 15.5% at YE16, a 40.1% CAGR on an exchange rate-adjusted basis, according the to the FSB. Euroarea shadow-banking assets were $10.1 trillion, as of YE16, falling to 22.4% of total global shadow-banking assets from 27.3% in 2010.
Of the $45 trillion of global shadow-banking assets at YE16, 72% were held by collective investment vehicles, such as open-end fixed income, money market, and credit hedge funds, which largely drove asset growth for the last five years. The inherent redemption risk of these vehicles could pressure asset prices in the event of runs, particularly if material leverage is employed.
Globally, banks continue to have modest direct exposure to Other Financial Intermediaries (OFIs), the FSB’s broad measure of shadow-banking activity, both in lending and borrowing. At YE16, aggregate funding and credit interconnectedness between banks and OFIs approximated pre-crisis (2003-2006) levels after several years of decline. Banks’ claims on OFI assets were $6.3 trillion, or 5.6% of total bank assets, while funding from OFIs was $5.9 trillion, or 5.4% of total funding. That said, given the level of broader interconnectedness between banks and shadow-bank participants, and the potential for regulatory arbitrage to be employed by market participants, global regulatory scrutiny is expected to continue.
China’s regulators have responded to rapid shadow-banking growth with increased oversight, particularly on wealth management and trust products, the origination, of which, have begun to level off after years of growth. The increased regulation is aimed at improved transparency and disclosure in order to reduce contagion risks within the system, rather than reducing the scale of shadow banking, which could disrupt the stability and liquidity of the financial system. We believe the Chinese government will continue to focus on regulation as long as it does not materially hamper GDP and economic growth.
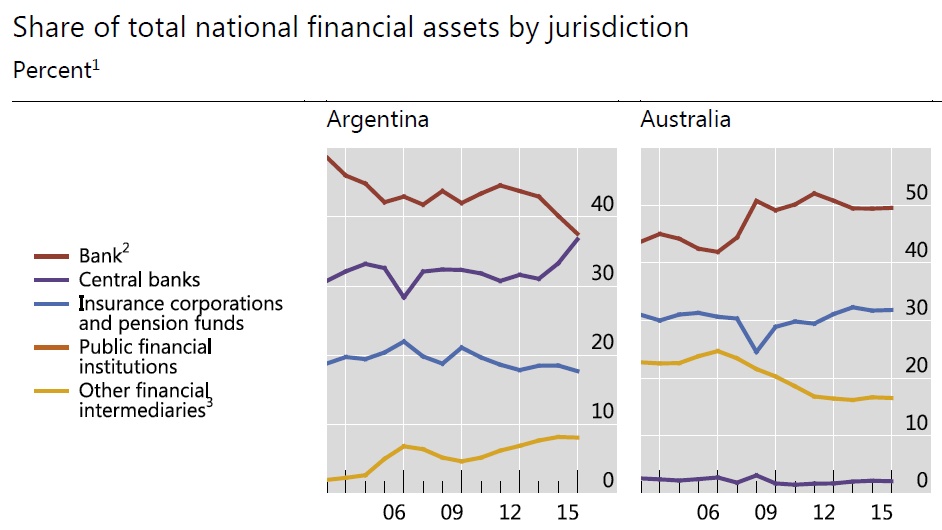
China’s shadow-banking sector is more systemic and complex than other more developed markets, with the extent of interconnectivity and risk, creating significant potential risk for Chinese banks. Unlike the US, where non-banks tend to be the dominant shadow-banking participants, banks are a key component in China’s shadow-banking ecosystem. While the shadow-banking products in China may be less complex than in the US, the evolving implicit/explicit guarantees in China make it more difficult to pinpoint who bears the ultimate investment risk. Smaller Chinese banks, relying on the interbank market and shadow banking for liquidity, may see rising funding costs as a result of increased regulation, while larger banks with stronger deposit franchises may be relatively better insulated than smaller, less capitalized peers.