According to Moody’s the new Focus on US Banks’ Sales Practices Is Another Revenue Challenge.
Last Tuesday, Thomas Curry, head of the US Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC), indicated during testimony before the US Senate Banking, Housing and Urban Affairs Committee that his agency will conduct a horizontal review of sales practices at the nation’s largest banks. Later, Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) Director Richard Cordray added that his agency would be “doing a joint action” with the OCC.
We believe regulators will conduct a particularly thorough review of the industry’s sales practices in response to the media and political spotlights on Wells Fargo & Company’s (A2 stable) recently disclosed wrongdoings, the unauthorized opening of up to 2.1 million deposit or credit card accounts. For the banks, the additional regulatory focus is credit negative because it will increase scrutiny on deposit fees, which are a meaningful contributor to their revenue.
Deficient sales practices have only been highlighted at Wells Fargo and nowhere else. Nonetheless, in underscoring the need for a broader review, Mr. Curry highlighted the importance of incremental product sales and fees, noting that protracted low interest rates put the industry, not just Wells Fargo, “under enormous margin pressure.”
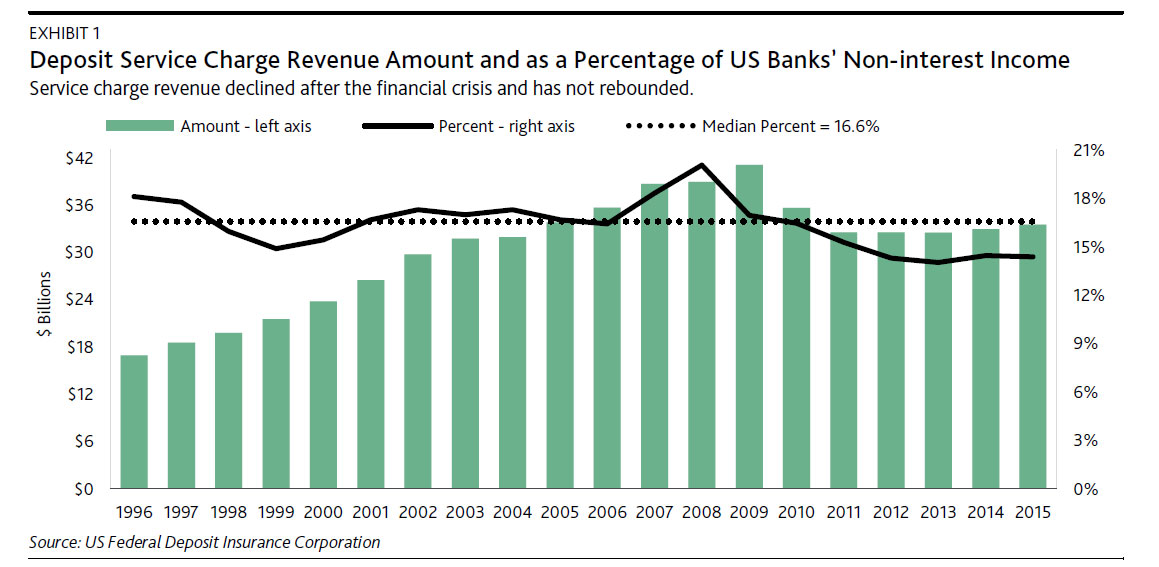
As shown in Exhibit 1, Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) data show that service charges on deposit accounts are significant for the industry, totaling nearly $34 billion in 2015, or 14% of total noninterest revenue. Large as this number is, it has fallen in absolute terms and as a percentage of non-interest income since the 2008-09 financial crisis, primarily because of heightened regulation. The additional exams announced last week will only reinforce existing scrutiny over specific revenue sources, such as overdraft fees.
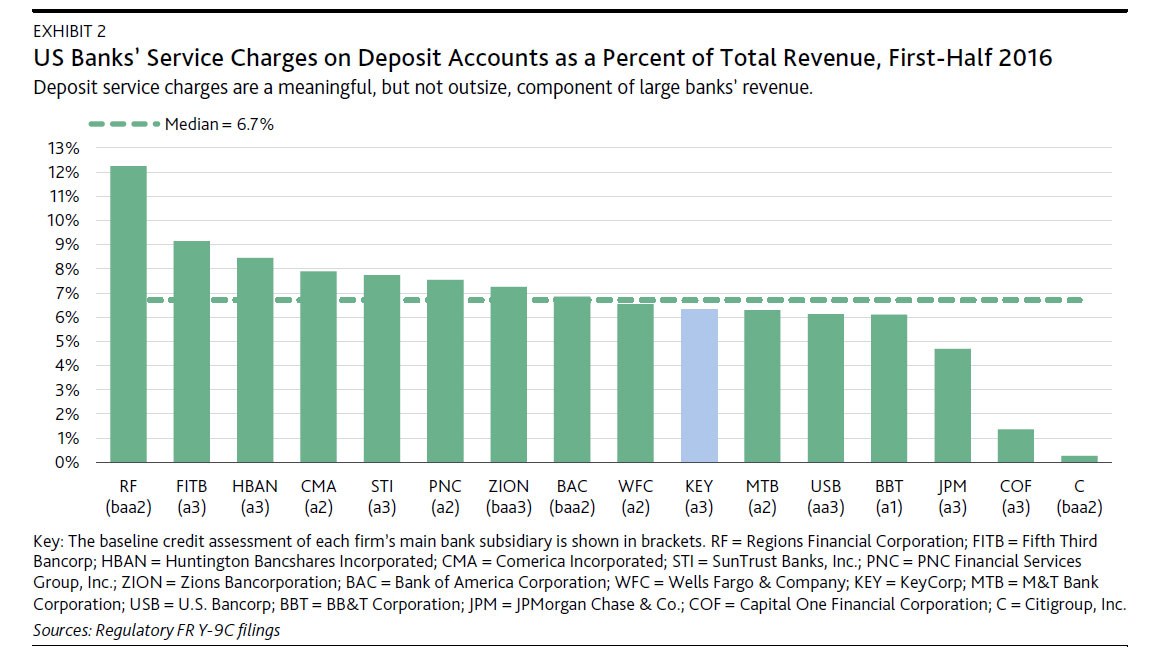
The misconduct at Wells Fargo has put all large banks in the regulators’ crosshairs. Exhibit 2 shows that for most large banks, deposit service charges are a meaningful contributor to overall revenue; that is, the combination of net-interest income and non-interest income. Specifically, for the first six months of 2016, 16 large banks reported a median contribution to total revenue of 6.7% from service charges on domestic deposit accounts, with one bank in the group, Regions Financial Corporation (Baa3 review for upgrade), earning 12% of its total revenue from this source.
Although some senators at last week’s hearing highlighted their worry that inappropriate sales practices could be widespread, that determination has not yet been made. Regardless, we believe the revelations at Wells Fargo will cause banks to tread cautiously before rolling out more aggressive sales initiatives in the current environment. That alone will constrain their revenue growth