Given the range of issues already exposed by the Royal Commission into Financial Services Misconduct, including selling loans outside suitable criteria, fees from advice not given and other factors; we need to ask about the impact on the profitability of the banks and so share prices.
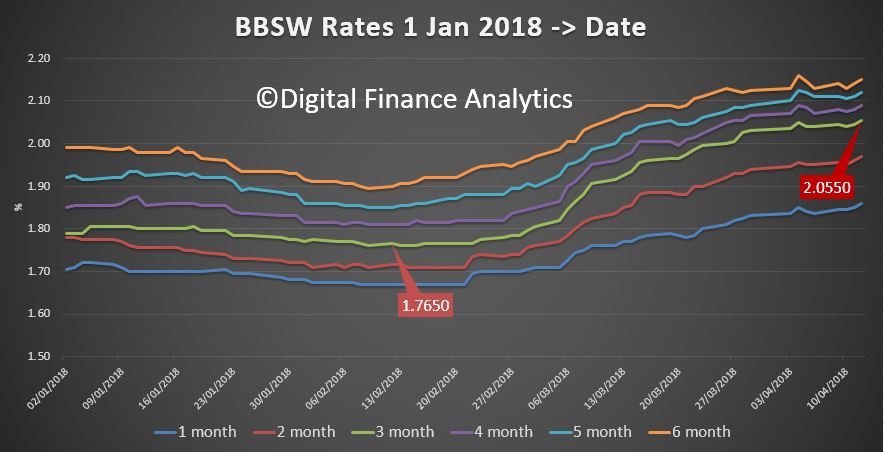
And all this is in the context of higher funding costs already hitting.
 A number of international investors and hedge funds have placed shorts on the major banks, signalling an expectation of further falls in share price ahead, but the majors have already dropped by around 15% in the past year.
A number of international investors and hedge funds have placed shorts on the major banks, signalling an expectation of further falls in share price ahead, but the majors have already dropped by around 15% in the past year.
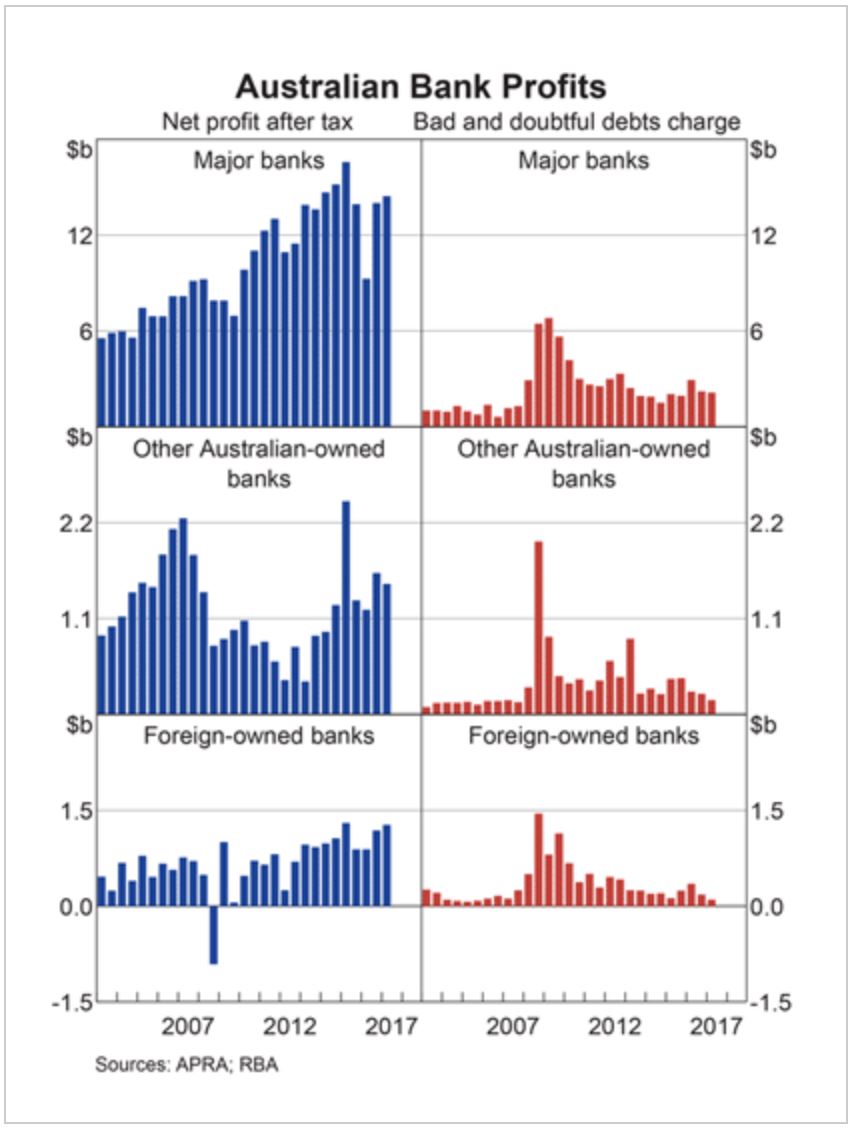
The recent RBA chart pack contained this picture on profitability. Bad and doubtful debts are very low, thanks to low interest rates. But that may change if rates were to rise, and “liar loans” are wide spread. There is no good data on the potential impact so far.
 It is important to remember the Productive Commission recently called out that :
It is important to remember the Productive Commission recently called out that :
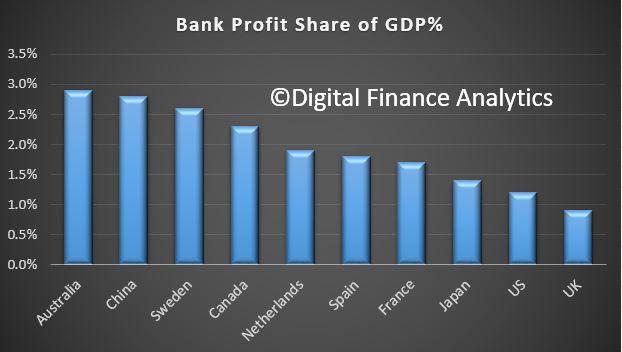
Data from news.com.au from 2016 shows the relative profit to GDP across several countries. Australia Wins.
That means 2.9 per cent of every $100 earned in Australia ends up as bank pre-tax profit, compared to the US and UK at $1.2 and 90 cents per cent respectively.
China is the highest after Australia at $2.80, Sweden $2.60 and Canada $2.30.
The Australia Institute also pointed to public money being used to secure the banking sector.
“Excessive profits provide a drag on the economy and hurt consumers who pay higher margins on bank products. The Reserve Bank found the big four banks enjoy an implicit government subsidy worth up to $4 billion dollars a year,”
The Royal Commission revelations have the potential to impact the market value of the banks as reflected in their share prices, and also raises questions about the financial stability of the entire system in Australia. APRA, in particular and the RBA have been (over?) focussed on financial stability, as the recent Productive Commission draft report highlighted.
Regulators have focused on a quest for financial stability prudential stability since the Global Financial Crisis, promoting the concept of an unquestionably strong financial system.
The institutional responsibility in the financial system for supporting competition is loosely shared across APRA, the RBA, ASIC and the ACCC. In a system where all are somewhat responsible, it is inevitable that (at important times) none are. Someone should.
The Council of Financial Regulators should be more transparent and publish minutes of their deliberations. Under the current regulatory architecture, promoting competition requires a serious rethink about how the RBA, APRA and ASIC consider competition and whether the Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC) is well-placed to do more than it currently can for competition in the financial system.
Over the next few days we will try to assess the potential impact ahead, from higher loss rates, lower fee income and potential fines and penalties. Then of course, there is the question, will these additional costs be passed on to investors and shareholders, or simply recovered from the current customer based by higher fees.
We expect banks to start making provisions for the revenue hits ahead. ANZ, for example, said their RC legal bill will be around $15 million. CBA made a $200 million expense provision for expected costs relating to currently known regulatory, compliance and remediation program costs, including the Financial Services Royal Commission.
To start the journey lets look at the relative performance of the banks’ share prices over the past year. Westpac share price is 16.8% lower compared with a year ago.
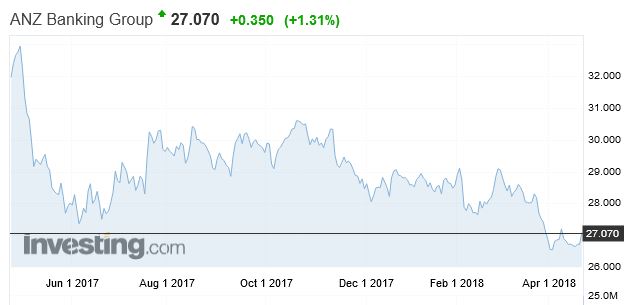
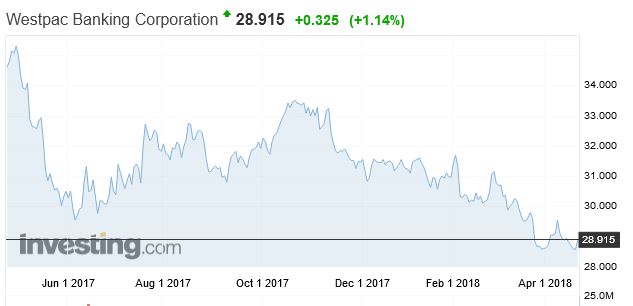 ANZ is down 16% over the same period
ANZ is down 16% over the same period
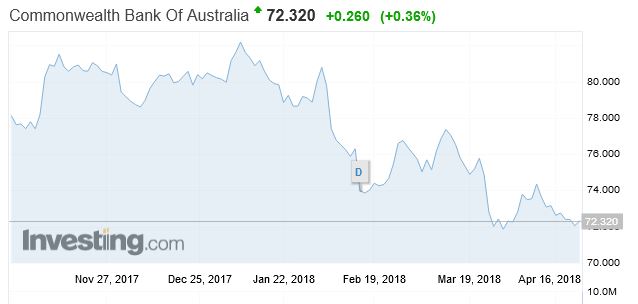
 CBA has fallen 15.9% in the past 12 months.
CBA has fallen 15.9% in the past 12 months.
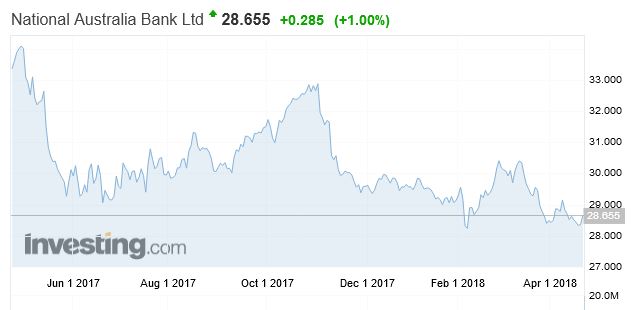
 and NAB’s share price dropped 14.2% over the same period.
and NAB’s share price dropped 14.2% over the same period.
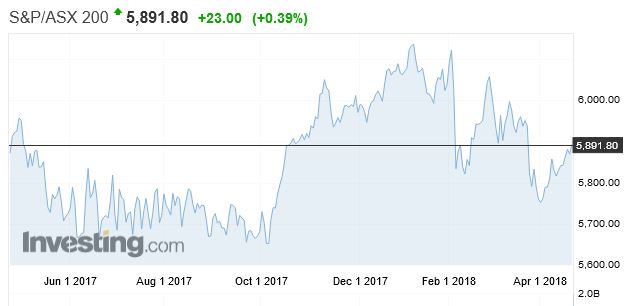
 In comparison, the ASX 200 is up 0.25% over the past year.
In comparison, the ASX 200 is up 0.25% over the past year.
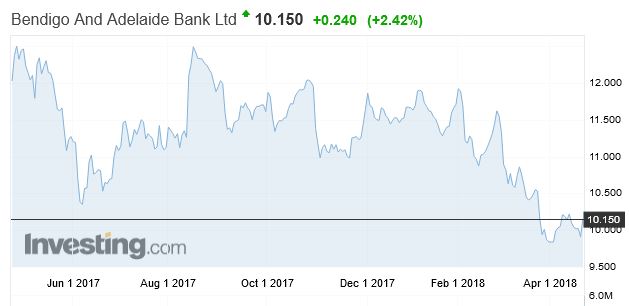
 Among the regional banks, Bendigo Bank has fallen 16.6%
Among the regional banks, Bendigo Bank has fallen 16.6%
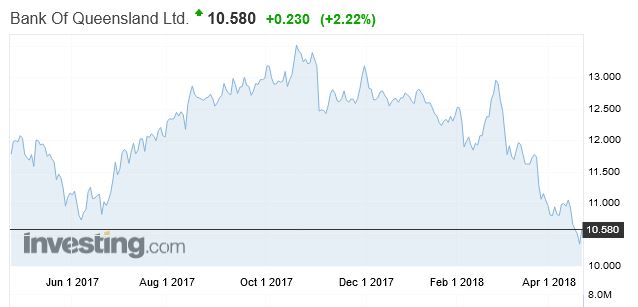
 Bank Of Queensland has fallen 11.7% over the past year.
Bank Of Queensland has fallen 11.7% over the past year.
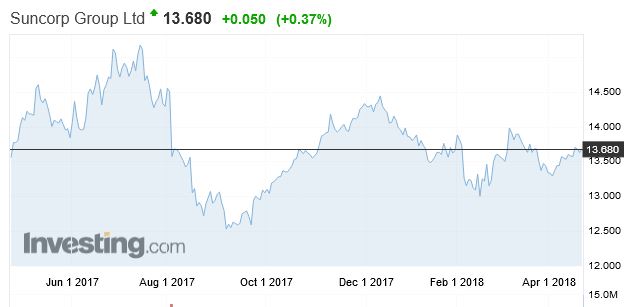
 In contrast Suncorp is 0.74% higher
In contrast Suncorp is 0.74% higher
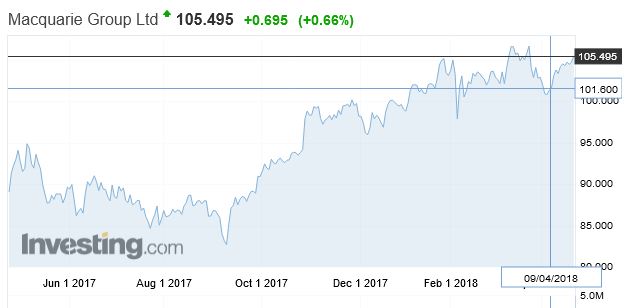
 and Macquarie Group was up 19.5%. They of course have more than half their business offshore now.
and Macquarie Group was up 19.5%. They of course have more than half their business offshore now.
Next time, we try to size the revenue hits ahead, and think about what that may mean for the banks and their customers.