Treasurer Morrison has release the report by King & Wood Mallesons partner Scott Farrell today in to open banking which aims to give consumers greater access to, and control over, their data. It mirrors recent UK developments, and is another nail in the competitive advantage the large players currently have. Later the scheme could be widened to other industry sectors, such as energy or telecommunications.
 This “open banking” regime mean that customers, including small businesses, can opt to instruct their bank to send data to a competitor, so it can be used to price or offer an alternative product or service.
This “open banking” regime mean that customers, including small businesses, can opt to instruct their bank to send data to a competitor, so it can be used to price or offer an alternative product or service.
The report recommends that the open banking regime should apply to all banks, though with the major banks to join it first. For non-banks and fintechs, the report wants a “graduated, risk-based accreditation standard”. Superannuation funds and insurers are not included for now.
In fact, all authorised deposit-taking institutions (ADIs) will automatically be accredited to receive data.
There are exclusions. For example, value added data which is created by banks as a result of their analysis will not be included in the regime. Know your customer data though should be sharable. De-identified aggregate data would not be sharable.
Data provided under the regime will initially be “read only”, but the successful adoption of open banking “could also lead to ‘write access’ reforms” in the future. The following products are called out as in scope.
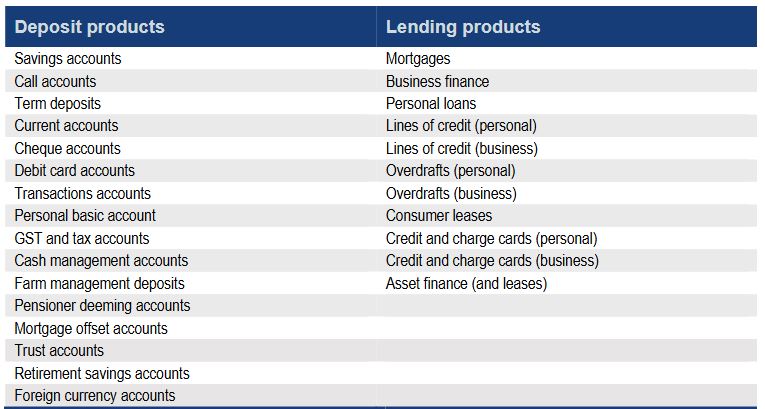 Transfer of data should be made free of charge, the report says.
Transfer of data should be made free of charge, the report says.
Safeguards will be important, including under the Privacy Act, and a customer’s consent under Open Banking must be explicit, fully informed and able to be permitted or constrained according to the customer’s instructions. Joint accounts will need some special considerations in terms of authority, and advice.
An appropriate data standard will need to be agreed, and a clear and comprehensive framework for the allocation of liability between participants in Open Banking should be implemented. This framework should make it clear that participants in Open Banking are liable for their own conduct, but not the conduct of other participants. To the extent possible, the liability framework should be consistent with existing legal frameworks to ensure that there is no uncertainty about the rights of customers or liability of data holders.
In terms of implementation, data holders should be required to allow customers to share information with eligible parties via a dedicated application programming interface, not screen scraping.
The starting point for the Standards for the data transfer mechanism should be the UK Open Banking technical specification.
A period of approximately 12 months between the announcement of a final Government decision on Open Banking and the Commencement Date should be allowed for implementation. From theCommencement Date, the four major Australian banks should be obliged tocomply with a direction to share data under Open Banking. The remaining AuthorisedDeposit-taking Institutions should be obliged to share data from 12 months after the
Commencement Date, unless the ACCC determines that a later date is more appropriate.
The ACCC as lead regulator should coordinate the development and implementation of a timely consumer education programme for Open Banking. Participants, industry groups and consumer advocacy groups should lead and participate, as appropriate, in consumer awareness and education activities.
The ABA welcomed the report:
Banks are excited to enter the Open Banking age that will spark new innovations and deliver cutting edge products, with customers the big winner.
The Farrell Report into Open Banking released by the Treasurer today recognises both the opportunities and challenges that data sharing will bring. While the Australian Bankers’ Association has some concerns surrounding the implementation, the report lays out a broadly sensible path to Open Banking. Mr Farrell’s report should be commended for its focus on customers and its commitment to work with stakeholders to design a safe and secure data sharing framework.
Giving customers greater access to their own data will boost choice in banking and further simplify the application process for a financial product.
Australians have one of the most innovative and technologically advanced banking systems in the world. Examples of this is 24-hour banking, payWave and the soon to be launched PayID and New Payments Platform.
As the Productivity Commission affirmed this week, Australian banks are at the forefront of global innovation which has delivered a superior customer experience. Investments in how banks use data are already leading to new innovations that are improving the customer experience and this is set to continue under Open Banking.
A reform as large as Open Banking must be carefully considered and properly implemented.
Research shows that Australians trust their banks with personal information, more than online retailers, social media companies and even governments. It’s important that banks maintain this trust and ensure that the open data reforms don’t place personal information at risk.
Banks will continue to work with stakeholders like consumer groups, FinTech’s, regulators and government to get this right so it is a good model for all industries and customers are protected.
The ABA looks forward to carefully analysing Mr Farrell’s report and working with members and stakeholders to address any challenges to ensure its success. Banks would also like to thank Mr Farrell for his thorough and thoughtful inquiry
