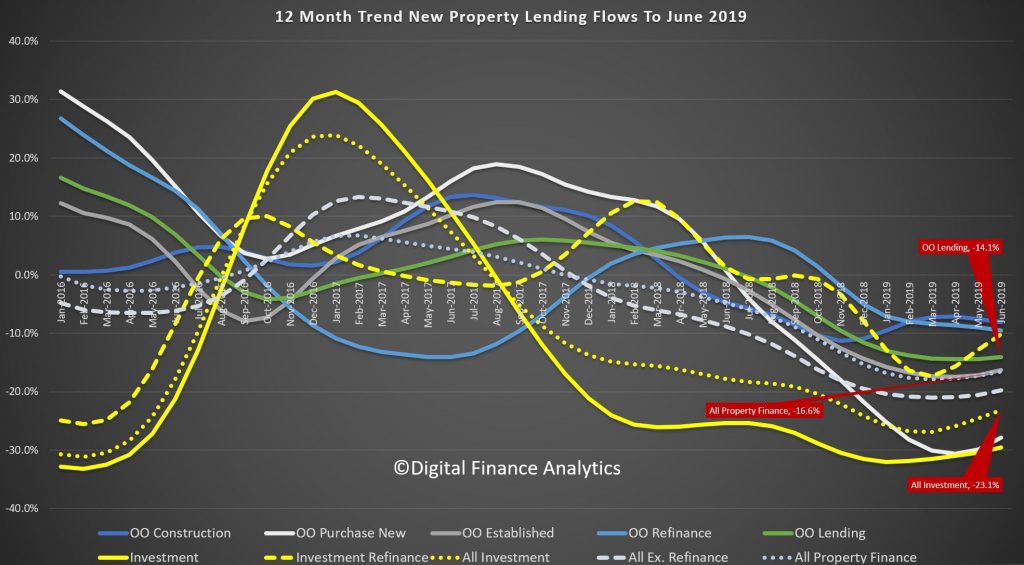
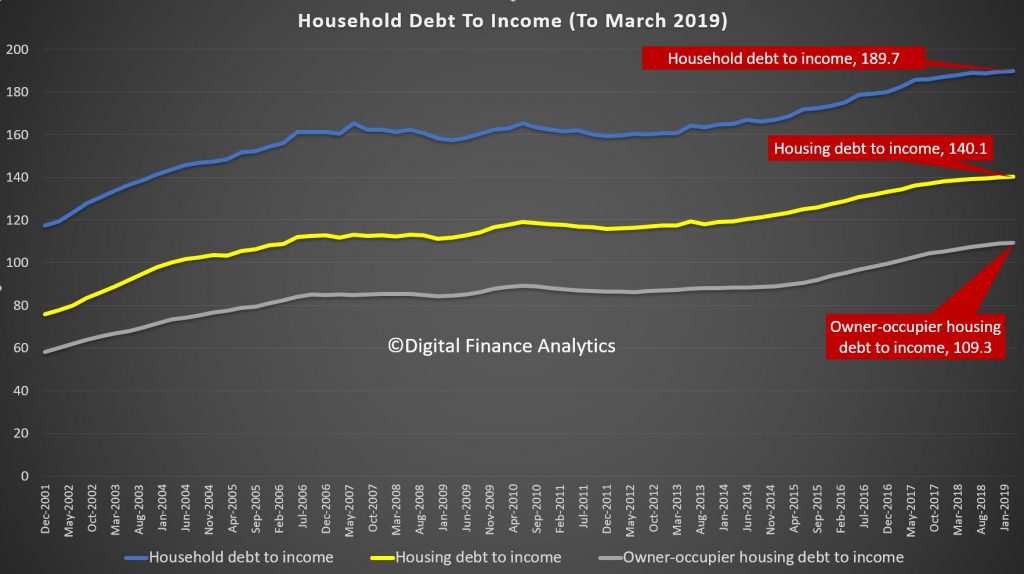
The latest UBS study, the fifth in their series looking at lending standards, and based on a survey of around 900 home loan applicants reveals that (perhaps surprisingly) there was a rise in “porkys” being told as part of the mortgage application, despite the Banking Royal Commission.
As a result, more than a third of Australian home loans could have ‘liar loans’ based on inaccurate information.
UBS Analyst Jonathan Mott said:
While asking detailed questions appears to be prudent, it does not appear to be effective as many factually inaccurate mortgages are still working their way through the process.
Of the borrowers who said their application was not completely factual in the past year, 20 per cent overstated their income, 23 per cent understated debts, 34 per cent understated their living costs, and 23 per cent misstated multiple categories.
Now, this is consistent with the DFA surveys where true incomes and costs are often higher than might be expected. And the extra granularity now required by the banks (many categories of costs, more detail on incomes etc) can create a false sense of accuracy – especially when many households are making best guesses to provide information to support their applications.
And financial intermediaries still appear to be part of the story, with a higher percentage of borrowers who misstated information on applications through a mortgage broker (40 per cent) than through the banks (27 per cent).
UBS said that a “large number” of survey respondents indicated their mortgage consultant advised them to misrepresent elements of their application.
At a time when the mortgage growth stops are being pulled, and lower rates are expected in a highly competitive market, this will simply create a bigger bust later.
And remember that on an international basis, we are right at the top of the international benchmarks in terms of household debt.
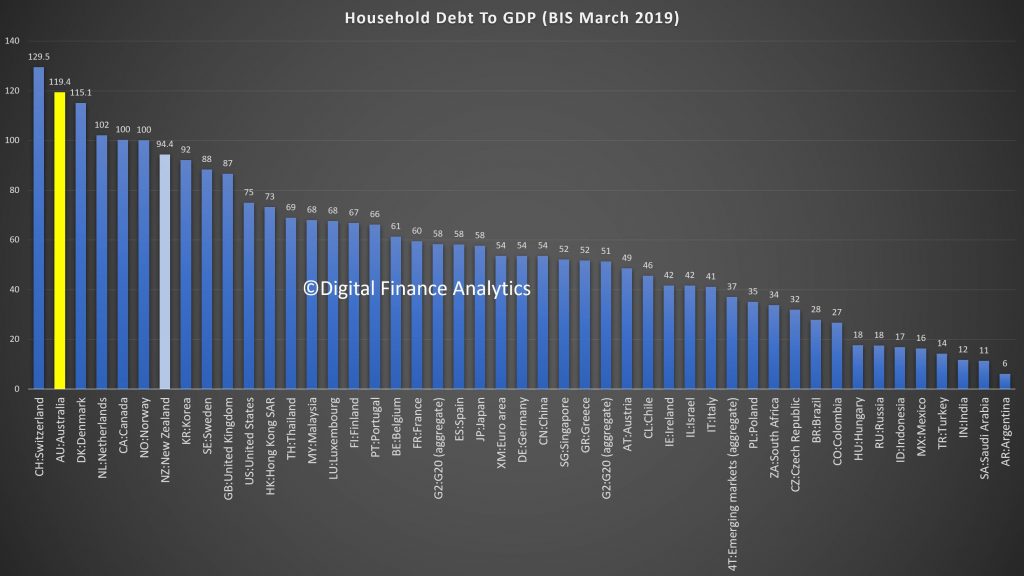
In fact according to the latest BIS data we lead in terms of debt servicing ratios.
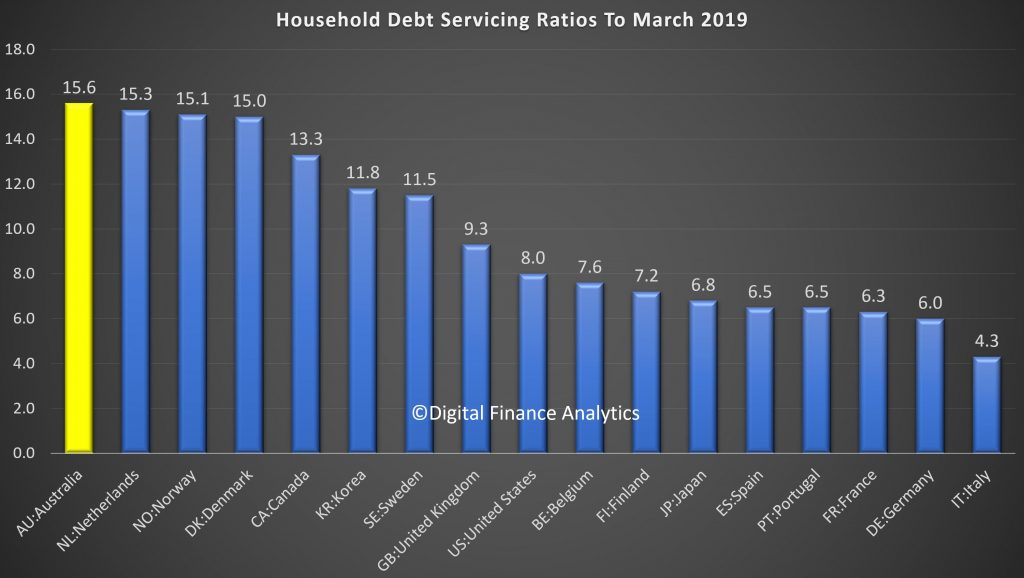
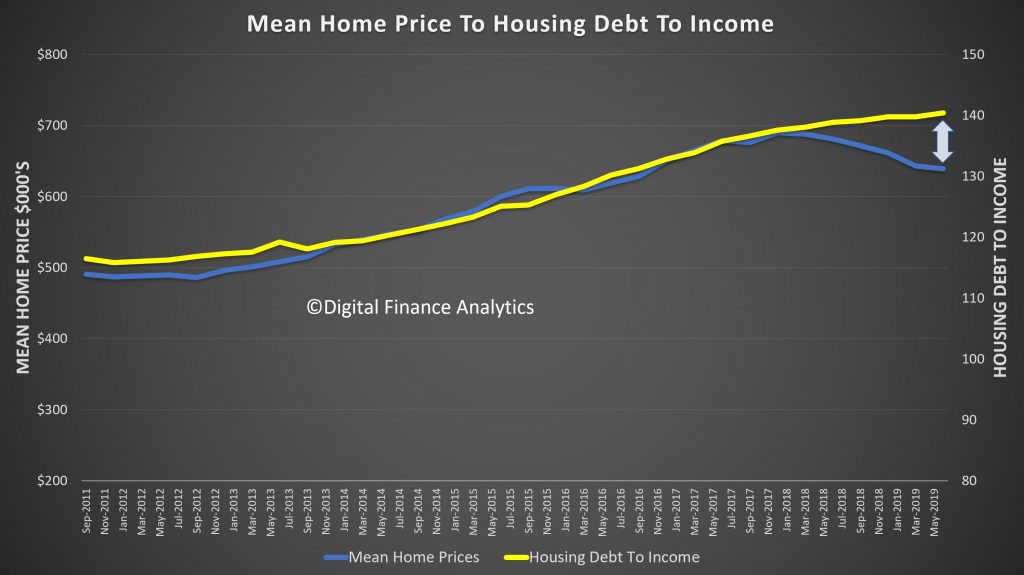
And the falls in prices have created a significant gap which highlights the risks in the system.
You can watch our recent show where we look at household debt in more detail including the data above.