The New Zealand Reserve Bank has issued their latest financial stability report. They say that New Zealand’s financial system remains sound. Household debt is firmly in the frame as the biggest potential risk!
The banking system holds sufficient capital and liquidity buffers, guided by our prudential regulatory requirements. These buffers reduce New Zealand banks’ exposure to adverse shocks.An ongoing driver of financial soundness is the conduct and culture of banks and insurance companies. These features are being jointly reviewed by the Financial Markets Authority and ourselves, and we will report our findings over coming months. The financial system vulnerabilities are much the same as we discussed in our previous Financial Stability Report.
Household mortgage debt remains high. However, financial risk has lessened with both lending and house price growth slowing in the last 12 months – in part due to our imposition of loan-to-value (LVR) ratio restrictions. This more subdued lending growth needs to be further sustained before we gain sufficient confidence to again ease the LVR restrictions.
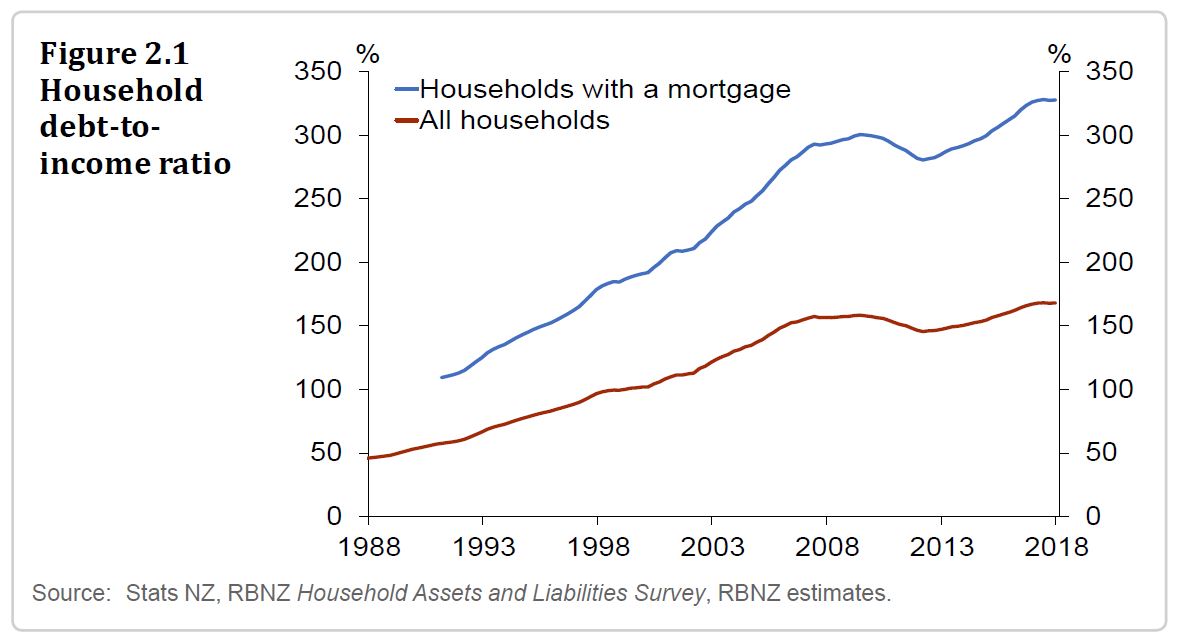
However, the banks says the high level and concentration of household sector debt in New Zealand is the largest single vulnerability of the financial system. Some households are vulnerable to developments that reduce their debt servicing capacity, such as higher interest rates or a change in financial circumstances. Households with severe debt servicing problems could default on their loans, creating losses for lenders. If debt servicing problems were widespread, weaker consumption and investment could reduce incomes and contribute to an economic downturn. This could threaten financial stability by causing households and businesses to default, and by reducing the value of assets against which banks have lent, such as houses.
The high level and concentration of household sector debt in New Zealand is the largest single vulnerability of the financial system. Some households are vulnerable to developments that reduce their debt servicing capacity, such as higher interest rates or a change in financial circumstances. Households with severe debt servicing problems could default on their loans, creating losses for lenders. If debt servicing problems were widespread, weaker consumption and investment could reduce incomes and contribute to an economic downturn. This could threaten financial stability by causing households and businesses to default, and by reducing the value of assets against which banks have lent, such as houses.
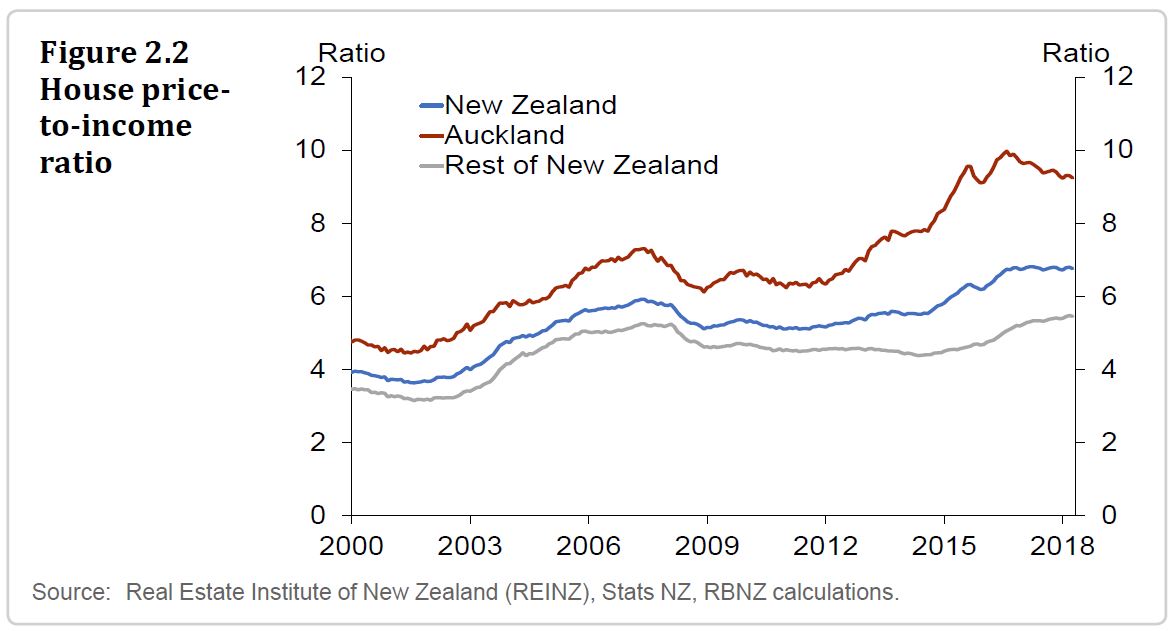
The rise in household debt since 2012 has coincided with a sharp rise in house prices, particularly in Auckland (figure 2.2). The simultaneous rise in household debt and house prices could partly reflect a self-reinforcing cycle, where bank lending has boosted house prices and, in turn, higher house prices have supported more bank lending, by increasing the value of homeowners’ collateral. But this cycle can also operate in reverse, driving down bank lending and house prices. This negative interaction can amplify the financial stability impact of a household income shock, by lowering collateral values and reducing households’ ability to service their existing debts by increasing their borrowing.
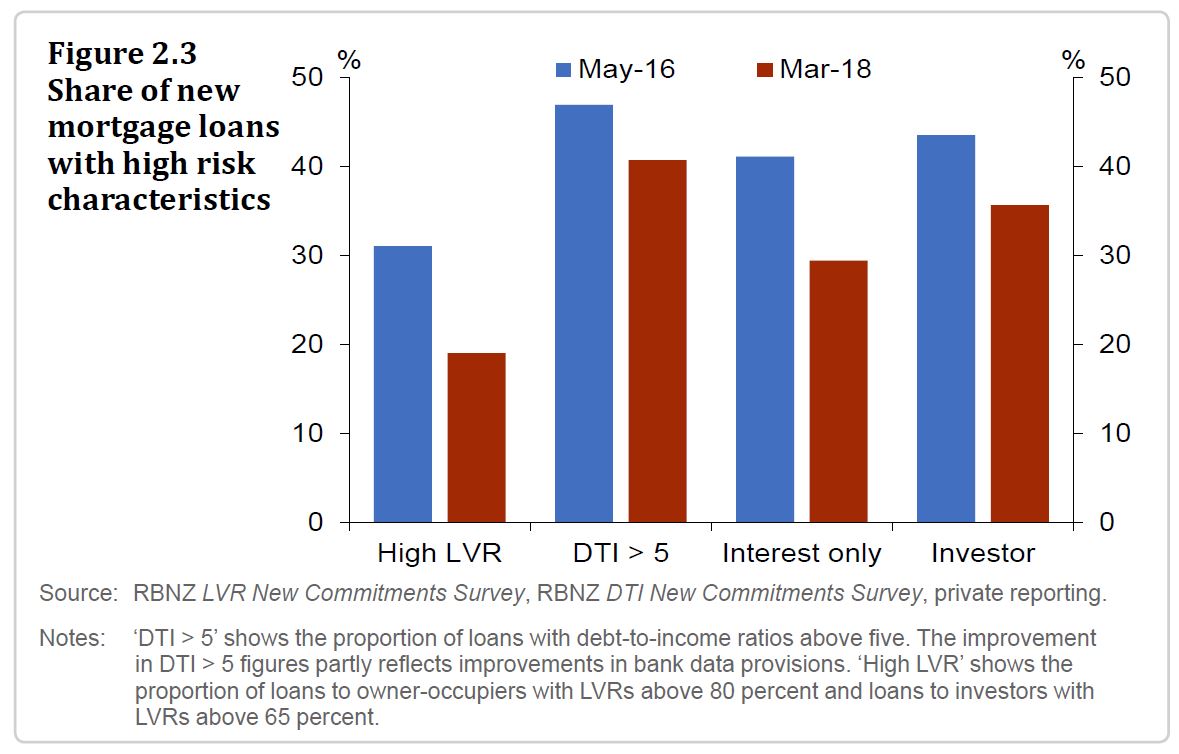
In the past two years, concerns about vulnerabilities in the household sector have caused a tightening in bank lending standards to the sector. This is partly the result of the Reserve Bank tightening its restrictions on new mortgage lending, particularly to investors, at high loan-tovalue ratios (LVRs) in October 2016.1 It also reflects actions by banks to tighten lending standards, such as the use of higher household living cost assumptions when assessing borrowers’ ability to service loans. As a result, a lower proportion of banks’ new mortgage loans have high risk characteristics than in 2016.
However, the share of new lending with high risk characteristics is still concerning. The proportion of new mortgage lending to borrowers with debt-to-income ratios above five is high compared to international peers, such as the UK. Households with this level of indebtedness are
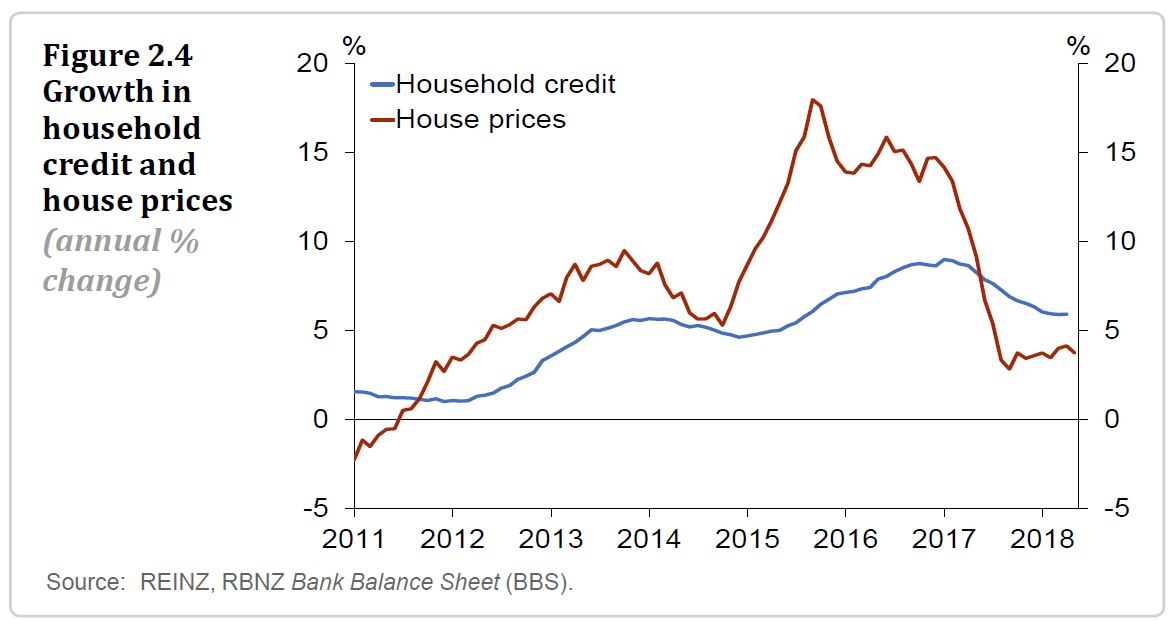
particularly vulnerable to even modest changes in income or interest rates.The tightening in lending standards has contributed to the annual growth rate of household credit slowing to 6 percent, slightly above the rate of income growth (figure 2.4). This has coincided with a slowdown in national house price growth, to 4 percent in the year to April. The
decline in house price inflation partly reflects the announcement and implementation of government policies (such as KiwiBuild, the extension of the bright-line test and plans for ‘loss ring-fencing’). But low mortgage rates and high net migration continue to support house prices.
The growth rates of household debt and house prices have been fairly stable over the past six months. Combined with tighter bank lending standards, this suggests the financial system’s vulnerability to household debt has not changed materially since the previous Report.
Ultimately, continued stabilisation, or a further reduction, in the growth rates of household debt and house prices, will be required before the risk to the financial system is normalised. Bank lending standards will have an influence over both. Currently, banks expect to keep their lending standards relatively tight for the rest of 2018.
In a similar vein, the dairy farming sector remains highly indebted. Most dairy farms are currently cash-flow positive, but remain vulnerable to any possible downturn in dairy prices and agriculture shocks. Reducing this bank lending concentration risk requires more prudent lending practices.
The high dairy-farm indebtedness, and the fact that LVRs were necessary, reflects that banks’ allocative efficiency – eg deciding how much to lend to whom – can be impaired due to the pursuit of short-term, rather than longer-term, profits.
The report also commented on the Australia Economy:
The Australian economy is growing steadily. But vulnerabilities have risen in recent years, particularly in the household sector, which carries a relatively high level of debt. House prices also appear stretched in some cities. Regulators have responded in a number of ways, including by requiring banks to conduct more rigorous loan serviceability assessments. These changes, coupled with a broader improvement in lending standards and an easing in housing market conditions, have improved the outlook for risks in the Australian household sector. But the Australian financial system remains vulnerable to developments that could weaken households’ ability to service their debts.