The New Zealand Reserve Bank today left the Official Cash Rate (OCR) unchanged at 1.75 percent.
Global economic growth has increased and become more broad-based over recent months. However, major challenges remain with on-going surplus capacity and extensive political uncertainty.
Stronger global demand has helped to raise commodity prices over the past year, which has led to some increase in headline inflation across New Zealand’s trading partners. However, the level of core inflation has generally remained low. Monetary policy is expected to remain stimulatory in the advanced economies, but less so going forward.
The trade-weighted exchange rate has fallen by around 5 percent since February, partly in response to global developments and reduced interest rate differentials. This is encouraging and, if sustained, will help to rebalance the growth outlook towards the tradables sector.
GDP growth in the second half of 2016 was weaker than expected. Nevertheless, the growth outlook remains positive, supported by on-going accommodative monetary policy, strong population growth, and high levels of household spending and construction activity.
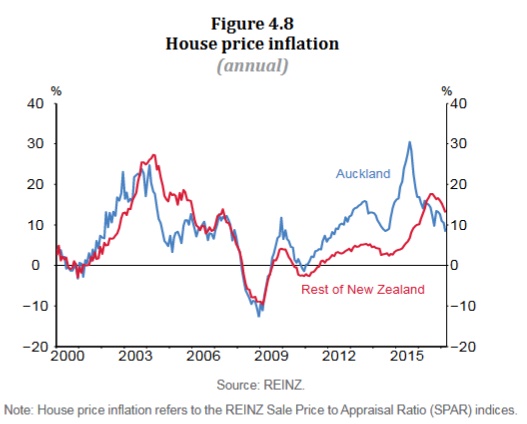
House price inflation has moderated further, especially in Auckland. The slowing in house price inflation partly reflects loan-to-value ratio restrictions and tighter lending conditions.
Despite ongoing strength in the fundamental drivers of housing demand,namely population growth and low mortgage interest rates, housing activity has slowed since mid-2016. This likely reflects a range of factors,including changes to LVR policy, and increases in mortgage rates in 2016, and increasing pressure on affordability. This moderation is projected to continue, although there is a risk of resurgence given the continuing imbalance between supply and demand.Mortgage rates have stabilised since the February Statement,with reduced upward pressure from lower wholesale interest rates (figure 4.5). Mortgage rates remain at low levels relative to history, but recent changes to LVR policy have tightened credit availability for some households. Lending conditions for residential property development have tightened.
The increase in headline inflation in the March quarter was mainly due to higher tradables inflation, particularly petrol and food prices. These effects are temporary and may lead to some variability in headline inflation over the year ahead. Non-tradables and wage inflation remain moderate but are expected to increase gradually. This will bring future headline inflation to the midpoint of the target band over the medium term. Longer-term inflation expectations remain well-anchored at around 2 percent.
Developments since the February Monetary Policy Statement on balance are considered to be neutral for the stance of monetary policy.
Monetary policy will remain accommodative for a considerable period. Numerous uncertainties remain and policy may need to adjust accordingly.