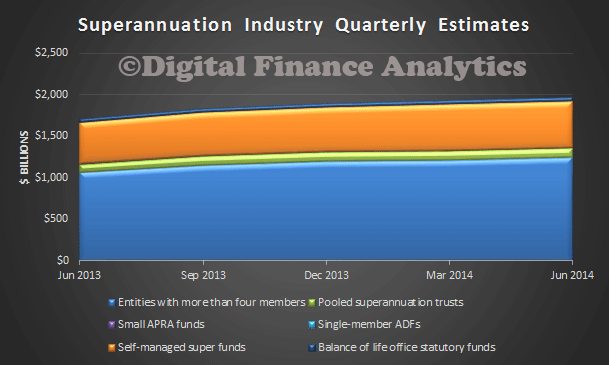
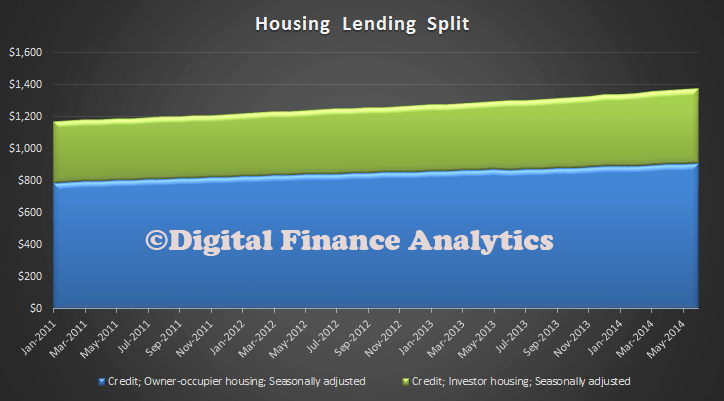
The RBA has made a supplementary submission to the Financial System Inquiry. Of note, they want to limit the extent to which SMSF’s can borrow, especially for property purchase; acknowledges the potential systemic risk from more housing lending, and the potential impact on business lending; and continues to be skeptical about the potential benefits of macroprudential tools. A couple of contextual charts may help – $1.85 billion in superannuation, 30% in SMSF, and the property sector is worth $5.2 trillion, with borrowing of $1.375 trillion, and a greater proportion for investment purposes, with a rise in interest only loans.
Assets should be managed in the best interests of members. Measures to lower costs and fees, optimise liquidity management and limit leverage should be considered”. The Bank endorses the observation that leverage by superannuation funds may increase vulnerabilities in the financial system and supports the consideration of limiting leverage. The general absence of leverage in superannuation was a key source of resilience in the Australian financial system during the financial crisis. Furthermore, the compulsory and essential character of retirement savings implies that it should remain largely unlevered. While still in its infancy, the use of leverage by superannuation funds to enhance returns appears to have been mainly taken up by self-managed superannuation funds (SMSFs). The Bank has previously commented on the risks that may arise from geared property investment through SMSFs, which may act as an additional source of demand that exacerbates property price cycles. Nonetheless, some limited leverage for liquidity management purposes may be appropriate.
HOUSING MARKET
The Interim Report finds little evidence of a shortage of mortgage finance in Australia, a view that the Bank shares. Even so, the Interim Report raises a number of options in the context of competition in the mortgage market that, if implemented, could result in relatively more finance being directed towards housing. These options should be assessed in terms of the end benefits and risks for consumers and the broader economy. Relevant considerations include whether the policy change might accelerate household borrowing, and the associated implications for systemic risk and the available funding for Australian businesses. As noted in the Bank’s initial submission, housing is generally not a particularly risky asset, but because of its size, importance to the real economy and interconnectedness with the financial system it poses systemic risk. With regards to Capital Requirements, the Interim Report highlighted several options for aiding competition through Australia’s capital framework, including changes to mortgage risk weights and providing capital inducements for ADIs that use Lenders’ Mortgage Insurance. Because of the cyclical nature of risk-taking and the large social and economic costs of instability in financial systems, it is crucial that institutions’ capital be allocated according to risk. Hence, changes to the capital framework on competitive grounds should not come at the expense of greater risk, and should not amount to a weakening relative to global regulatory minima.
MACROPRUDENTIAL
The Bank concurs with the Interim Report’s caution regarding unproven macroprudential tools. The Bank and the other CFR agencies view macroprudential policy as being subsumed within the broader financial stability policy framework in Australia. The Interim Report notes the existing framework where APRA, in consultation with the Bank and other CFR agencies, is responsible for administering prudential regulation. Consistent with its existing mandate to promote financial stability, APRA has adapted its prudential intensity in light of developments in systemic risk. For example, following signs of increased risk appetite in the mortgage market, APRA recently surveyed mortgage underwriting standards, released guidance on managing mortgage risk, and asked the major banks to specify how they are monitoring lending standards and the ensuing risks to the economy. Tools like loan-to-valuation ratio and debt-servicing ratio limits on mortgages have only recently begun to be used in developed countries. It is still too early to judge their effectiveness with the available evidence so far mixed; the effects of particular initiatives are not easily disentangled from those of other policy settings, including changes in monetary policy. APRA already has the powers to implement these tools if it was decided they would be beneficial. The Bank is not attracted to arrangements whereby prudential policy setting is spread across multiple agencies or groups of agencies. Australian agencies will continue to closely monitor how these tools perform overseas.