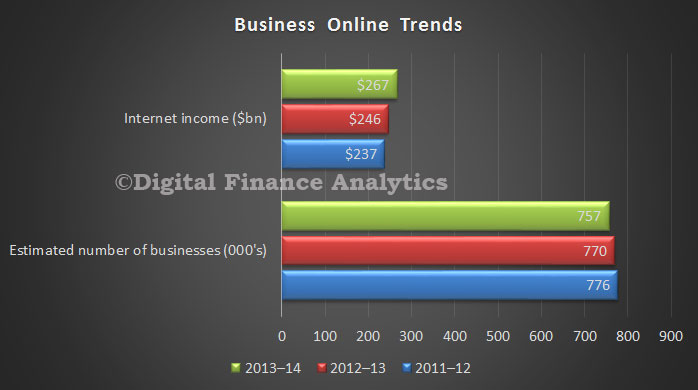
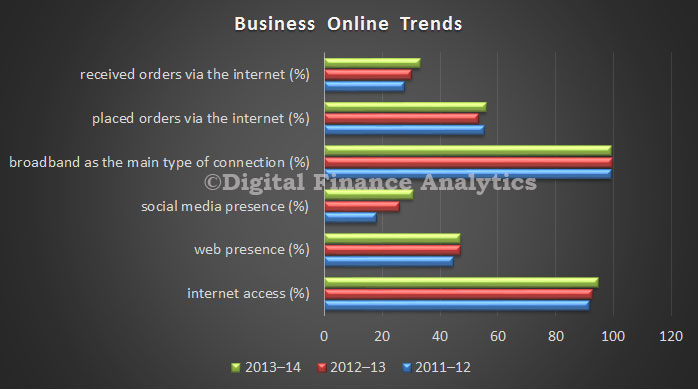
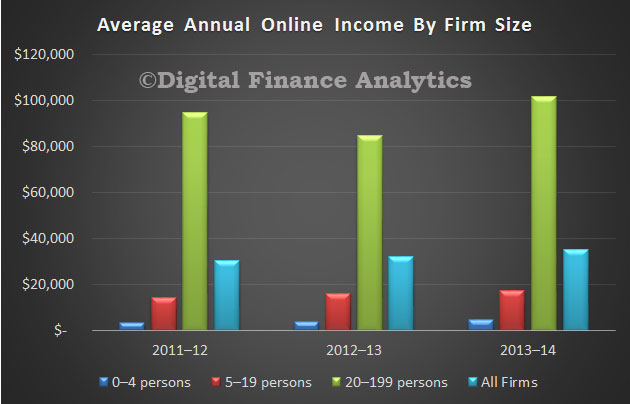
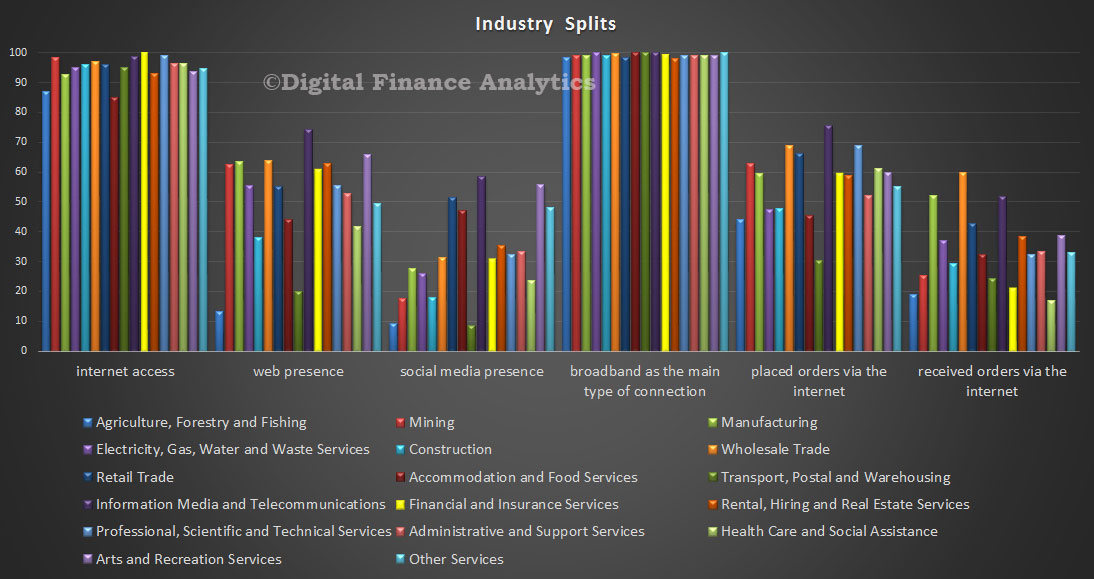
Last weekend the Property Council and the Real Estate Institute of Australia released a consultants’ report that tried to show renters would pay much more if generous tax concessions to landlords were wound back. So interesting to read an article by John Daley and Danielle Wood published by The Australian, Friday 3 July, and posted on the Institute website entitled “Rent rise fears are overstated”
With increasing public scrutiny of negative gearing and the capital gains tax discount at a time of rising budget pressures, the industry’s response was textbook: release an “independent” economic report alluding to frightening economic impacts and wait for an unquestioning media to breathlessly report them. As spooked tenants were rolled out lamenting hypothetical rent rises of $10,000 a year, no doubt the big developers congratulated themselves on a job well done.
But these misleading claims shouldn’t go untested. The report does not support the headline-grabbing $10,000-a-year rent rises. Rather, it suggests the immediate removal of negative gearing is likely to result in a portion of the average $9500 net rental loss being added to rental prices — without any attempt to define how large that impact may be.
The report’s use of the $9500 figure is highly misleading. This amount is the average loss deducted from tax for people with negatively geared investment properties. The report assumes these landlords will try to pass on some fraction of their higher tax costs by pushing up rents. But will they succeed? Many other landlords with investment properties that are profitable and therefore don’t qualify for negative gearing won’t be paying higher taxes. Tenants will try to beat rent rises by threatening to move. So competition in rental markets will limit material rent rises.
In any case, current rents are ultimately a consequence of the balance between demand and supply for rental housing. In property markets — as in other markets — returns determine asset prices, not the other way around. Rents don’t increase just to ensure that buyers of assets get their money back.
Some investors may sell their properties if tax concessions are less generous. This may reduce house prices, but it will not increase rents. Every time an investor sells a property, a current renter buys it, so there is one less rental property and one less renter, and no change to the balance between supply and demand of rental properties.
Claims that removing negative gearing will push up rents often rest on a folk memory of increasing rents in Sydney between 1985 and 1987. But as proper examination of that history shows, real rents didn’t increase in Melbourne, Brisbane and Adelaide. Other factors drove the Sydney rent rise.
The industry report argues negative gearing boosts the supply of new rental properties. But 93 per cent of all investment property lending is for existing dwellings. As the report itself points out, the main constraint on the supply of new housing is land release and zoning restrictions, not the profitability of developments. Providing tax concessions in this supply-constrained environment mainly just bids up prices for the limited new supply.
The other argument the industry advances is that “ordinary Australians” use negative gearing. Once again the numbers it uses are highly misleading. Its report shows that those with taxable incomes under $80,000 claim most tax benefits from negative gearing for property — 58 per cent of the rental losses. But people who are negatively gearing have lower taxable incomes because they are negatively gearing. Correcting for this by assessing income before rental loss deductions shows that less than one-third of rental losses are claimed by people with incomes below $80,000.
In other words, taxpayers with incomes more than $80,000 — the top 20 per cent of income earners — claim almost 70 per cent of the tax benefits of negative gearing. For capital gains, taxpayers with incomes of more than $80,000 capture 75 per cent of the gains. If we are trying to look after middle-income earners, then general changes to income tax rates would be fairer than allowing negative gearing for a small proportion of middle-income earners.
So why are the Property Council and the Real Estate Institute making such claims? Presumably because reforms would reduce the price of assets held by their members. They have a strong incentive to obscure how these tax benefits impose costs on other taxpayers, push home ownership further out of reach for young people and distort investment decisions.
Australia is one of few developed nations to allow full deductibility of losses against wage income. As other countries realise, negative gearing distorts investment decisions by allowing investors to write off losses at their marginal tax rate but pay tax on their capital gains at only half this rate. Investors who hold off selling until they are retired pay even less tax on their capital gains. As a result, investors favour assets that pay more in the way of capital gains and less in terms of steady income. It also makes debt financing of investment more attractive. It all leads to the leveraged and speculative investment of the Sydney property boom.
As well as restricting the deduction of investment losses against wage and salary income, the capital gains tax discount should also be reduced. The industry report argues capital gains should receive a discounted tax treatment to ensure the inflation component of gains is not taxed. But with inflation rates low relative to investment returns, the 50 per cent discount overcompensates most investors. The discount magnifies the tax advantages of capital gains over other investment income.
Yet despite the compelling arguments for change, it seems the industry’s aggressive lobbying efforts will be rewarded. The Treasurer and the Finance Minister have both defended negative gearing arrangements by warning, against all credible evidence, that change would bring higher rents. The message to lobby groups is clear: if you pay enough to “independent” consultants you may be able to buy favourable policy outcomes, irrespective of the costs to the community.