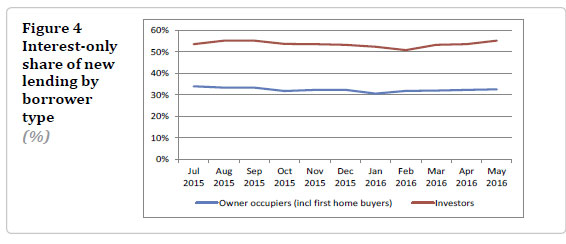
The New Zealand Reserve Bank has introduced new statistics on residential mortgage lending by payment type (i.e. interest-only and principal-and-interest). ‘Investor’ and ‘owner-occupiers’ are defined by the intended use of borrowed funds. A particular loan application may include a portion of both interest only and principal-and-interest payment terms. Figures in the new table represent the balance of new and existing lending for each payment type, not the number of loans.
In May 2016, almost 60 percent of all new mortgage lending was on principal-and-interest payment terms, while 40 percent was on interest-only payment terms. These proportions have been fairly stable since July 2015 when the data was first available. 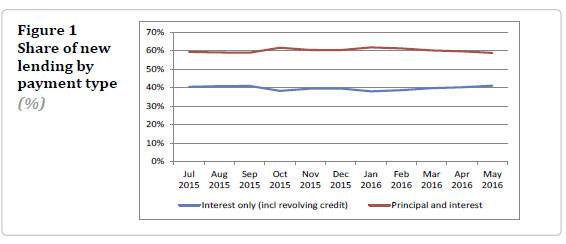 Interest-only loans tend to convert to principal-and-interest loans after a period of time. In March 2016, 40 percent of new lending was on interest-only payment terms. However on the banks’ loan books only 28 percent of all existing mortgages are on interest-only payment terms. These proportions have been fairly steady over time.
Interest-only loans tend to convert to principal-and-interest loans after a period of time. In March 2016, 40 percent of new lending was on interest-only payment terms. However on the banks’ loan books only 28 percent of all existing mortgages are on interest-only payment terms. These proportions have been fairly steady over time.
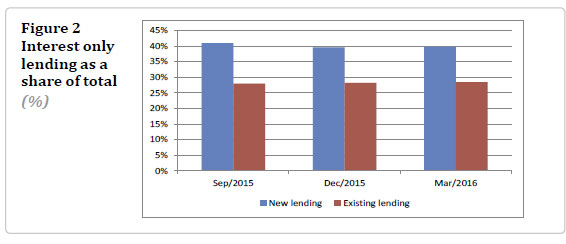 Interest-only lending is less likely to be high loan-to-value ratio (LVR greater than 80 percent) compared to principal-and-interest lending. The proportion of high LVR new lending has
Interest-only lending is less likely to be high loan-to-value ratio (LVR greater than 80 percent) compared to principal-and-interest lending. The proportion of high LVR new lending has
declined slightly for all payment types since data was first available in July 2015. The portion of high LVR lending for all existing mortgages is somewhat higher than for new lending (12.9 percent compared to 7.9 percent in March 2016) but this has also been declining over time. The lower ‘high-LVR’ portion on new lending is due to the LVR restrictions, which will gradually filter through to existing lending as new lending is added to the banks’ loan books.
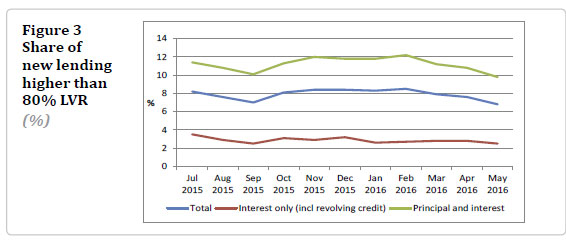 In May 2016, about 55 percent of new lending for investor purposes was on interest-only terms compared to about 33 percent for owner-occupier purposes.These proportions have
In May 2016, about 55 percent of new lending for investor purposes was on interest-only terms compared to about 33 percent for owner-occupier purposes.These proportions have
been fairly steady over time. Only 1 percent of interest-only lending for investor purposes is above 80 percent LVR and this has been declining over time.