Moody’s says that relaxed regulatory oversight for the largest US regional banks would be credit negative.
On 31 October, the US Federal Reserve (Fed) proposed revisions to the prudential standards for the supervision of large US bank holding companies to implement the Economic Growth, Regulatory Relief, and Consumer Protection Act (the Act) that became law in May of this year. The proposal would apply less rigorous capital and liquidity standards to most large regional bank holding companies with less than $700 billion of consolidated assets or less than $75 billion of cross-jurisdictional activity, a credit-negative.
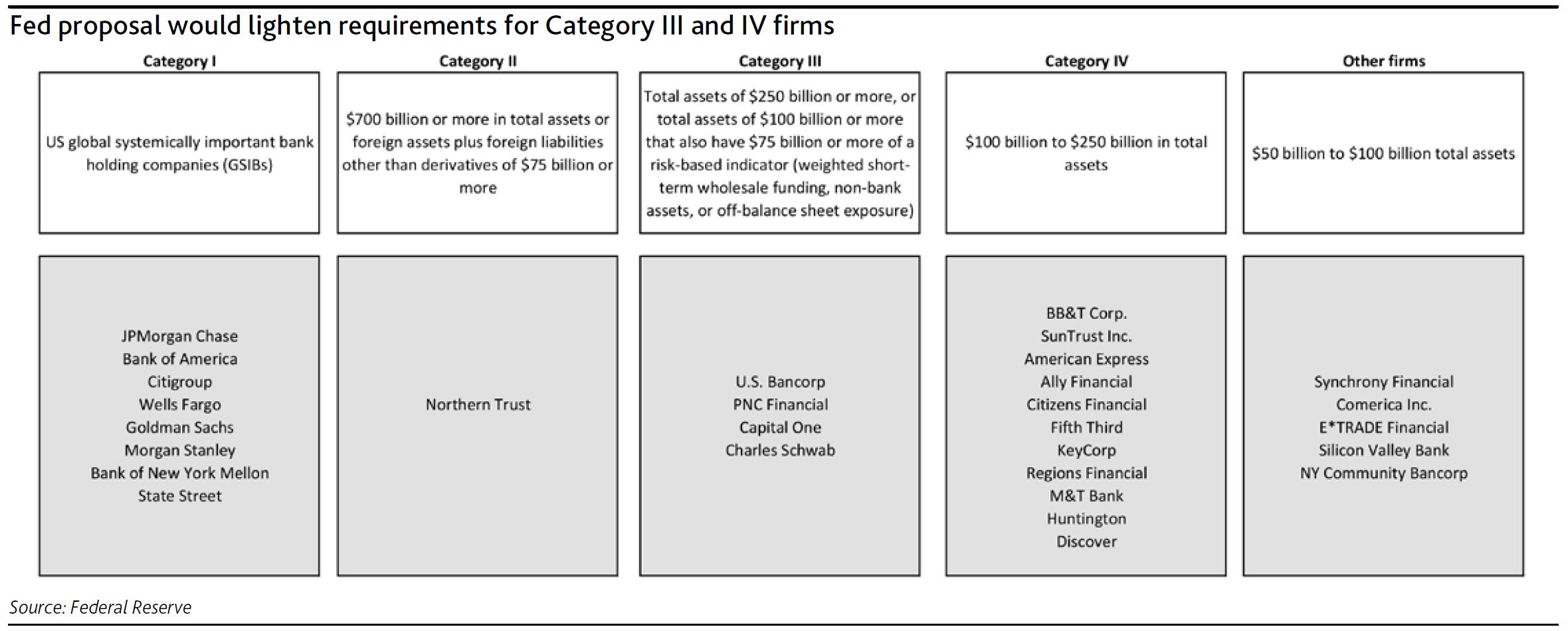
In particular, the Fed proposals would relax current supervisory requirements for banks with assets of more than $250 billion, which goes beyond the Act’s primary focus on banks below that threshold. However, the proposal is still consistent with the Act’s emphasis on regulation that increases in stringency with a firm’s risk profile, defining four categories of banks as described and named in Exhibit 1 (other firms are no longer subject to the Fed’s enhanced prudential standards under the Act).
The 11 firms in Category IV would be subject to significantly reduced regulatory requirements under the proposal, including public supervisory stress testing every two years instead of annually. These firms would also be permitted to exclude accumulated other comprehensive income (AOCI) from capital and would no longer be subject to the liquidity coverage ratio (LCR) or proposed net stable funding ratio (NFSR) rules. Internal liquidity stress-testing would be required quarterly rather than monthly.
The four firms in Category III would be subject to modestly reduced regulatory requirements under the proposal. They would no longer have to apply the advanced approaches (internal models-based) risk-based capital requirements but would remain subject to the standardized approach requirements. Like Category IV firms, they could elect to exclude AOCI from capital. However, they would still be subject to the annual public supervisory stress tests. Their LCR and NFSR requirements would be reduced to between 70% and 85% of full requirements.
The changes in capital and liquidity requirements for Category III and IV firms are likely to reduce their capital and liquidity buffers, a credit negative. Moreover, the reduced frequency of capital and liquidity stress testing could lead to more relaxed oversight and afford banks greater leeway in managing their capital and liquidity, as well as reduce transparency and comparability, since fewer firms will participate in the public supervisory stress test.
Category I and II firms would not see any changes to their capital or liquidity requirements. The proposals do not address the US operations of foreign banking organizations, but a proposal on their supervision will likely be forthcoming.