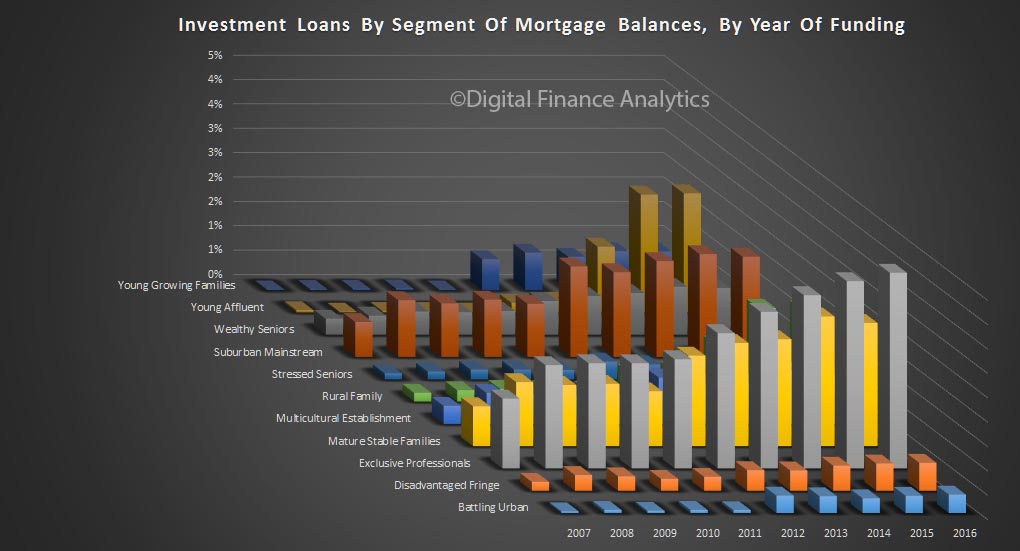
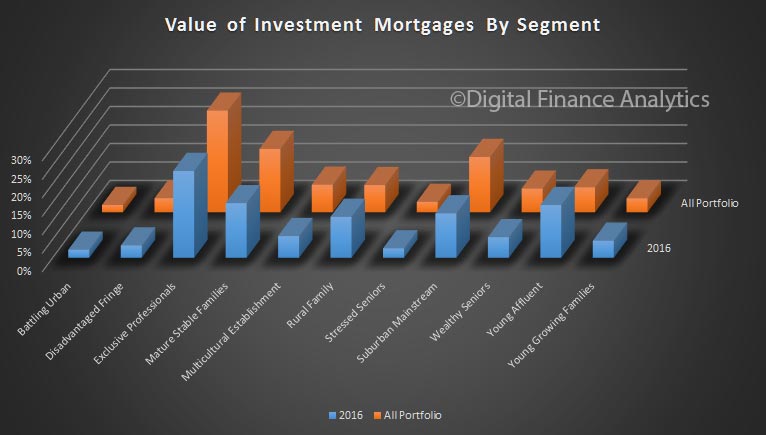
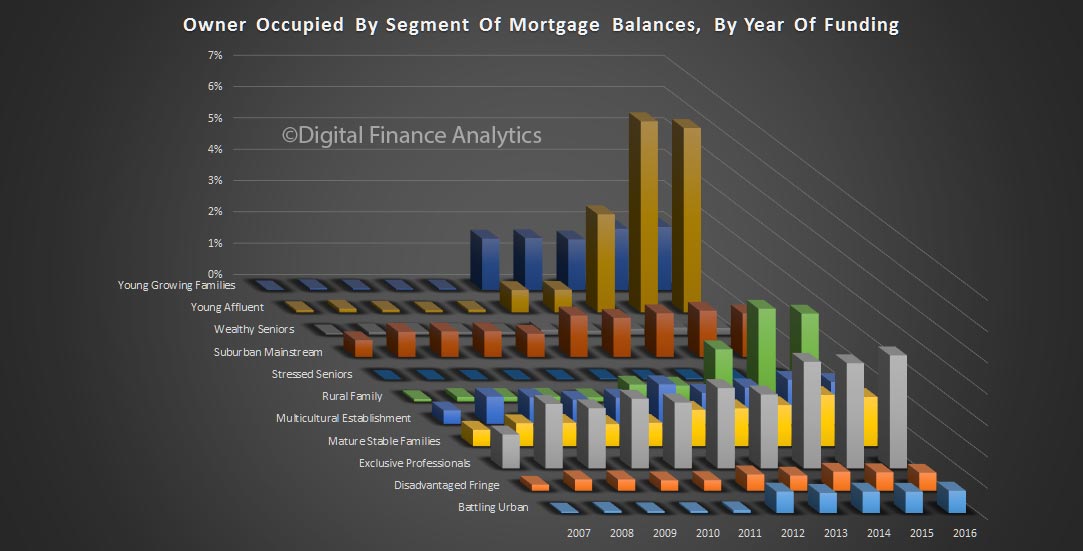
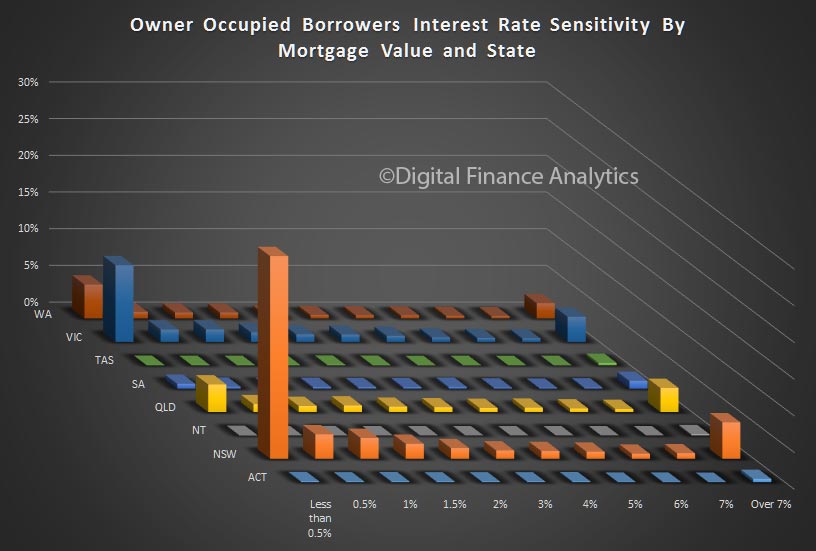
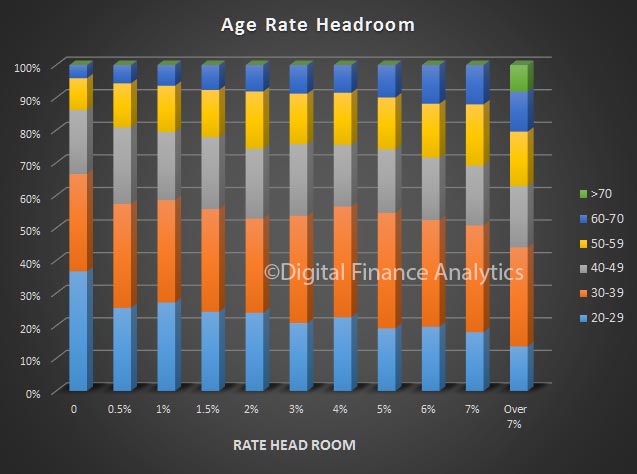
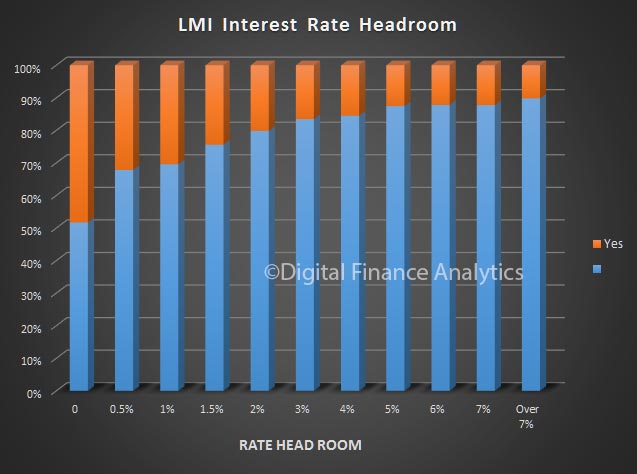
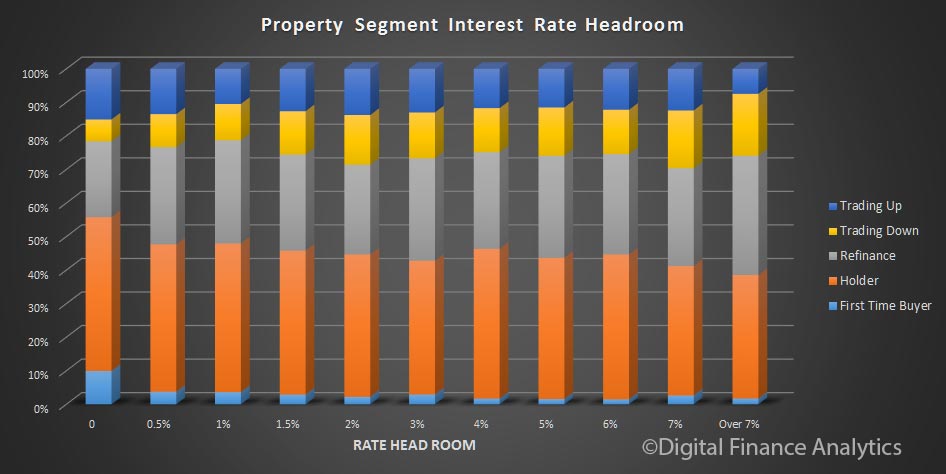
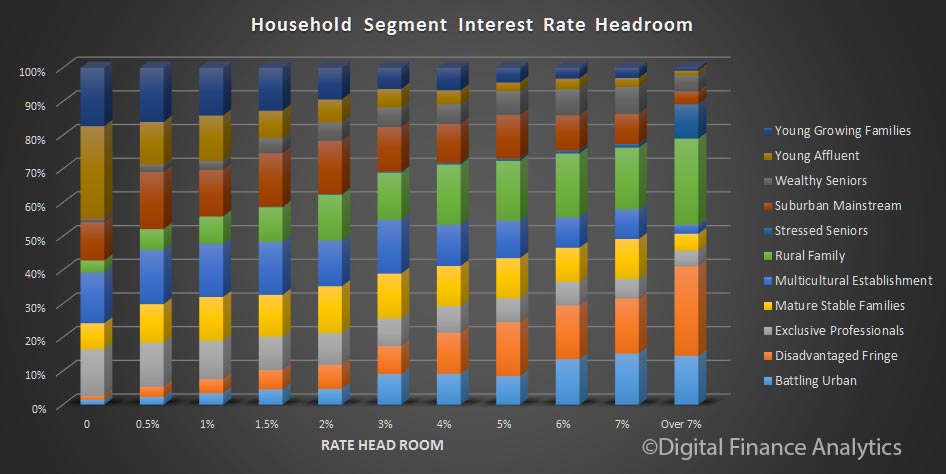
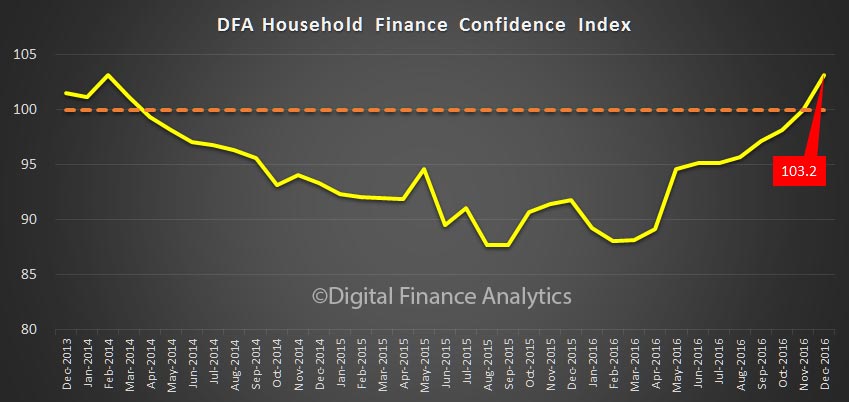
The latest Digital Finance Analytics Household Finance Confidence Index, to end December is released today. Overall household confidence is buoyant, and above the neutral setting. Sitting at 103.2, it is up from 100.02 in November.
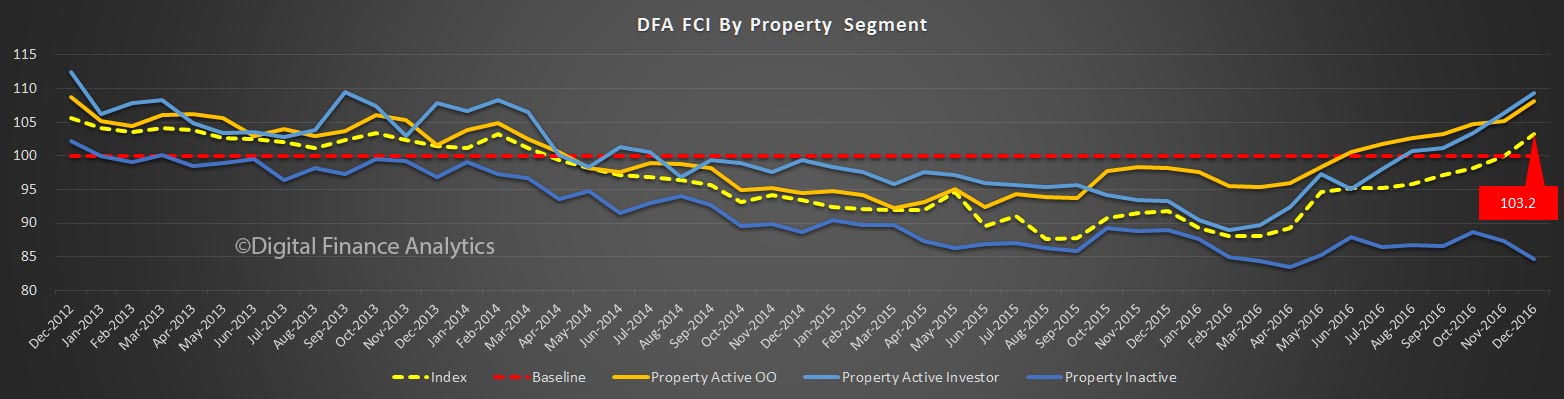
 The property “fairy” has been generous in that property is the key to the index at the moment, with positive news on home price rises, and the effect of the low interest rates following the last RBA cash rate cut flowing through. Home owners with an investment property have now overtaken the confidence score of owner occupied property holders, but both are higher. Those households who are not property active however continue to languish.
The property “fairy” has been generous in that property is the key to the index at the moment, with positive news on home price rises, and the effect of the low interest rates following the last RBA cash rate cut flowing through. Home owners with an investment property have now overtaken the confidence score of owner occupied property holders, but both are higher. Those households who are not property active however continue to languish.
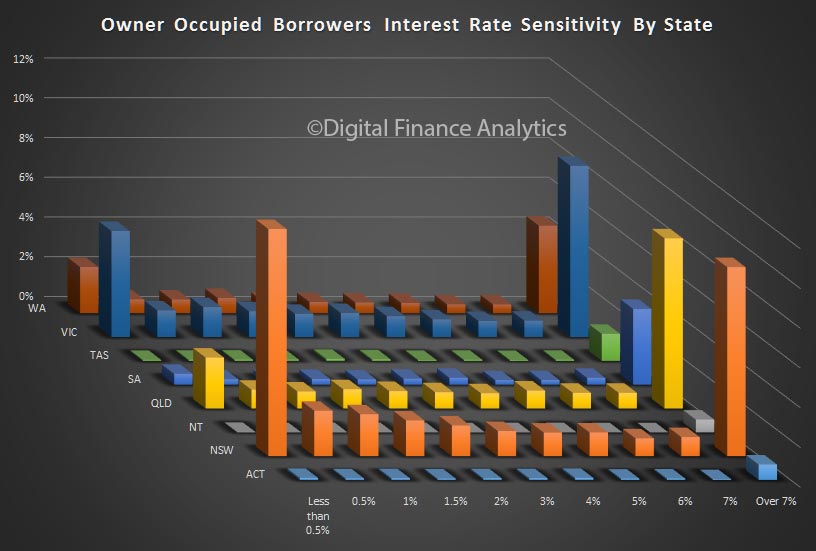
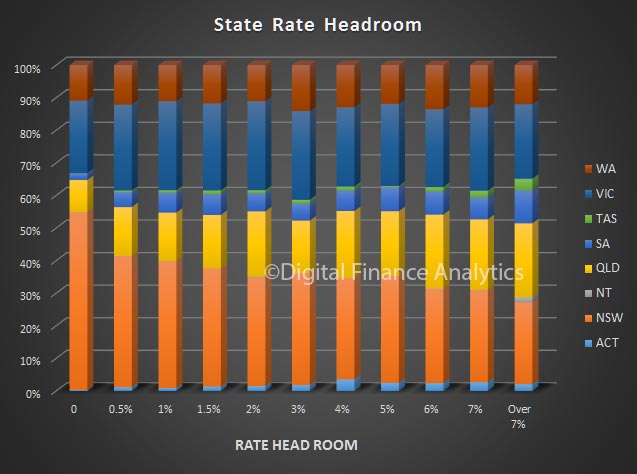
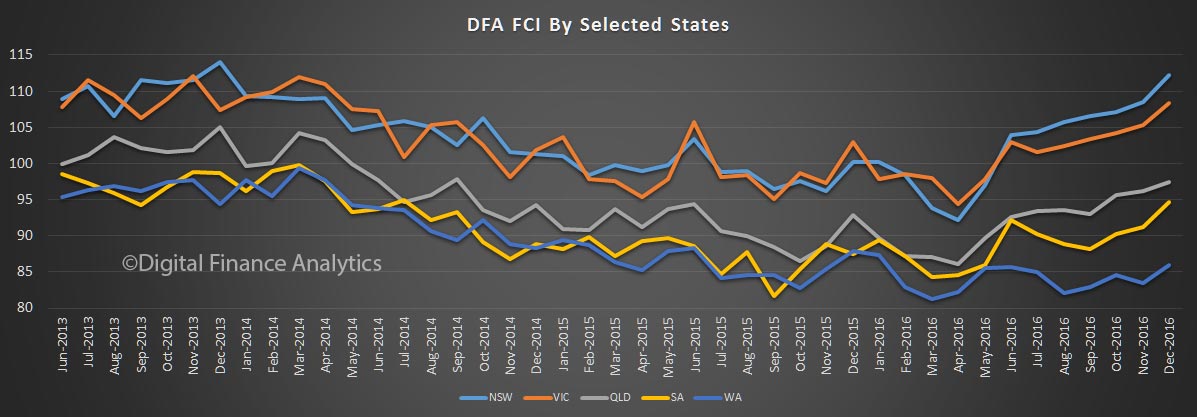
 We see significant state variations, with those in NSW and VIC most confident, whilst those in WA, although slightly higher, is significantly off the pace. The impact of changes to the first owner grant there will not flow through into the results for some time to come.
We see significant state variations, with those in NSW and VIC most confident, whilst those in WA, although slightly higher, is significantly off the pace. The impact of changes to the first owner grant there will not flow through into the results for some time to come.
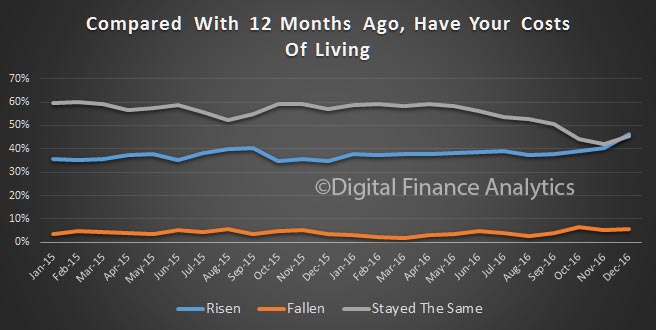
 The impact of positive property news has swamped a couple of the negative indicators. For example, more households are saying their costs of living have risen in the past 12 months.
The impact of positive property news has swamped a couple of the negative indicators. For example, more households are saying their costs of living have risen in the past 12 months.
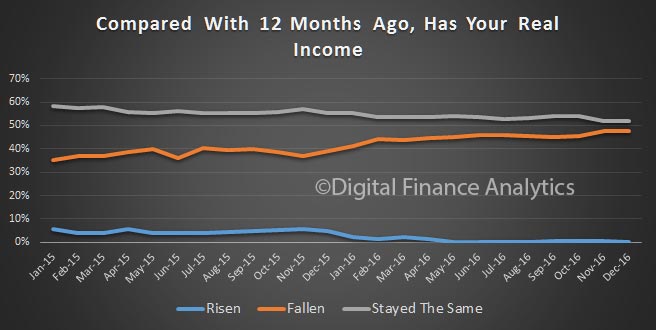
 In addition, real incomes, after adjusting for inflation are static or falling. Very few have had any pay rises above inflation, and many none at all.
In addition, real incomes, after adjusting for inflation are static or falling. Very few have had any pay rises above inflation, and many none at all.
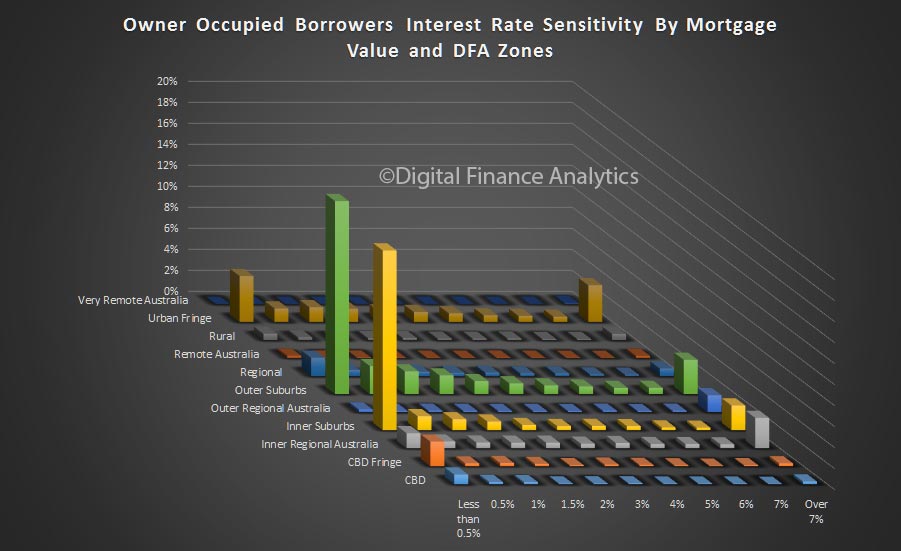
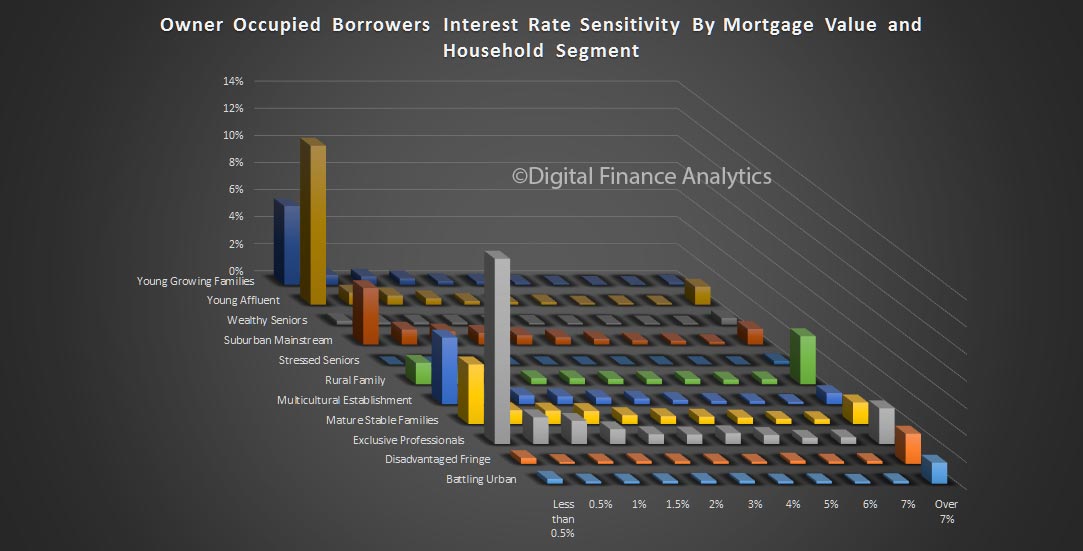
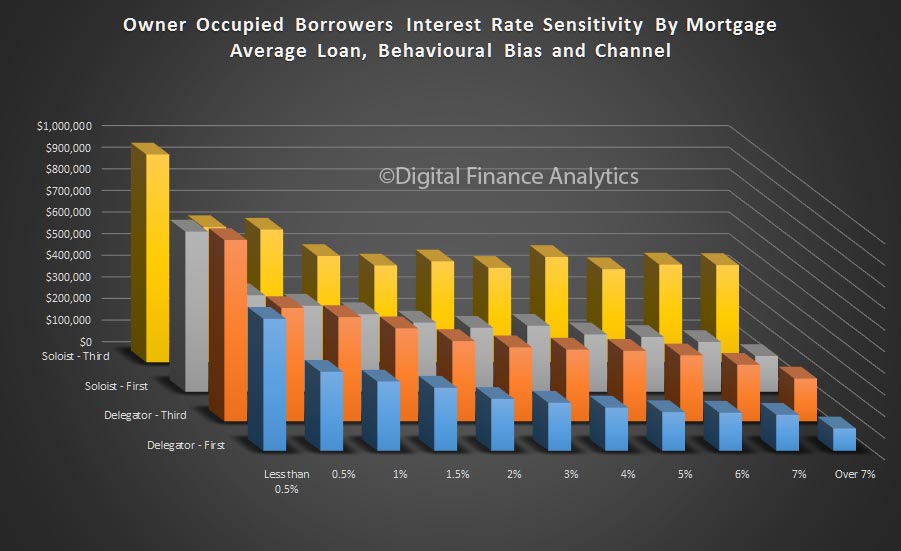
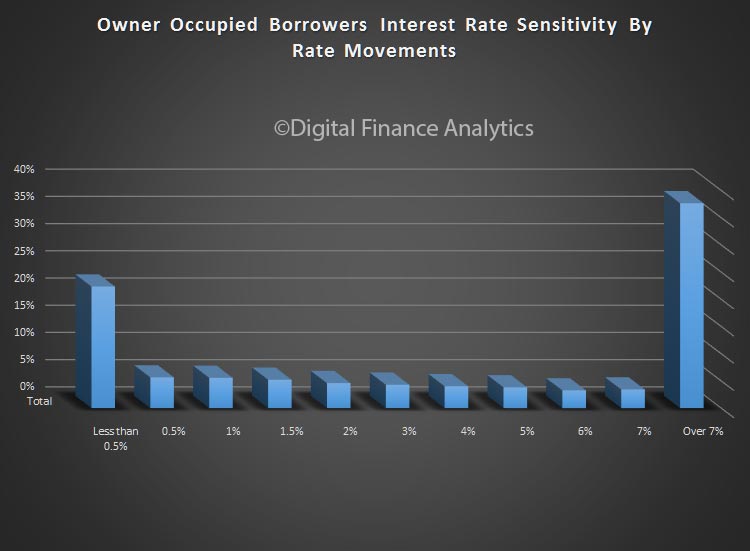
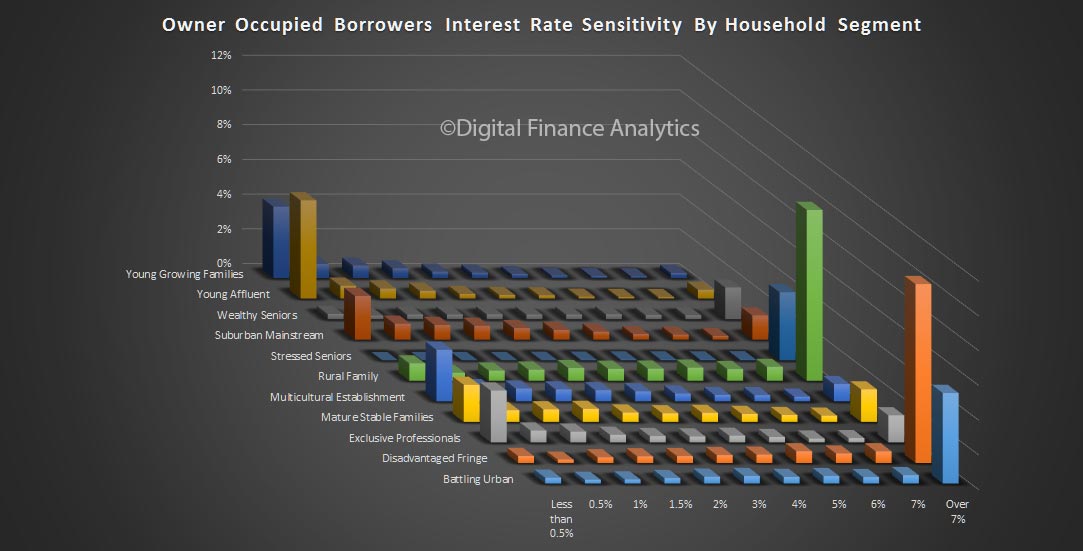
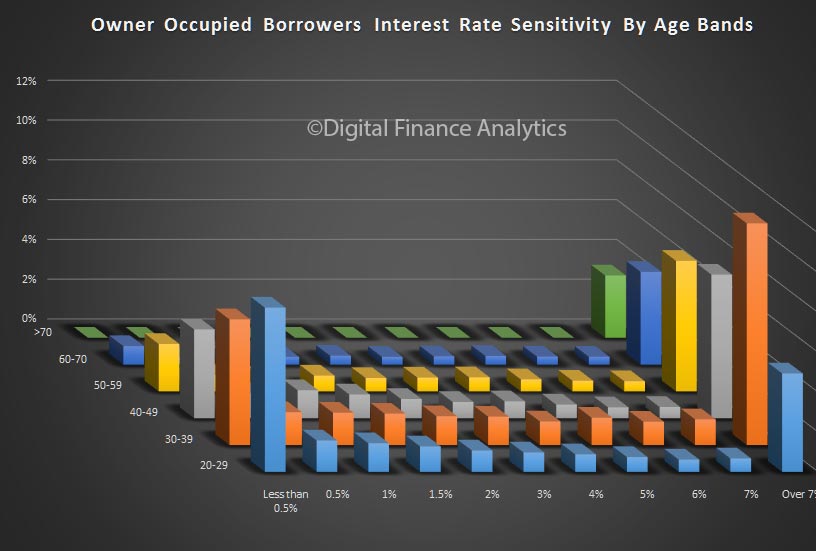
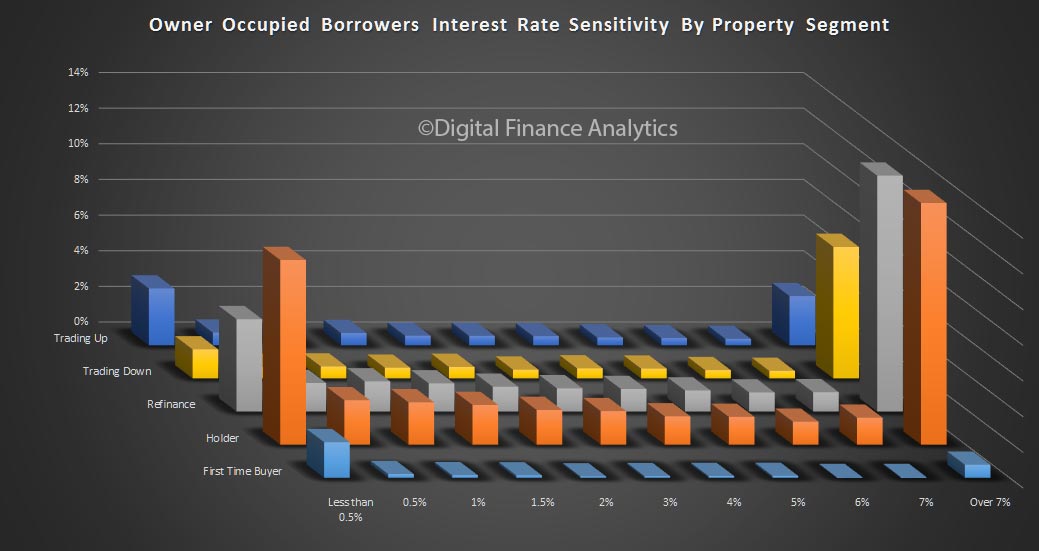
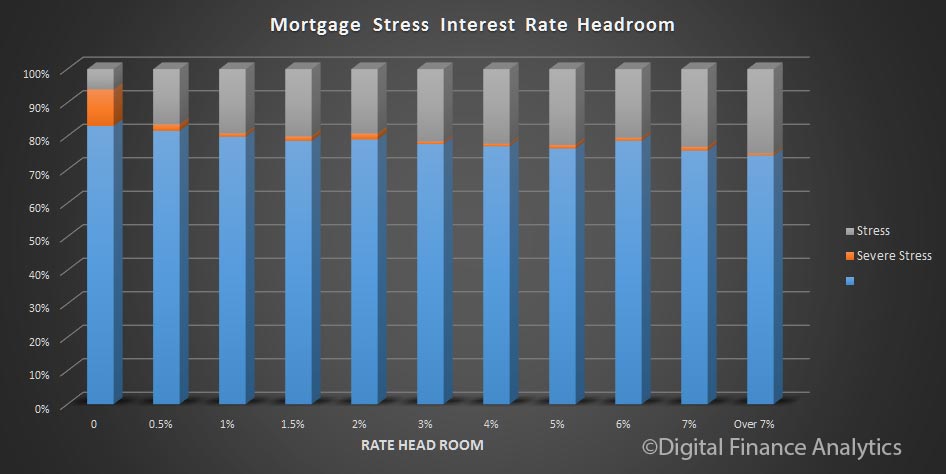
 So, it seems the future of household confidence is joined at the hip with the future of property. In the light of our recent mortgage default modelling, in a rising interest rate market, this may be a concern as we progress through 2017. But at the moment, households are having a party!
So, it seems the future of household confidence is joined at the hip with the future of property. In the light of our recent mortgage default modelling, in a rising interest rate market, this may be a concern as we progress through 2017. But at the moment, households are having a party!
By way of background, these results are derived from our household surveys, averaged across Australia. We have 26,000 households in our sample at any one time. We include detailed questions covering various aspects of a household’s financial footprint. The index measures how households are feeling about their financial health. To calculate the index we ask questions which cover a number of different dimensions. We start by asking households how confident they are feeling about their job security, whether their real income has risen or fallen in the past year, their view on their costs of living over the same period, whether they have increased their loans and other outstanding debts including credit cards and whether they are saving more than last year. Finally we ask about their overall change in net worth over the past 12 months – by net worth we mean net assets less outstanding debts.