According to APRA, interest only loans continue to grow as a proportion of all home loans. Recently Moodys warned about the increased risks which may stem from this type of loan. So the question is, should we be concerned, bearing in mind the recent RBA comments “indicative of speculative demand motivating a rising share of housing purchases. Consistent with mortgage interest payments being tax-deductible for investors, the interest-only share of approvals to investors remains substantially higher than to owner-occupiers”?
There are a number of reasons why interest only loans are attractive, especially for those using negative gearing. But the main reason is that the monthly payment are lower, thus improving servicability. Here is an example, of a $300,000 Principal and Interest Loan, at a nominal 6.5%. The monthly repayment over 30 years is $1,896.
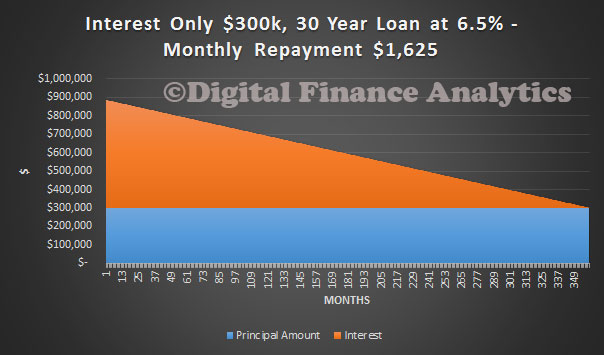
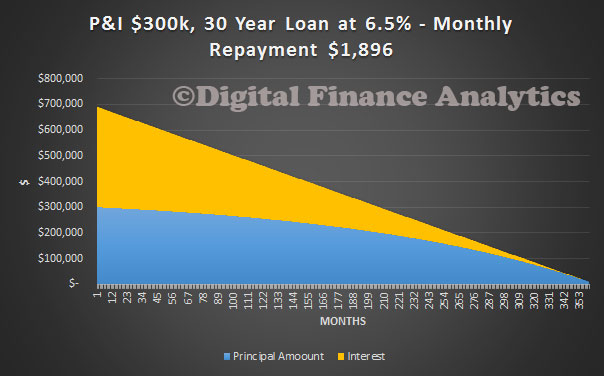 However, on an interest only basis, using the same values, the repayment drops to $1,625, more than $250 a month lower. The small problem though is that in 30 years time, you still have to repay the capital balance. Now of course, in real terms the value will be eroded by inflation, and house prices are likely to rise, so the assumption is that the value generated in the property can then be realised, repaying the loan, (or from other sources e.g. superannuation?). In practice, interest rates may move, and sometimes people switch to P&I after a period of time.
However, on an interest only basis, using the same values, the repayment drops to $1,625, more than $250 a month lower. The small problem though is that in 30 years time, you still have to repay the capital balance. Now of course, in real terms the value will be eroded by inflation, and house prices are likely to rise, so the assumption is that the value generated in the property can then be realised, repaying the loan, (or from other sources e.g. superannuation?). In practice, interest rates may move, and sometimes people switch to P&I after a period of time.
So, now lets look at the UK experience. There are 11.3 million mortgages in the UK, with loans worth over £1.2 trillion. At the end of 2013 there were an estimated 2.2 million pure interest-only loans outstanding, and a further 620,000 part interest-only, part repayment mortgages outstanding on lenders’ books. Compared to 2012 this represents a fall of around 300,000 pure interest-only mortgages (down 12%), and around 90,000 part-and-part mortgages (down 13%).
According to the Council for Mortgage Lenders, at the peak of their popularity in the late 1980s, interest-only mortgages accounted for more than 80% of all loans taken out. This year, however, lenders are likely to advance only around 40,000 new interest-only loans for residential house purchase, less than 10% of the total.
Among first-time buyers, the decline in interest-only borrowing has been particularly pronounced. CML data shows that only 2% are taking out interest-only mortgages, with 98% opting for repayment loans. Interest-only accounts for a higher proportion of new borrowing by existing owner-occupiers who are moving (10%) and those remortgaging (13%).
Most new interest-only borrowing is in the buy-to-let market (aka investment mortgage), where this option remains the norm for very good reasons. Fixed-rate interest-only mortgages minimise costs for landlords and are more likely to produce a profitable margin. Interest-only mortgages also enable landlords to meet lenders’ requirements that their rental income produces an average minimum cover of 125% of their borrowing costs.
A couple of years back, there were concerns in the UK that interest only loans may be a problem, and alongside regulatory commentary, CML produced an “interest-only toolkit” designed to help mortgage lenders to work with their interest only mortgage customers, especially those loans due for repayment before 2020.
The regulators reached the conclusion that 90% of interest-only mortgage holders have a repayment strategy in place. Lenders made a commitment with the regulator (the Financial Conduct Authority) to contact interest-only loan holders and ask about their repayment plans. The CML via it lender members found that Lenders have been using a variety of contact strategies. In addition to reminders and mailings requesting the customer’s written response (including questionnaire responses), telephone calls, face-to-face meetings and even home visits are also used by some lenders. Overall, around 30% of customers contacted have so far responded.
Among those borrowers who have responded, around four out of five already had a clear plan. Among those who did not, the survey found that the solutions and approaches lenders are offering typically include term extensions, permanent conversions to capital and interest, and overpayments.
There has also been a positive set of changes in the loan-to-value profile of outstanding interest-only mortgages. Two-thirds of outstanding interest-only mortgages have loan-to-value (LTV) ratios of less than 75% – and the vast majority of these are not due to mature until after 2020.
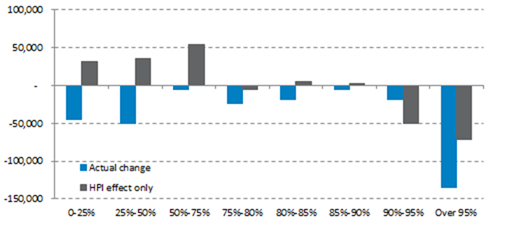
The chart shows that a large number of loans would have moved into a lower LTV band as a result of house price inflation alone. However, it also shows that borrowers are taking additional action to reduce their mortgage balances, as the effect of house price inflation alone would not have resulted in the improvements in outstanding LTVs that have been seen over the past year. Indeed, the number of loans in every LTV band below 75% would have seen an increase on the basis of house price inflation alone (as loans moved down from higher LTV bands) – but, in fact, every band saw a decrease.
Changes in interest-only loans outstanding, September 2012-December 2013, by LTV
 Under the new mortgage regulations now in force in the UK, lenders may offer interest only loans, but only if a borrower has a credible repayment plan, at the time of application.
Under the new mortgage regulations now in force in the UK, lenders may offer interest only loans, but only if a borrower has a credible repayment plan, at the time of application.
So some points to ponder.
1. How many interest only loans in Australia have a credible repayment strategy? To what extent is this considered by borrowers and lenders at the time of application?
2. Will rising house prices be the solution to interest-only loan repayment?
3. Are the review processes (on average each 5 years in Australia, even if the loan term is 25/30 years) sufficiently robust to identify potential issues?
4. Does Negative Gearing lead to a greater dependence on interest-only loans?



