Saxo Bank 2020 Outrageous Predictions:
Saxo Bank, a leading global multi-asset facilitator of capital markets products and services, has today released its 10 Outrageous Predictions for 2020. The predictions focus on a series of unlikely but underappreciated events which, if they were to occur, could send shockwaves across financial markets.

While these predictions do not constitute Saxo’s official market forecasts for 2020, they represent a warning of a potential misallocation of risk among investors who typically see just a one percent likelihood to these events materialising. It’s an exercise in considering the full extent of what is possible, even if not necessarily probable. Inevitably the outcomes that prove the most disruptive (and therefore outrageous) are those that are a surprise to consensus.
Commenting on this year’s Outrageous Predictions, Chief Economist at Saxo Bank, Steen Jakobsen said:
“This year’s Outrageous Predictions all play to the theme of disruption, because our current paradigm is simply at the end of the road. Not because we want it to end, but simply because extending the last decade’s trend into the future would mean a society at war with itself, markets replaced by governments, monopolies as the only business model and an utterly partisan and a highly fragmented and polarised public debate.
“It’s an environment where negative yields are now used to discriminate against access to mortgages for low income households, the elderly and students as regulatory capital requirement demands make credit hurdles too high for that group to get credit. Instead, they rent at twice the price of owning – a tax on the poor if ever there was one, and a driver of inequality. This, in turn, risks leaving an entire generation without the savings needed to own their own house, typically the only major asset that many medium and lower income households will ever obtain. Thus, we are denying the very economic mechanism that made the older generations ‘wealthy’ and risk driving a permanent generational wealth gap.
“We see 2020 as a year where at nearly every turn, disruption of the status quo is an overriding theme. The year could represent one big pendulum swing to opposites in politics, monetary and fiscal policy and, not least, the environment. In politics, this would mean the sudden failure of populism, replaced by commitments to “heal” instead of to divide. In policymaking, it could mean that central banks step aside and maybe even slightly normalise rates, while governments step into the breach with infrastructure and climate policy-linked spending.”
The Outrageous Predictions 2020 publication is available here with headline summaries below:
1. Australia’s nominal GDP to 8% on MMT

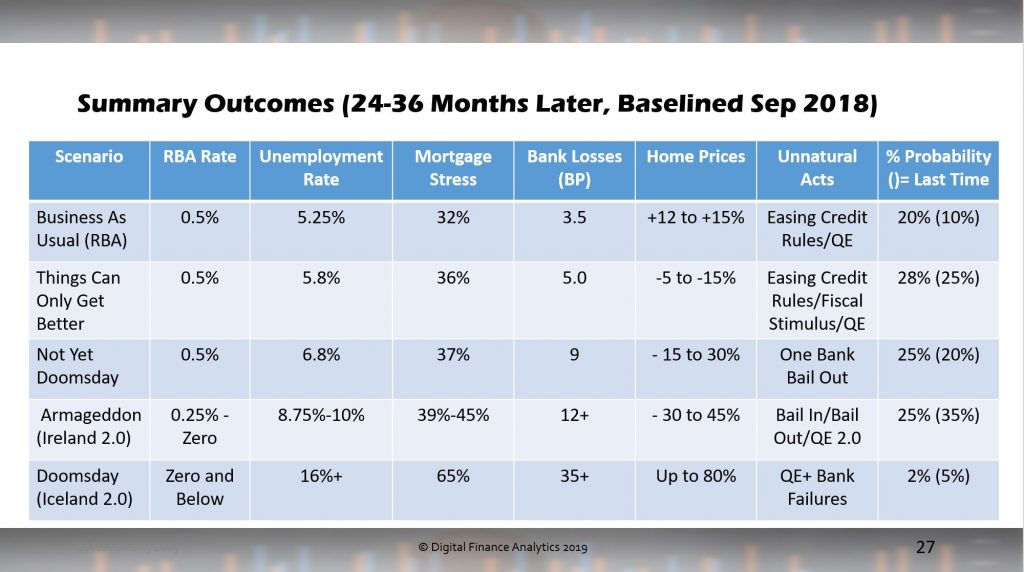
In 2020, economic red flags point to more downside ahead for the Australian economy. In Q1 of 2020, retail sales and cash register activity plunge to their lowest level since the 1991 recession and houses become more unaffordable, with Sydney and Melbourne being ranked among the world’s most expensive cities for housing. In Australia’s five biggest cities, more than 30% of average earnings are absorbed by mortgage repayments, leading to lower consumption and higher consumer stress.
The Australian economy could get a lift from the improving China credit impulse next year, but it is unlikely to be a game-changer as China’s credit transmission is still too slow. On the top of that, domestic monetary policy is also constrained as the effective zero-bound approaches and has limited positive effects on the real economy. RBA governor Philip Lowe was very vocal in 2019 on the limits of monetary policy and repeatedly explained that further rate cuts have only a marginal effect on GDP growth — arguing that fiscal stimulus is the only way to bring relief if the economy continues to weaken.
As consumer confidence and employment begin to plunge in early 2020, the government decides to embark on an MMT-inspired economic policy aimed at restoring confidence, stimulating GDP growth and attracting investment. This is the largest fiscal stimulus programme in Australia for at least 30 years. It leads to a massive increase in public spending in infrastructure, the health system and education, as well as the implementation of ambitious programmes to reduce the cost of living, provide affordable housing, reduce taxation and address environmental issues.
The strong rise in fiscal spending contributes to a jump in consumption and investment, almost doubling Australia’s nominal GDP rate to 8% in 2020. The business community applauds this bold new economic policy stance. Confidence and risk appetite are back. After being hit by a perfect storm that drove the Australian dollar down nearly 20% versus the greenback since early 2018, the AUD is among the best performing currencies in 2020.
2. The sudden arrival of stagflation rewards value over growth
The iShares MSCCI World Value Factor ETF leaves the FANGS in the dust, outperforming them by 25%.The world has now come full circle from the end of the Bretton Woods system, when it effectively shifted from a gold-based USD to a pure fiat USD system, with trillions of dollars borrowed into existence — not only in the US but all over the world. Each credit cycle has required ever lower rates and greater doses of stimulus to prevent a total seizure in the US and global financial system. With rates at their effective lower bound, and the US running enormous and growing deficits, the incoming US recession will require the Fed to super-size its balance sheet beyond imagination to finance massive new Trump fiscal outlays to bolster infrastructure in hopes of salvaging his election chances. But a strange thing happens: wages and prices rise sharply as the stimulus works its way through the economy, ironically due to the under-capacity in resources and skilled labour from prior lack of investment. Rising inflation and yields in turn spike the cost of capital, putting zombie companies out of business as weaker debtors scramble for funding. Globally, the USD suffers an intense devaluation as the market recognises that the Fed will only accelerate its balance sheet expansion while keeping its policy rate punitively low.
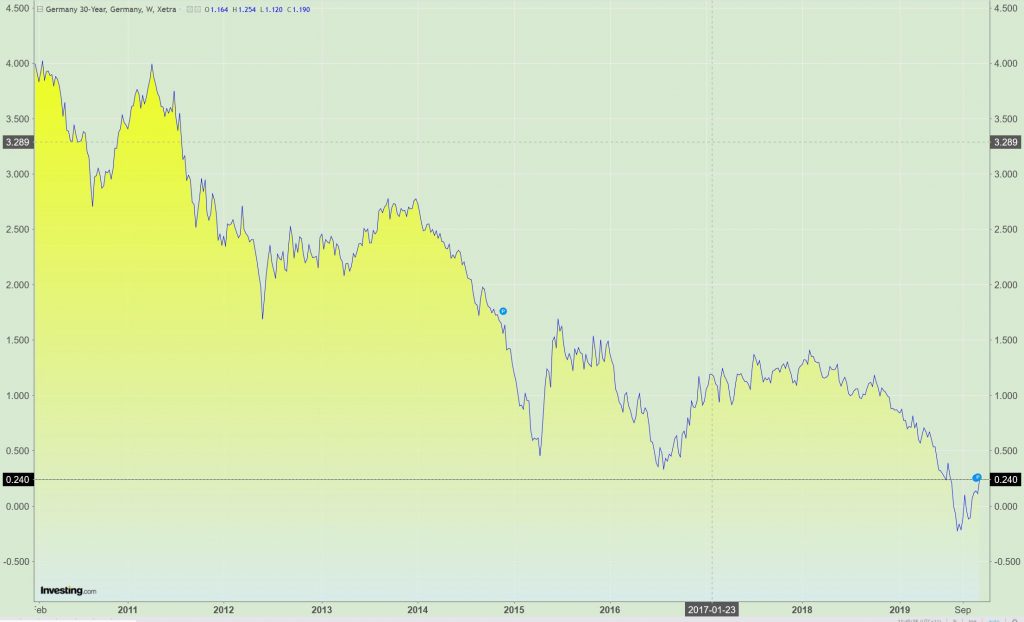
3. ECB folds and hikes rates
European banks on the comeback trail as the EuroStoxx bank index rises 30% in 2020.Despite the recent introduction of the tiering system, which has helped to mitigate the negative consequences of negative rates, banks are still facing a major crisis. They are confronted with a challenging economic and financial environment: marked by structurally ultra-low rates, an increase in regulation with Basel IV — which will further reduce the banks’ ROE — and competition from fintech companies in niche markets. In an unprecedented turn of events, in early January 2020, the new president of the ECB, Christine Lagarde — who has previously endorsed negative rates — executes a volte-face and declares that monetary policy has overreached its limits. She points out that maintaining negative deposit interest rates for a longer period could seriously harm the soundness of the European banking sector. In order to force euro area governments, and notably Germany, to step in and to use fiscal policy to stimulate the economy, the ECB reverses its monetary policy and hikes rates on January 23, 2020. This first hike is followed by another a short time later that quickly takes the policy rate back to zero and even slightly positive before year-end.
4. In energy, green is not the new black
The ratio of the VDE fossil fuel energy ETF to ICLN, a renewable energy ETF, jumps from 7 to 12. The oil and gas industry came roaring out of the financial crisis after 2009, returning some 131% from 2008 until the peak in June 2014 as China pulled the world economy out of its historic credit-led recession. Since then, the industry has been hurt by two powerful forces. The first was the advent of US shale gas and rapid strides in globalising natural gas supply chains via LNG. Then came the US shale oil revolution, which saw the US become the world’s largest oil and petroleum liquids producer. The second force has been the increasing political and popular capital behind fighting climate change, causing a massive surge in demand for renewable energy. The combined forces of lower prices and investors avoiding the black energy sector have pushed the equity valuation on traditional energy companies to a 23% discount to clean energy companies. In 2020, we see the tables turning for the investment outlook as OPEC extends production cuts, unprofitable US shale outfits slow output growth and demand rises from Asia once again.And not only will the oil and gas industry be a surprising winner in 2020 — the clean energy industry will simultaneously suffer a wake-up call.
5. South Africa electrocuted by ESKOM debt
USDZAR rises from 15 to 20 as the world cuts credit lines to South Africa. The very bad news is the South African government announcement late this year that in order to continue to bail out troubled utility ESKOM and keep the nation’s lights on, the budget next year is projected to balloon to its worst in over a decade at 6.5% of GDP, a sharp deterioration after the government managed to stabilise finances at a near constant -4% of GDP for the last few years. Worse still, the World Bank estimates that its external debt has more than doubled over that period to over 50% of GDP. The ESKOM fiasco may be the straw that will break the back of creditors’ willingness to continue funding a country that hasn’t had its financial or governance house in order for decades. Other uncreditworthy EMs will be drawn into the abyss as well in 2020, with the most differentiated performance across EM economies in years. The country teeters toward default.
6. US President Trump announces America First Tax to reduce trade deficit
A tax on all foreign-derived revenue scrambles supply lines and spikes inflation. US 10-year inflation-protected treasuries yield 6% in 2020 thanks to a rush of investor interest as the CPI rises. The year 2020 starts with reasonable stability on the trade policy front after the Trump administration and China manage at least a temporary détente on tariffs, currency policy and purchases of agricultural goods. But early in 2020 the US economy struggles for air and US trade deficits with China fail to materially improve, while Chinese purchases of agricultural products can’t realistically increase further. Eyeing polls showing a resounding defeat in the 2020 US Presidential election, Trump quickly grows restive and his administration drums up a new approach in a last-ditch effort to steal back the protectionist narrative: the America First Tax. Under the terms of this tax, the US corporate tax schedule is completely reconstructed to favour US-based production under the claimed principles of “fair and free trade”. The plan cancels all existing tariffs and instead slaps a flat value-added tax of 25% on all gross revenues in the US market that are sourced from foreign production. This brings stinging protests from trading partners for what are really just old tariffs in new clothes, but the administration counters that foreign companies are welcome to shift their production to the US to avoid the tax.
7. Sweden breaks bad
A massive and pragmatic attitude shift washes over Sweden as it gets to work to better integrate its immigrants and overstretched social services, driving a huge fiscal stimulus and steep rally in SEK. As often seems the case in Swedish policymaking, just as they took progressive taxation too far and collapsed the economy in the early 90’s, they have now taken political correctness on immigration so far that they have become politically incorrect. They are ignoring the large and growing contingent of Swedes who are questioning that policy, shutting them out of the debate. A parliamentary democracy should allow all groups of reasonable size a voice in the debate, but the traditional main parties of Sweden have taken the unusual collective decision to ignore the anti-immigration voice which has grown to represent more than 25% of the Swedish voters. The justification and intentions were good: openness and equality for all and safeguarding the Swedish open economic model. But anything taken too far can overwhelm, and to survive, all models need to be able to change when facts change. The other Nordic countries now talk of “Sweden conditions” as a threat, not as a model of best practice. Sweden is now in recession and with its small open economy status is extremely sensitive to the global slow down. This sense of crisis, social and economic, will create a mandate for change.
8. Democrats win a clean sweep in the US 2020 election, driven by women and millennials
The 2020 US election puts the Democrats in control of the presidency and both houses of Congress. Big healthcare and pharma stocks collapse 50%. The polls going into 2020 don’t look promising for Trump, and neither does the electorate. The marginal Trump voter in 2016 and in 2020 is old and white, a demographic that is fading in relative terms as the largest generation in the US now is the maturing millennial generation of 20-40-year-olds, a far more liberal demographic. Millennials and even the oldest of “generation Z” in the US have become intensely motivated by the injustices and inequality driven by central bank asset market pumping and fears of climate change, where President Trump is the ultimate lightning rod for rebellion as a climate change denier. The vote on the left is thoroughly rocked by dislike of Trump – with suburban women and millennials showing up to express their revulsion for Trump. The Democrats win the popular vote by over 20 million, grow their control of the House, and even narrowly take the Senate. Medicare for all and negotiations for drug pricing bring a massive haircut to the industry’s profitability.
9. Hungary leaves the EU
Hungary has been an impressive economic success since it joined the EU in 2004. But the 15-year marriage now seems in trouble after the EU initiated an Article 7 procedure against the country, citing Hungary’s – or really PM Orbán’s — ever-tighter restrictions on free media, judges, academics, minorities and rights groups. The push back from Hungary’s leadership is that the country is only protecting itself: mainly protecting its culture from mass immigration. It’s an unsustainable status quo, and the two sides will find it tough to reconcile in 2020 as the Article 7 procedure moves slowly through the EU system. PM Orbán is even openly talking about how Hungary is a ‘blood brother’ with the renegade Turkey as opposed to a part of the rest of Europe, a big shift in rhetoric, a change of tone which coincides with EU transfers all but disappearing over the next two years. Hungary’s currency, the forint (HUF) is on the back foot and reaches a much weaker level of 375 in EURHUF terms as the markets fear the disengagement or reversal of capital flows as EU companies reconsidered their investment in Hungary.
10. Asia launches new reserve currency in move away from US dollar dependence An Asian, AIIB-backed digital reserve currency takes the US dollar index down by 20% and tanks the US dollar 30% versus gold. To confront a deepening trade rivalry and vulnerabilities from rising US threats to weaponise the US dollar and its control of global finances, the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank creates a new reserve asset called the Asian Drawing Right, or ADR, with 1 ADR equivalent to 2 US dollars, making the ADR the world’s largest currency unit. The move is clearly aimed at de-dollarising regional trade. Local economies multilaterally agree to begin conducting all trade in the region in ADRs only, with major oil exporters Russia and the OPEC nations happy to sign up due to their growing reliance on the Asian market. The redenomination of a sizable chunk of global trade away from the US dollar leaves the US ever shorter of the inflows needed to fund its twin deficits. The USD weakens 20% versus the ADR within months and 30% against gold, taking spot gold well beyond USD 2000 per ounce in 2020.