ASIC says Westpac has admitted breaching its responsible lending obligations when providing home loans and agreed to submit to a $35 million civil penalty to resolve Federal Court proceedings under the National Consumer Credit Protection Act 2009 (Cth) (the National Credit Act). A three-week trial for this matter was due to commence in the Federal Court yesterday.
The parties have jointly approached the Federal Court seeking orders that Westpac contravened the responsible lending provisions of the National Credit Act because its automated decision system:
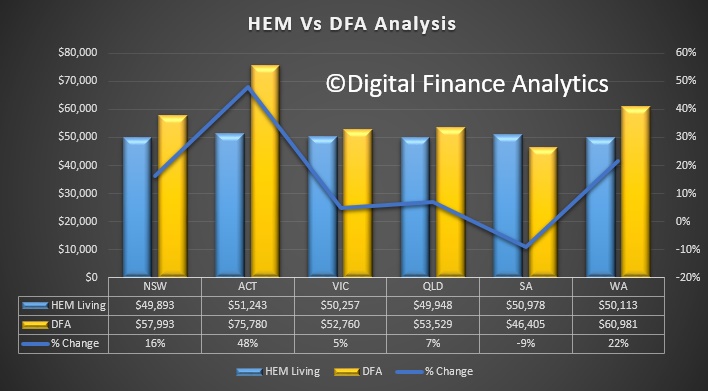
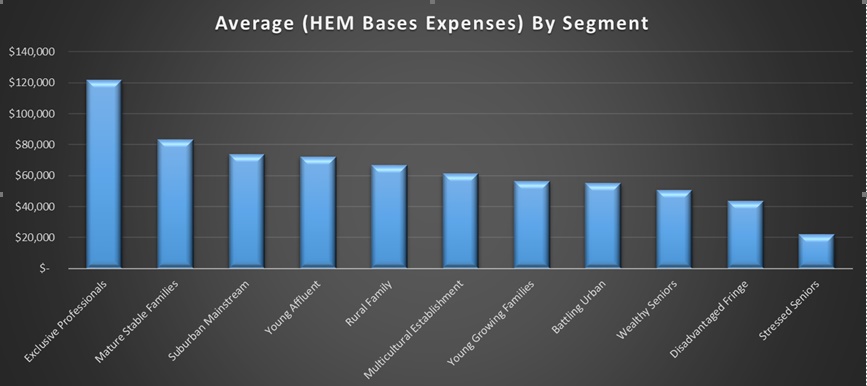
- did not have regard to consumers’ declared living expenses when assessing their capacity to repay home loans, and instead used a benchmark (the Household Expenditure Measure); and
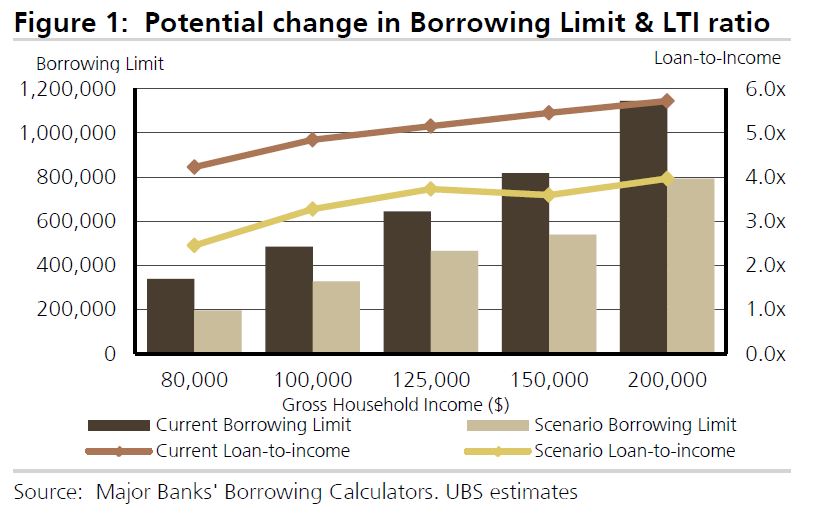
- for home loans to owner occupiers with an interest-only period, failed to use the higher repayments at the end of the interest-only period when assessing a consumer’s capacity to repay the loan. For example, for a loan of $500,000 at 5.24% with a term of 30 years and a 10-year interest-only period, the assumed repayment using the incorrect method is $2,758 per month, whereas the actual repayment after the expiry of the interest-only period using the correct method is $3,366 per month.
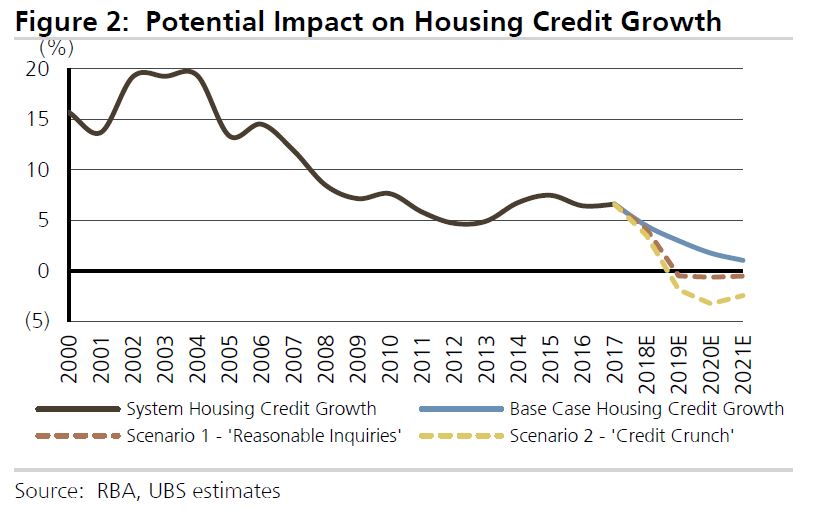
The litigation related to Westpac’s home loan assessment process during the period December 2011 and March 2015, during which approximately 260,000 home loans were approved by Westpac’s automated decision system. For approximately 50,000 home loans, Westpac received, and did not use, consumers’ actual expense information that was higher than the Household Expenditure Measure. For approximately 50,000 home loans, Westpac used the incorrect method when assessing a consumer’s capacity to repay a home loan at the end of the interest-only period. Of these approximately 100,000 loans, Westpac should not have automatically approved approximately 10,500 loans.
If approved by the Federal Court, this will represent the largest civil penalty awarded under the National Credit Act.
Westpac admitted contraventions of the National Credit Act and the parties filed a Statement of Agreed Facts and joint submissions as to the appropriate penalty. Westpac will also pay ASIC’s litigation and investigation costs.
The National Credit Act provides consumer protections to ensure that credit providers make reasonable inquiries about a borrower’s financial situation, verify the information that they obtain and assess whether a loan contract will be unsuitable for the borrowers.
The responsible lending laws are designed to ensure that lenders have regard to all relevant information about the consumer before approving a loan to minimise the risk of adverse outcomes for the consumer over the course of the loan. Lenders must have in place the right processes to ensure that they comply with these important obligations.
ASIC Chair James Shipton said, ’This is a very positive outcome and sends a strong regulatory message to industry that non-compliance with the responsible lending obligations will not be tolerated. Responsible lending in the home lending market is absolutely vital to consumers, banks and our economy.
‘This outcome, and ASIC’s actions in relation to responsible lending, reinforce that all lenders must obtain information from individual borrowers about their financial situation to ensure that they can properly assess the ability of the customer to repay the loan. Lenders must then verify the information to ensure that it is true, and then assess whether the loan is unsuitable for the borrower. Taken together, these responsible lending obligations are a cornerstone protection for both borrowers and lenders,’ he said.
‘This outcome is a warning to all lenders that they must comply with the responsible lending obligations. If they do not, ASIC will take action to enforce the law.’
Background
ASIC published its review of interest-only loans in August 2015 (refer: 15-220MR), as part of a broader review by the Council of Financial Regulators into home-lending standards. The review included 11 lenders, including the big four banks, and found that lenders were often failing to consider whether an interest-only loan would meet a consumer’s needs, particularly in the medium to long-term (refer: 15-220MR). ASIC was particularly concerned with Westpac’s home loan assessment process, and with Westpac providing very lengthy interest-only periods (up to 15 years) for owner occupiers.
As part of the outcomes of ASIC’s work, ASIC required lenders and brokers to raise standards to ensure they were complying with responsible lending obligations. The 11 firms in our review, including Westpac, all committed to implementing stronger standards.
ASIC has provided guidance on responsible lending in Regulatory Guide 209 Credit licensing: Responsible lending conduct (RG 209). ASIC is updating its guidance this year and will be engaging in a full public consultation as part of this process.
ASIC has also been engaging with the Government in relation to comprehensive credit reporting and a proposed open banking regime. These initiatives will assist in improving responsible lending standards by making high-quality information about consumers’ financial situation available to lenders when assessing the suitability of a loan.