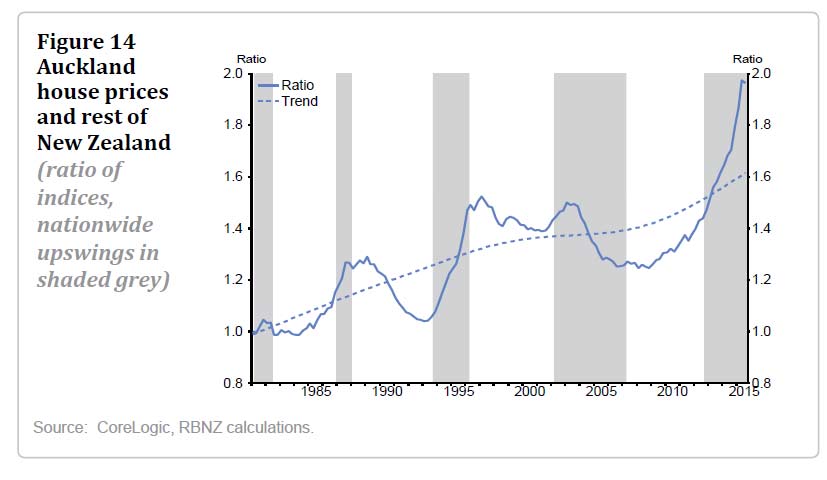
Growing imbalances in the housing market require policy action on a number of fronts, New Zealand Reserve Bank Deputy Governor Grant Spencer said today. In an excellent speech he draws important links between the elements driving house prices, and also underscores the limits of the banks range of options, especially considering the target inflation range of 1-3%.
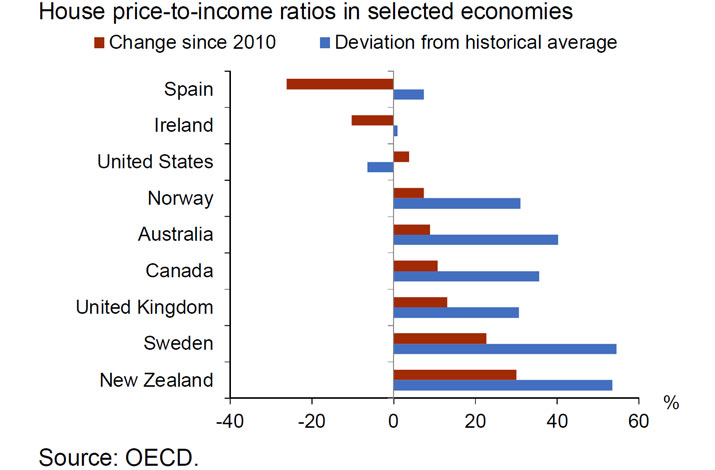
New Zealand is experiencing a housing market boom. House prices are increasing at 13 percent per annum nationally, and at 15-20 percent in Auckland and close-by regions. Evidence from housing cycles in several advanced economies suggests that the longer this continues, the more likely there will be a severe correction.
Speaking to the Wellington Branch of the New Zealand Institute of Valuers, Mr Spencer said that a range of factors had contributed to strong demand for housing, including record low interest rates, rising credit growth, and population increases.
While housing demand has been strong, the housing supply response has been constrained by rigid planning and consent processes, community preferences in respect of housing density, inefficiencies in the building industry, and infrastructure development constraints around financing and resource consents.
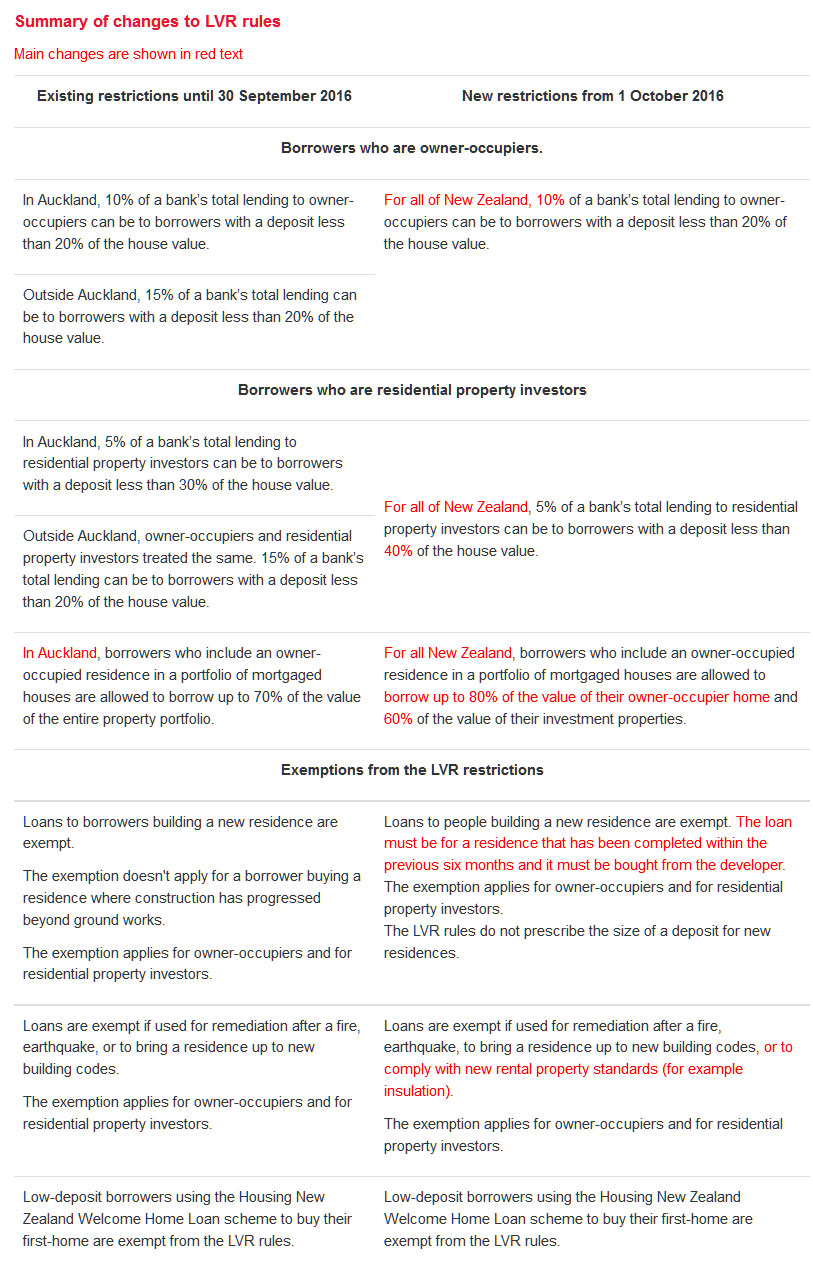
When the Bank had introduced LVR restrictions in 2013, they saw some markets slowing, but “House price pressures have re-emerged in Auckland following an easing in late 2015 and have also strengthened across other regions”.
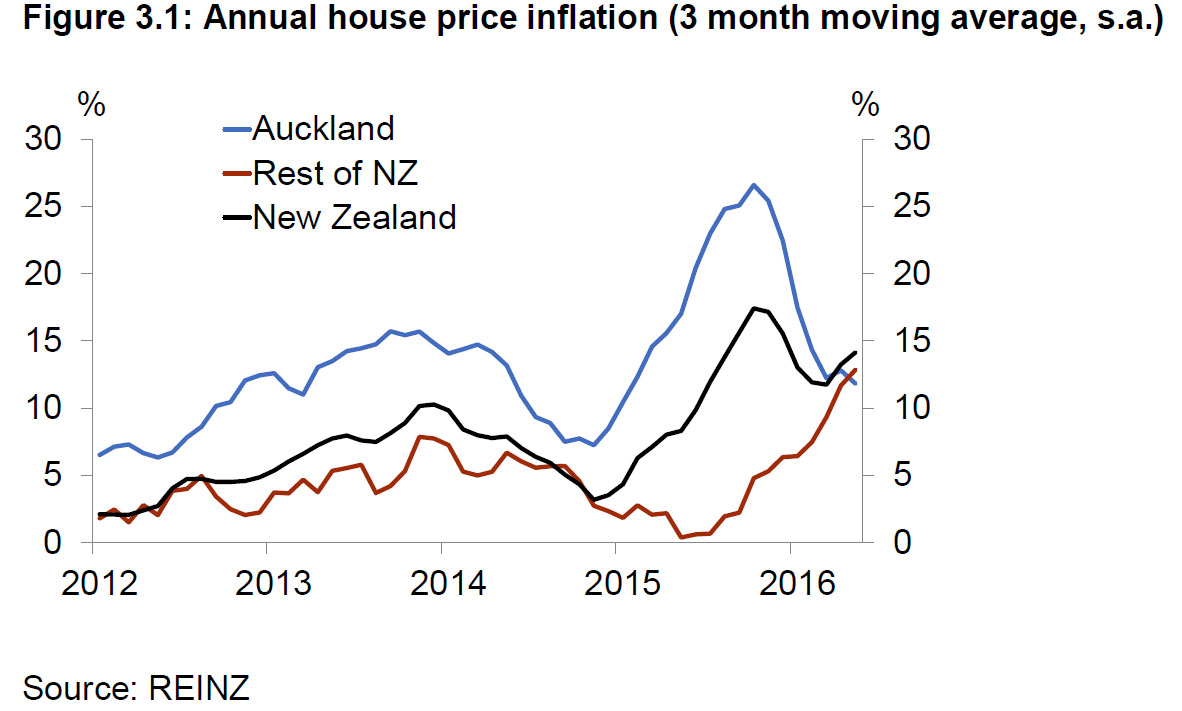
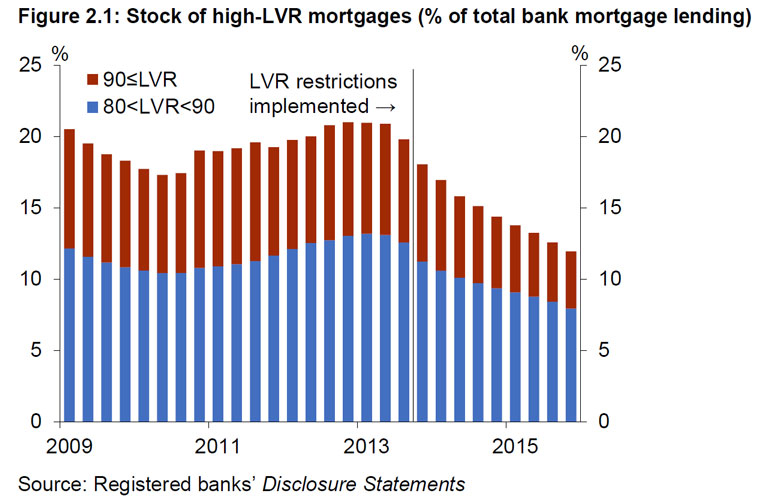 New Zealand house price inflation began to accelerate again from around March 2016 as demand pressures intensified in Auckland. In the meantime, other regions were contributing to higher national house price inflation from mid-2015, particularly those areas adjacent to Auckland. Most regional centres are now experiencing annual house price inflation in excess of 8 percent. Similarly, sales activity increased across the country in the first half of 2016. Reflecting the underlying housing shortage, new listings have remained flat. Listings as a proportion of sales are now 40 percent below the previous low seen at the height of the pre-GFC boom in 2007.
New Zealand house price inflation began to accelerate again from around March 2016 as demand pressures intensified in Auckland. In the meantime, other regions were contributing to higher national house price inflation from mid-2015, particularly those areas adjacent to Auckland. Most regional centres are now experiencing annual house price inflation in excess of 8 percent. Similarly, sales activity increased across the country in the first half of 2016. Reflecting the underlying housing shortage, new listings have remained flat. Listings as a proportion of sales are now 40 percent below the previous low seen at the height of the pre-GFC boom in 2007.
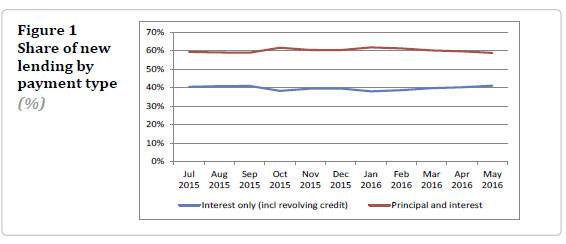
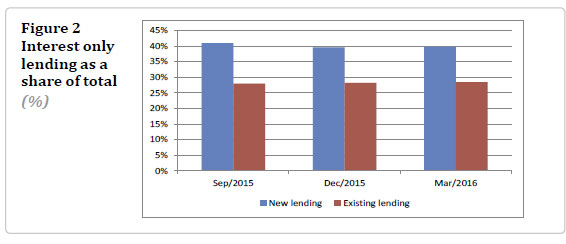
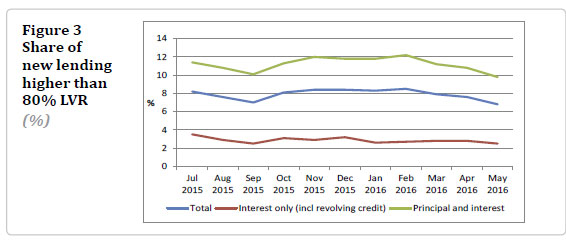
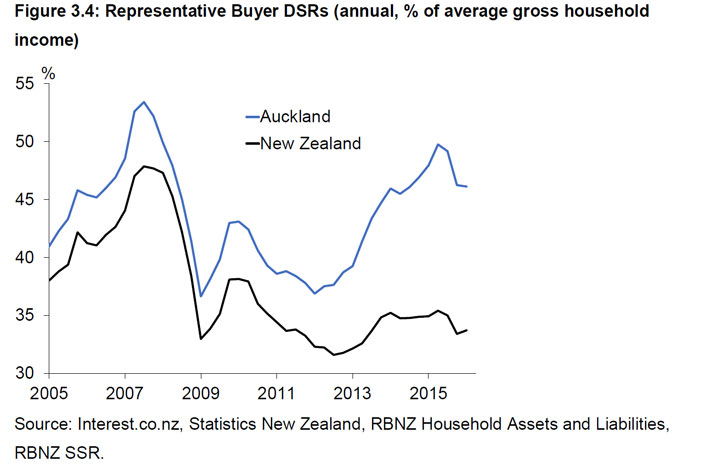
 He also highlighted an increase in investor purchases, and significant mortgage refinance, including increased interest-only and high debt-to-income lending. New mortgage commitments are also elevated, running at an annual rate of 35%. Debt servicing ratios are also elevated.
He also highlighted an increase in investor purchases, and significant mortgage refinance, including increased interest-only and high debt-to-income lending. New mortgage commitments are also elevated, running at an annual rate of 35%. Debt servicing ratios are also elevated.
 Supply is not meeting demand he concluded. This is a recipe for potential disaster.
Supply is not meeting demand he concluded. This is a recipe for potential disaster.
The longer the boom continues, the more likely we will see a severe correction that could pose real risks to the financial system and broader economy.
Mr Spencer said a broad range of initiatives is necessary to increase the long-term housing supply response, particularly in Auckland, and to help ensure housing demand is kept in line with supply capacity.
The Reserve Bank has no direct influence over supply, but can influence housing demand through the credit channel. In this regard, we see the Reserve Bank as part of a team effort.
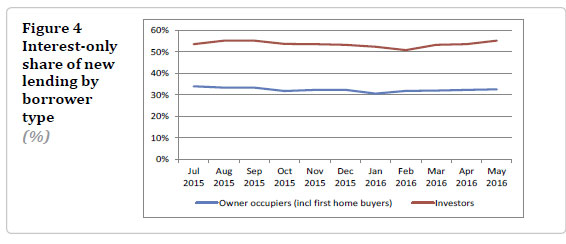
A dominant feature of the housing resurgence has been an increase in investor activity, which increases the risk inherent in the current housing cycle.
The Reserve Bank is considering tightening Loan-to-Value Ratios (LVRs) further to counter the growing influence of investor demand in Auckland and other regions, and to further bolster bank balance sheets against fallout from a housing market downturn. Such a measure could potentially be introduced by the end of the year.
Limits on Debt-to-Income ratios (DTIs) might also have a role to play but would be a new instrument that would have to be agreed by the Minister of Finance under the Memorandum of Understanding on Macro-prudential policy. Further investigation of this option will be undertaken.
A third option is a housing capital overlay. The Reserve Bank has already indicated that it will be conducting a full review of bank capital requirements over the coming year.
Consideration might be given to further reducing the tax advantage of investing in residential housing. Supply side issues also need attention. But much of this lays beyond the remit of the Central Bank.
He concluded that the causes of the imbalances are complex with a number of important drivers on both the demand and supply side. Addressing these imbalances will require policy action by a variety of agencies on a number of fronts. The underlying housing shortage needs to be urgently addressed, particularly in Auckland where population growth continues to outstrip housing construction. A step up in supply is required and finalisation of the Auckland Unitary Plan will be a key opportunity to facilitate such a step.
On the demand side, the key drivers are population growth and easy credit. The low cost of credit is making higher debt levels affordable, particularly for investors who can deduct interest costs from taxable income. Residential investors are accounting for an increasing share of house sales and new mortgage credit.
The Bank’s interest rate policy must have regard to financial stability concerns, but the global environment is likely to keep interest rates low for some time yet. Macro-prudential policy can assist in containing the growing risk to financial stability as the current housing market reaches new extremes. In light of the growing risk, the Reserve Bank is closely considering measures that could be progressed in the coming months.