The Reserve Bank in New Zealand has released an excellent Analytical Note on Crypto-currencies “Crypto-currencies – An introduction to not-so-funny moneys“. It is one of the best I have read, so far!
The paper introduces the distributed ledger technology of crypto-currencies. They aim to increase public understanding of these technologies, highlight some of the risks involved in using crypto-currencies, and discuss some of the potential implications of these technologies for consumers, financial systems, monetary policy and financial regulation.
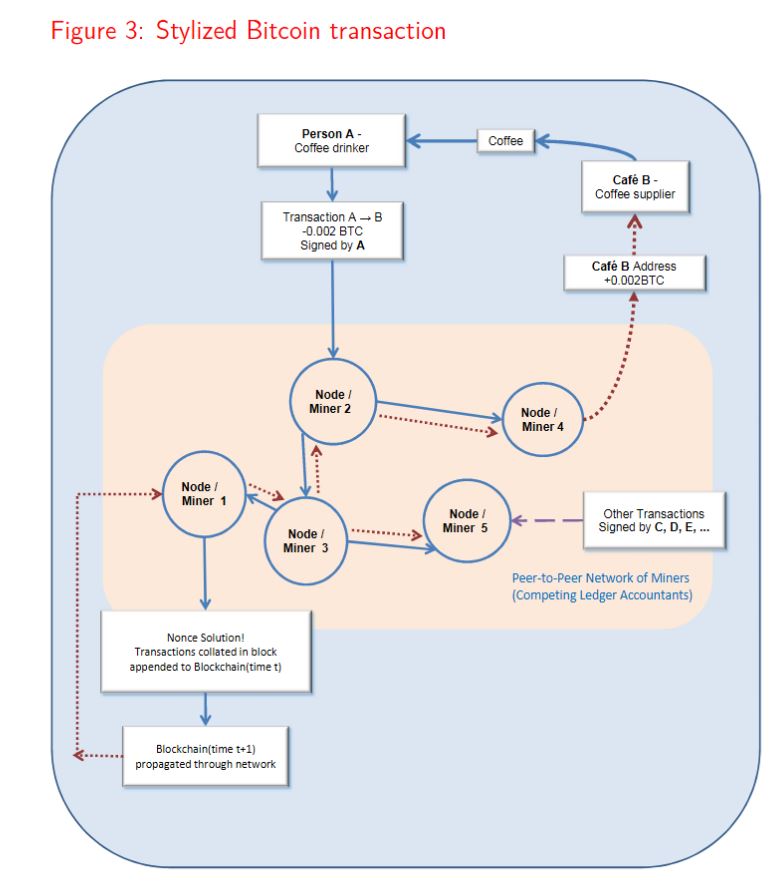
Crypto-currencies have no physical existence, but are best thought of as electronic accounting systems that keep track of people’s transactions and hence remaining purchasing power. Cryptocurrencies are typically decentralised, with no central authority responsible for maintaining the ledger and no central authority responsible for maintaining the code used to implement the ledger system, unlike the ledgers maintained by commercial banks for example. As crypto-currencies are denominated in their own unit of account, they are like foreign currencies relative to traditional fiat currencies, such as dollars and pounds.
They conclude that Crypto-currencies offer some distinct features, such as quicker cross-border transactions, possibly lower transaction fees, pseudo-anonymity, and transaction irreversibility. These features help to explain the growing demand for crypto-currencies, even though they fail to satisfy many of the basic functions of money.
Most crypto-currency accounts lie dormant and many of the active accounts are used only for online gambling or speculative purposes. Perceptions of anonymity have also created a demand for such currencies to facilitate illegal transactions, but the anonymity embodied in crypto-currencies has been over-stated. There have been a significant number of crypto-currency prosecutions in relation to money laundering and other crimes, illustrating that there is no guarantee of anonymity.
While crypto-currencies are growing in popularity, they currently facilitate a very small proportion of transactions. Because crypto-currencies intermediate such a small proportion of transactions, central banks do not presently view crypto-currencies as a material threat.Since crypto-currencies are not well-adapted to the provision of borrowing and lending, we also foresee an enduring role for traditional financial intermediaries.
Crypto-currencies and blockchain technology could well become an important part of global payment systems, but wide-scale adoption will depend on competition from alternative transaction technologies, and on regulation to provide users with security. Crypto-currencies will also need to address technical, scalability issues if they wish to intermediate the volume of transactions undertaken globally.
We conclude that all crypto-currencies are experimental in nature and users face material risks by transacting with them or by holding significant crypto-currency balances. Individual cryptoReserve Bank of New Zealand currencies may be more Betamax than VHS, and more MySpace than Facebook. Even if some of the constructs are enduring, such as distributed ledgers and the use of cryptography, specific crypto-currencies may be supplanted by competing transaction technologies. We close with a Latin expression much-beloved by contract lawyers and economists alike – caveat emptor – buyer beware.
The Analytical Note series encompasses a range of types of background papers prepared by Reserve Bank staff. Unless otherwise stated, views expressed are those of the authors, and do not necessarily represent the views of the Reserve Bank