The Productivity Commission report into Competition in The Financial Services Sector has shone a light on home loan pricing, and especially the fact that it is almost impossible for consumers to effectively compare products and prices. We think this is deliberate obfuscation by the industry. So today we look at home loan pricing section of the report in more detail.
 The so called standard variable rate (SVR) is the starting point. This is an artificial price, an interest rate that each lender sets by taking into account their cost of funds, operating costs and target profit margins. Lenders make reference to their own SVR when pricing home loans and advertising home loan interest rates. They use it as their benchmark rate to which a margin may be added or (more usually) subtracted when making offers to consumers. Linking actual home loan interest rates to an SVR in this way allows lenders to easily increase or decrease prices on all variable rate loans on their books in response to changes in business or regulatory conditions.
The so called standard variable rate (SVR) is the starting point. This is an artificial price, an interest rate that each lender sets by taking into account their cost of funds, operating costs and target profit margins. Lenders make reference to their own SVR when pricing home loans and advertising home loan interest rates. They use it as their benchmark rate to which a margin may be added or (more usually) subtracted when making offers to consumers. Linking actual home loan interest rates to an SVR in this way allows lenders to easily increase or decrease prices on all variable rate loans on their books in response to changes in business or regulatory conditions.
The SVR provides a useful mechanism for each bank to control its entire book of variable rate mortgages while price discriminating between customers. While SVRs are individually set by each bank, they are public information and the SVRs set by different ADIs are closely related.
But the SVR is a source of misinformation for consumers The SVR is the advertised price of a home loan. But it is not the true market price, for almost anyone. Moreover, this ‘rate’ provides consumers with little useful information. It does not provide a meaningful price benchmark for the consumer regarding the actual price of home loans being offered in the market, as most home loans are priced below the SVR.
Almost no-one has to pay the SVR. In addition, customers might not have full information about the products and prices offered by other providers, preventing them from making an informed choice. For instance, transparency in the small business and home loan markets can be poor given the prevalence of unadvertised discounts to the standard variable rate, in many cases negotiated directly. Under these circumstances a customer will have difficulty determining the competitive price without incurring large search costs.
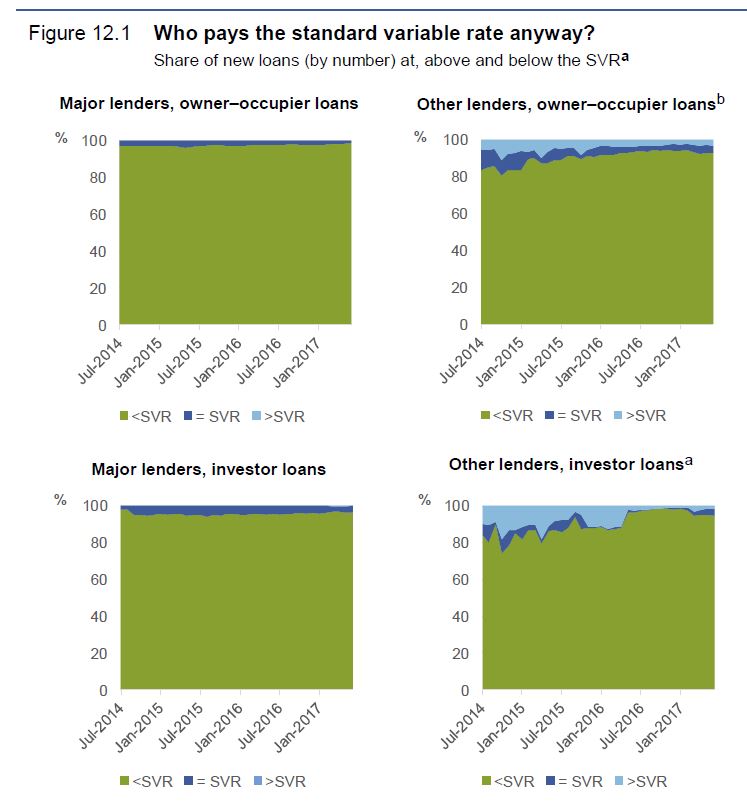
Looking at unpublished data on actual home loan interest rates, the PC found that, the overall discounting relative to the SVR is more prevalent among major lenders, discounting is slightly more widespread for loans issued to investors compared to owner-occupiers; this is more pronounced for non-major lenders. The shares of investor and owner-occupier loans at or below the SVR issued by non-major lenders have been similar in more recent years.
This strongly suggest there is no ‘discount’, just a hidden price that varies between consumers at the discretion of the lender. ASIC noted “that pricing and comparative pricing of mortgages is somewhat opaque at the moment, partly because the standard variable rate is not what a lot of people get, and it’s hard to know whether the discount you’re getting is the same as the discount other people are getting.”
These unpublished discretionary discounts can apply to a substantial portion of loans — for example, NAB submitted that, as at June 2017, discretionary pricing was being applied to up to 70% of new NAB-branded home loans. With the majority of successful home loan applicants offered a lower rate than the SVR, this suggests that the discretionary ‘discounts’ being offered by lenders, including those offered as part of a home loan package, are potentially being used to lull consumers into feeling good about accepting the offer without further negotiation on price or other aspects of the home loan.
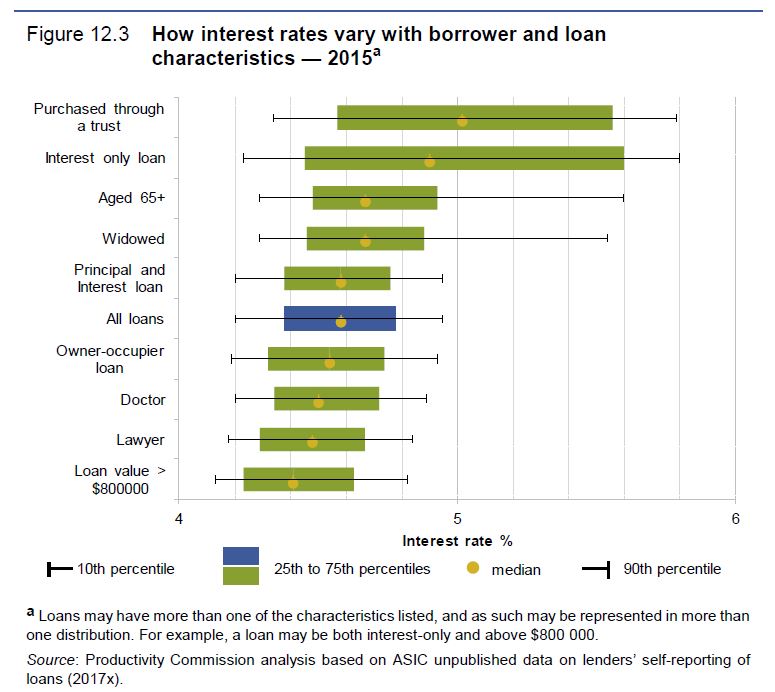
In 2017 Deloitte noted that the long-term average discount on lenders’ back books was about 70 basis points. The ACCC reported that discounts on the headline interest rate on home loans by the four largest banks range from 78 to 139 basis points, over the period of 30 June 2015 to 30 June 2017. For major banks, the gap between SVRs and actual interest rates has increased over time. While only some of this gap is likely due to discounts on SVR, the gap nevertheless is in line with ASIC’s finding that, for most banks, the discount margin for home loans was larger in 2015 than in 2012. Similarly, RBA research found that interest rate discounts increased between 2014 and 2017, with home loan discounts higher for newer and larger loans.
 In addition to most consumers paying below the SVR, it is difficult for consumers to reliably discover the actual price for the loan they anticipate seeking, as few of the discounts offered to consumers are public. While anecdotes, apps and websites abound, there is no benchmark against which to genuinely judge the market price. Information about individually-negotiated or discretionary discounts are usually not published. The ACCC noted that ‘lenders know the size of discounts they are prepared to offer and the type of borrowers they are prepared to offer them to but this information is not publicly available’.
In addition to most consumers paying below the SVR, it is difficult for consumers to reliably discover the actual price for the loan they anticipate seeking, as few of the discounts offered to consumers are public. While anecdotes, apps and websites abound, there is no benchmark against which to genuinely judge the market price. Information about individually-negotiated or discretionary discounts are usually not published. The ACCC noted that ‘lenders know the size of discounts they are prepared to offer and the type of borrowers they are prepared to offer them to but this information is not publicly available’.
Furthermore, since the decision criteria for discretionary discounts vary across lenders, borrowers may find it difficult to identify and assess the discounts for which they are eligible. But the potential savings from the total discounts are significant with borrowers potentially saving almost $4000 in the first year of the loan — highlighting the need for price transparency.
Despite the empirical evidence to the contrary, CBA sought to claim that the information available is indicative of the rate received. The PC says the “CBA’s linkage of advertised rates, comparison websites and the actual end rates paid by customers implies an ease of access to information that cannot be observed in practice”.
To the contrary, brokers in discussion with the Commission confirmed that consumers are generally only able to be certain of the actual size of their ‘discount’ once they have formally had their home loan application assessed. For a complex product, the idea of starting again, if the offer is unattractive, is a substantial barrier to pro-competitive customer behaviour (despite potentially being the best course of action). A consumer’s main focus is buying the property; the home loan facilitates this goal.
Next, bundling increases complexity of pricing. Many financial institutions offer package home loans: a bundle of products that usually includes a home loan, a transaction, offset or savings account, a credit card, and some types of insurance.
Consumers are attracted to home loan packages as lenders offer ‘discounts’ on the interest rate, including the SVR, or waive fees on some or all of the components of the package. However, bundling of a number of products into a home loan package can obscure the price of individual products making it difficult for consumers to assess the value of each individual component. It can also lock consumers into ongoing use of products that become less competitive over time as financial circumstances change).
The RBA said that “product bundling and a lack of transparency in the pricing of mortgages (with the prevalence of large unadvertised discounts in interest rates from advertised standard variable rates), are impediments to competitive outcomes”.
But this means that comparison rates are meaningless. The National Consumer Credit Protection Act requires that when advertising home loan products, lenders provide a comparison rate that includes the interest rate as well as most fees and charges. The purpose of comparison rates is to allow consumers to compare products with different fees and charges.
However, comparison rates are calculated using SVRs as the base interest rate. While comparison rates could potentially improve the competitiveness of the home loan market, they are only as useful as the interest rates on which they are based. As discussed above, for more than 90% of customers, SVRs (or the advertised rate) are not the market rate.
ASIC highlighted that the comparison rate is based on the advertised rate, not on the rate that people get when they either talk to a broker or a lender. So again, it’s not a very good guide as to whether the rate you are being offered is a good rate. It also doesn’t include other things that, you know, affect the cost of the loan like LMI, because the requirement is that a comparison rate include mandatory fees, but not contingent fees, and LMI, being a contingent fee is not included within the comparison rate.
The P&N Bank also noted the lack of relevance of the comparison rate: “While the home loan comparison rate methodology was a way of demonstrating comparability across product rates and fees, we acknowledge that it may not reflect real life scenarios based on borrower type, LVR, actual loan terms/amounts — or how pricing strategies are applied over the duration of that loan. And a submission from Home Loan Experts, a specialist mortgage broker, further noted the lack of understanding of comparison rates among consumers “We have not seen a customer use comparison rates or one that understands them. They are largely ignored by the industry and customers alike. For this reason, we recommend scrapping them altogether. And finally Canstar noted additional problems with the comparison rate — the assumptions used in formulating the rate are no longer representative of the lending market (including the loan.
SO when you are buying a home loan, the rate you get is frankly rigged, and you will never know whether you really ever got a good deal. That might help support bank profits, but once again consumers are being taken to the cleaners, and the regulators appear happy to support the poor customer outcomes. Frankly this is a disgrace,