From The St. Louis Fed On The Economy Blog
On Feb. 6, the Wall Street Journal published a startling statistic: Between June 2016 and June 2017, more than 1,700 U.S. bank branches were closed, the largest 12-month decline on record.1
Structural Shift
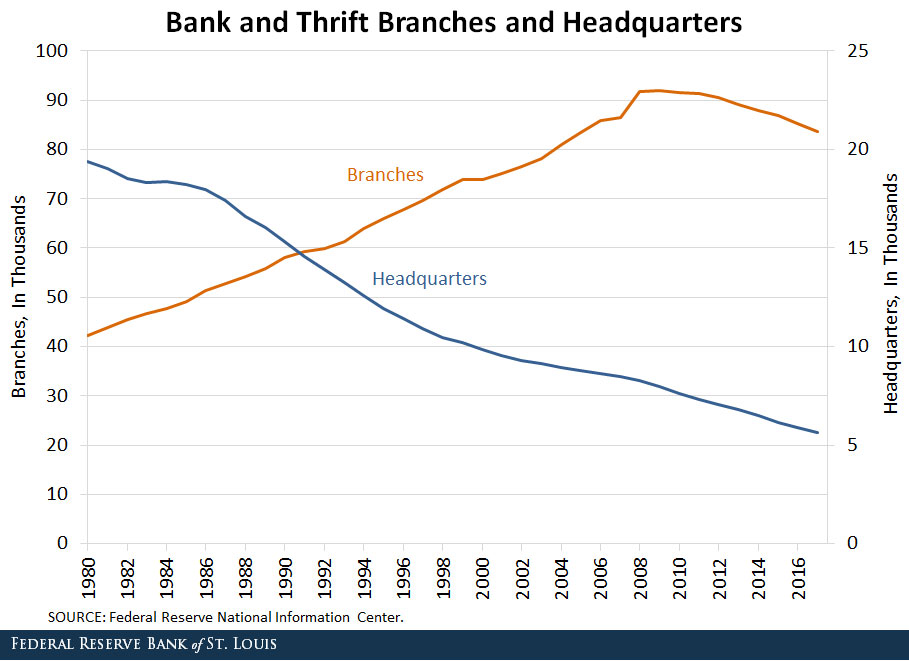
That large drop, while surprising, is part of a trend in net branch closures that began in 2009. It follows a profound structural shift in the number and size of independent U.S. banking headquarters, or charters, over the past three decades.
In 1980, nearly 20,000 commercial banks and thrifts with more than 42,000 branches were operating in the nation. Since then, the number of bank and thrift headquarters has steadily declined.
The reasons for the decline in charters and branches are varied. Regarding charters, the passage of the Riegle-Neal Interstate Banking and Branching Efficiency Act in 1994 played a significant role in their decline. Banks operating in more than one state took advantage of the opportunity to consolidate individual state charters into one entity and convert the remaining banks into branches. Almost all states opted in to a provision in the law permitting interstate branching, which led to a steady increase in branches.
Trend Reversal
Even before the number of charters declined, however, the number of branches grew steadily throughout the 1980s, 1990s and early 2000s. It peaked in 2009, when the trend reversed, as seen in the figure below.
Since 2009, the number of commercial bank and thrift branches has shrunk nearly 10 percent, or just over 1 percent per year.
The initial wave of closings can be attributed to a wave of mergers and failed bank acquisitions following the financial crisis. There was an immediate opportunity to reduce cost through the shuttering of inefficient office locations. Branch closings were also influenced by earnings pressure from low interest rates and rising regulatory costs.
More recently, changing consumer preferences and improvements in financial technology have further spurred the reduction in branches. Customers increasingly use ATMs, online banking and mobile apps to conduct routine banking business, meaning banks can close less profitable branches without sacrificing market share.
Uneven Changes
The reduction in offices has not been uniform. According to the Federal Deposit Insurance Corp., less than one-fifth of banks reported a net decline in offices between 2012 and 2017, and slightly more than one-fifth reported an increase in offices.
Just 15 percent of community banks reported branch office closures between 2012 and 2017. And though closures outnumber them, new branches continue to be opened. It’s also important to note that deposits continue to grow—especially at community banks—even as the number of institutions and branches decline.
The Industry of the Future
It seems inevitable that this long-term trend in branch closings will continue as consumer preferences evolve and financial technology becomes further ingrained in credit and payment services.
Although it is unlikely that the U.S. will end up resembling other countries with relatively few bank charters, it seems certain that consumers and businesses will increasingly access services with technology, no matter the size or location of bank offices. This change creates opportunities as well as operational risks that will need to be managed by banks and regulators alike.