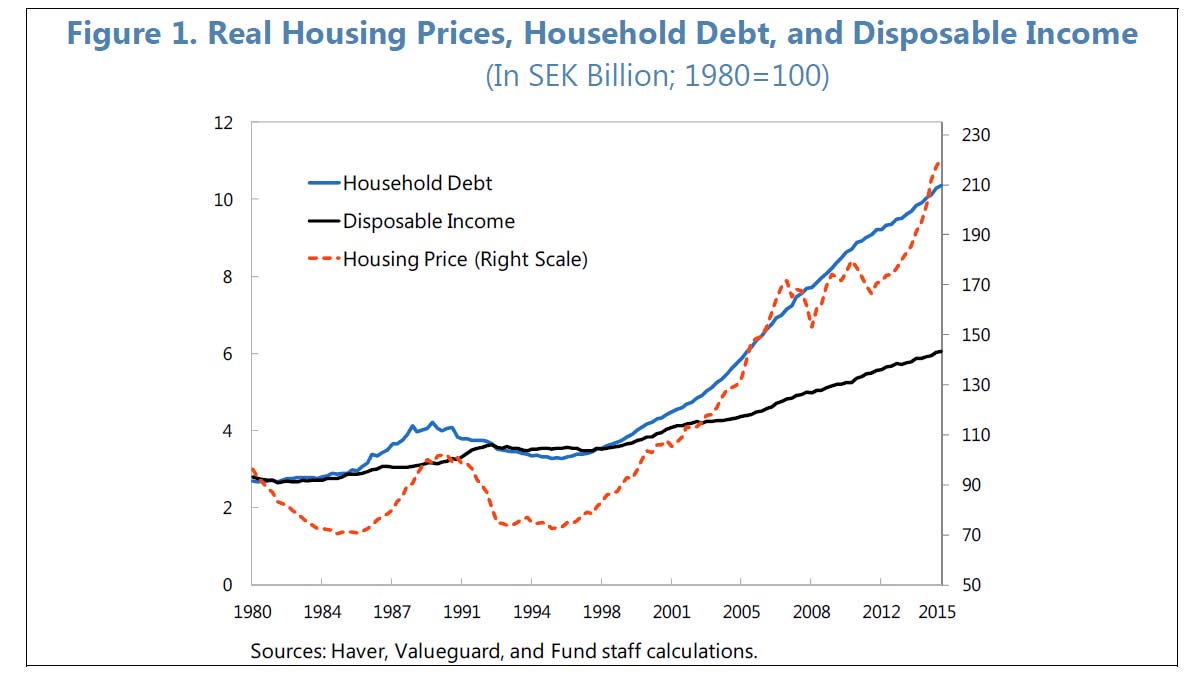
A newly published IMF working paper looks at the relationship between house prices and household debt, in Sweden. The work is interesting because house prices have risen significantly, and household debt has risen substantially at a time when supply was limited. Australia is not the only country with these synonyms!
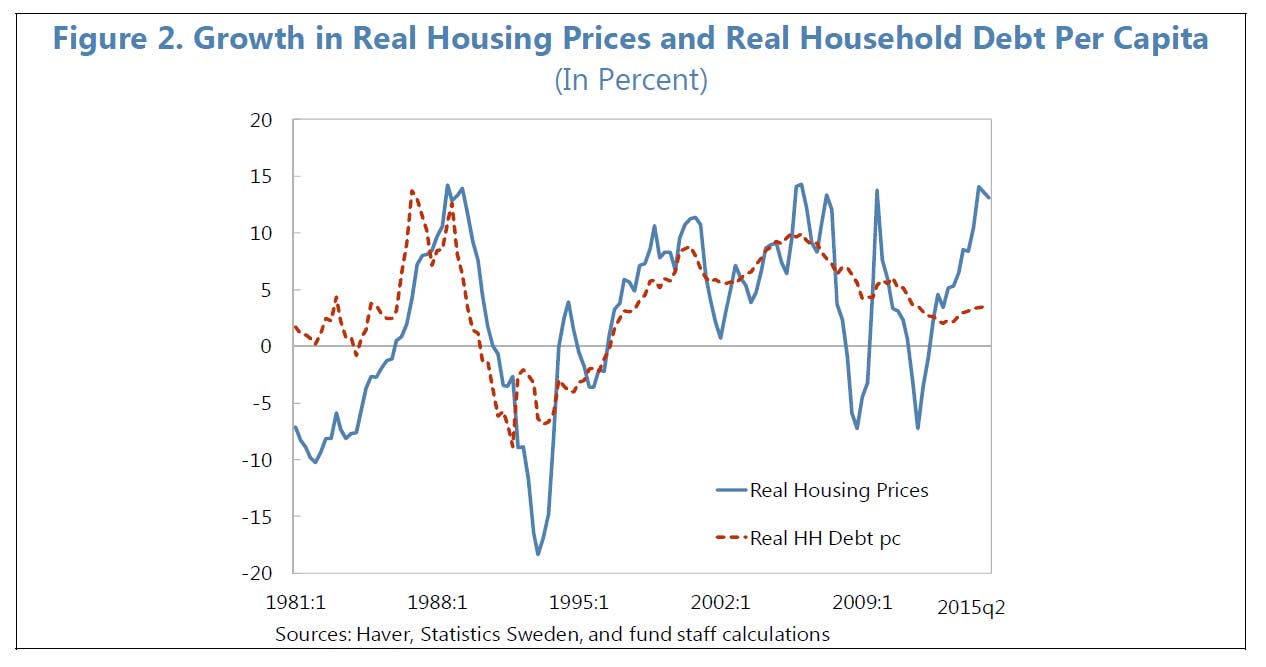
 The swings in house price growth have had wider amplitude than those of credit growth since the GFC. Whilst a loan-to-value ratio cap of 85 percent on all new mortgage loans was introduced in 2010 which may have affected lending growth, they still have tax relief on mortgage repayments.
The swings in house price growth have had wider amplitude than those of credit growth since the GFC. Whilst a loan-to-value ratio cap of 85 percent on all new mortgage loans was introduced in 2010 which may have affected lending growth, they still have tax relief on mortgage repayments.
 The question the paper examines is the relationship between these higher prices and household debt levels. A common interpretation of the link between these markets is that mortgage lending drives housing prices up, motivating measures to curb credit. Yet, mortgage lending can also be driven by rising housing prices through the wealth
The question the paper examines is the relationship between these higher prices and household debt levels. A common interpretation of the link between these markets is that mortgage lending drives housing prices up, motivating measures to curb credit. Yet, mortgage lending can also be driven by rising housing prices through the wealth
and collateral channels. Home ownership generally requires debt financing, especially as households usually acquire this major asset early in their life cycle. When house prices appreciate, households who own housing may perceive that their higher wealth allows for greater lifetime consumption, inducing households to borrow and spend more. At the same time, the higher value of housing assets expands the value of collateral against which borrowing is generally much cheaper than unsecured credit. Relaxing this collateral constraint thereby expands households’ borrowing capacity, which could be reflected in a combination of higher consumption and larger asset holdings. For households that do not yet own a house, higher prices increase the need to borrow but also relax collateral constraints.
The paper examines the interactions between housing prices and household debt using a three-equation model, finding that household borrowing impacts housing prices in the short-run, but the price of housing is the main driver of the secular trend in household debt over the long-run. Both housing prices and household debt are estimated to be moderately above their long-run equilibrium levels, but the adjustment toward equilibrium is not found to be rapid. Whereas low interest rates have contributed to the recent surge in housing prices, growth in incomes and financial assets play a larger role. Policy experiments suggest that a gradual phasing out of mortgage interest deductibility is likely to have a manageable effect on housing prices and household debt.
Note that IMF Working Papers describe research in progress by the author(s) and are published to elicit comments and to encourage debate. The views expressed in IMF Working Papers are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily represent the views of the IMF, its Executive Board, or IMF management.
