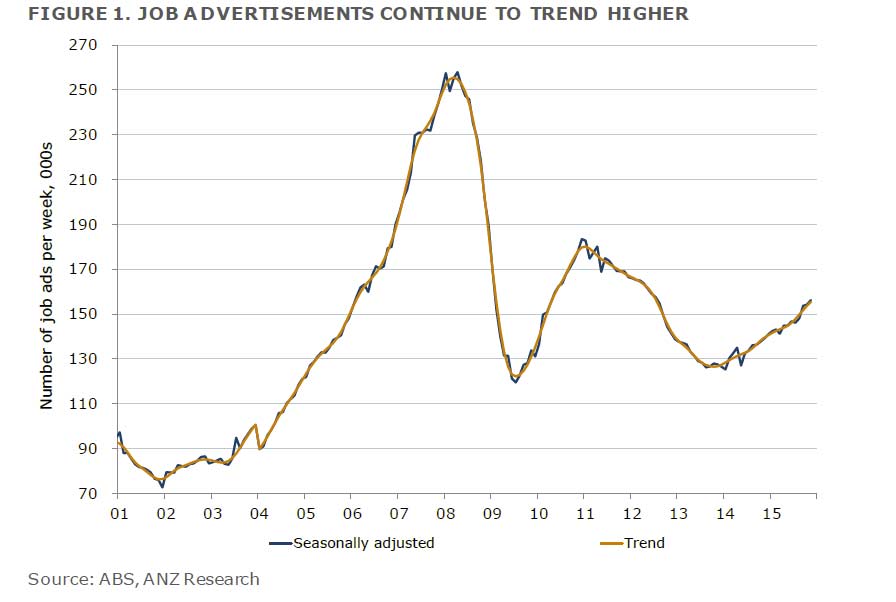
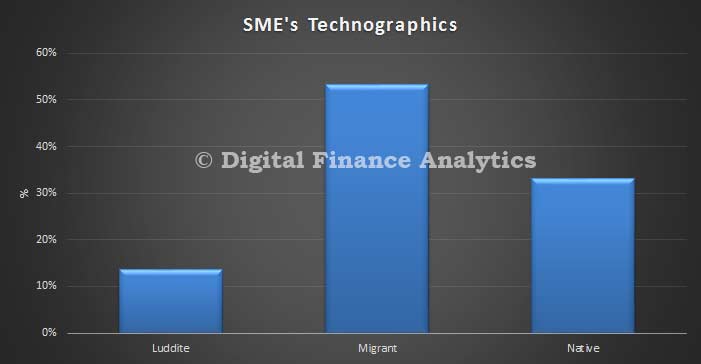
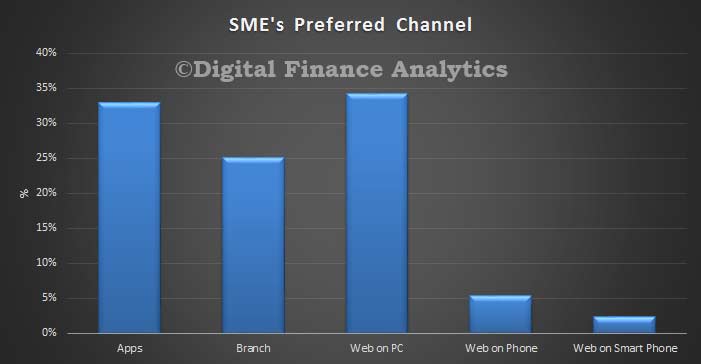
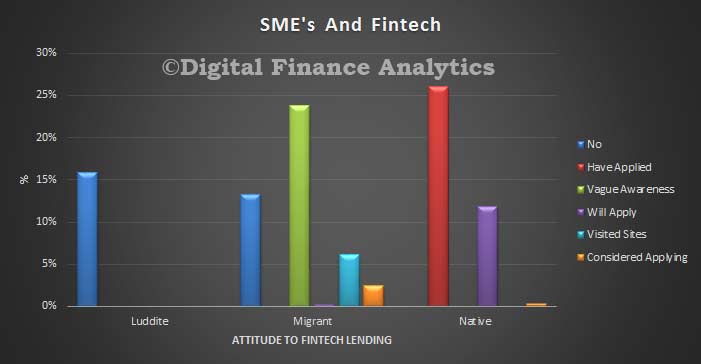
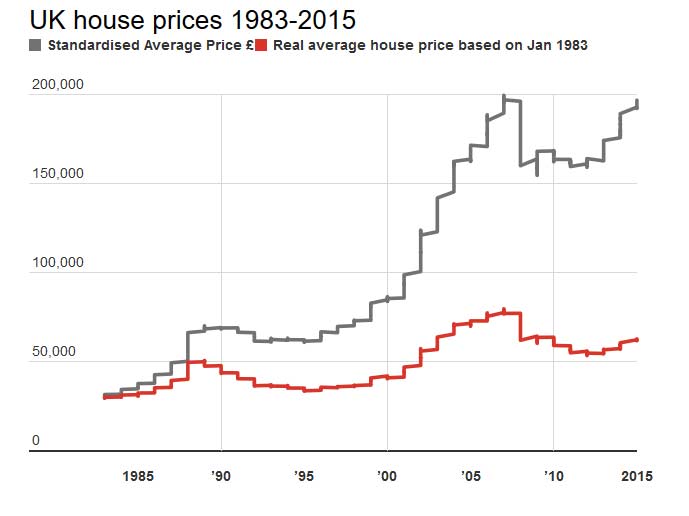
Average Australian household debt is four times what it was in 1988, rising from $60,000 to $245,000 after inflation, according to the latest AMP.NATSEM Income and Wealth report – Buy now, pay later: Household debt in Australia.
 The ratio of household debt to disposable income has almost tripled, from 64 per cent to 185 per cent during the same time. Declining interest rates, low unemployment and a strong economy have driven Australians to take on more debt and at the same time cushioned the impact of repayments.
The ratio of household debt to disposable income has almost tripled, from 64 per cent to 185 per cent during the same time. Declining interest rates, low unemployment and a strong economy have driven Australians to take on more debt and at the same time cushioned the impact of repayments.
But if interest rates were to rise by 2.5 percentage points, interest payments for Australia’s most indebted households with mortgages would rise to at least 58 per cent of household income, up from the current 42 per cent. These households would need to find an extra $16,615 a year just to cover interest payments, which would increase from $43,926 to $60,541 a year. For households with mortgages and typical levels of debt, a 2.5 percentage point increase would mean debt repayments would rise from 16 per cent to 23 per cent of income, taking annual interest payments from $15,464 to $21,687, or an extra $6,223 per year.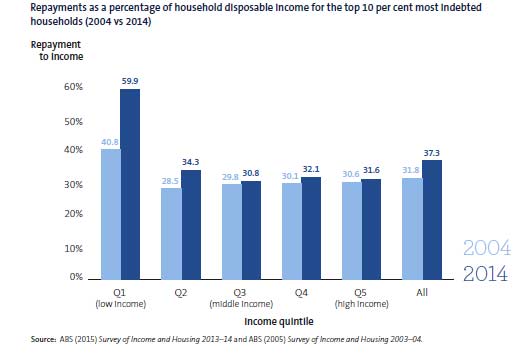
Other findings from the report include:
• Typical households headed by 30 to 50 year olds have been hit the hardest with their debt to income increasing from 149 per cent to 209 per cent during the past 10 years.
• For people aged over 65, mortgages make up almost a third of their household debt – up significantly from 20 per cent 10 years ago.
• For low-income households, debt is 43 per cent of their disposable income, almost doubling since 2004.
• The top 10 per cent most leveraged Australian households now have an average debt to disposable income ratio of 600 per cent.
Household debt in Australia has increased considerably
• In 1988, the average household could have paid off all its debt with the after-tax income it earned in eight months – it would now take almost two years.
• Australian household debt has grown at 5.3 per cent above inflation each year, outstripping income growth of 1.3 per cent.
• Australia’s most leveraged households have six times as much debt as their annual disposable income.
Australians are taking more debt into retirement
• Of the top 10 per cent most indebted households, it’s the over 65 year old households that have increased their level of debt the most – their repayments to income have almost doubled from 9 to 17 per cent.
First home buyers are taking on considerably more debt
• Rising house prices have seen first home buyers doing it tough with their debt levels at 3.6 times their annual disposable income, up from 3.1 since 2004.
• Typical first homebuyers would feel the greatest impact from rising interest rates – a 2.5 percentage point rise in rates would increase interest repayments as a percentage of disposable income from 21.2 per cent to 30.2 per cent or an extra $8,047 a year.
Lower income families have also taken on a lot more debt
• Among the top 10 per cent of indebted households, low-income households are in the most vulnerable position with their interest payments increasing from 40.8 per cent to 59.9 per cent of disposable income during the past 10 years.
The debt picture is precarious for the most leveraged households
• Australia’s debt boom has impacted all households, but it is the most indebted who have ramped up their leverage the most – for households with the top 10 per cent of debt levels, debt to income has increased from 4.4 to six times income, compared to the typical household which increased from 0.7 to 0.88 times income.
Australian households are among the most indebted in the world
• Australian households have the fifth highest debt levels in the world, with more average household debt than comparable economies like Canada.
Mortgage debt is highest for households headed by a 30-50 year old and over 65s have the most investor debt
• Home mortgages make up almost 63 per cent of debt for households headed by a person aged 30 to 50.
• Investor debt is highest for over 65 year old households at almost 60 per cent of their total debt.
Ninety per cent of Australian household debt is being used to buy a home or to build wealth through investing
• 56 per cent on mortgage and 36 per cent on investing (e.g. rental properties or shares).
Many Australian households experience financial stress
• A quarter of Australians currently experience financial stress from things like paying bills, raising emergency money or having to ask friends for financial assistance.
• Low income families experience six times the rate of financial stress than higher income families.
Single parents face significant financial stress
• Nearly two in three single parents are facing at least one financial stress, compared to just 13 per cent of couples who have children.
• Single parents are 10 times more likely to be experiencing at least three forms of financial stress compared to couples with children.
Regions with the highest typical repayment to income are in the outer suburbs of Sydney, Perth and Melbourne
• For households with the top 10 per cent of debt, it’s the inner city suburbs of Sydney, Perth and Melbourne with the highest repayment to income.
Tasmania and NSW households have the greatest share of mortgage debt
• As a share of debt, mortgage debt is highest in Tasmania, with almost 66 per cent of household debt tied to mortgages and New South Wales has the second highest level of mortgages at just over 58 per cent of total debt.
• The combined territories (Australian Capital Territory and Northern Territory) have the lowest share of mortgage debt at almost 50 per cent.
• Investor debt is highest in Australia’s territories, at 44 per cent, followed by Queensland and Western Australia at around 38 per cent each.
Of the most leveraged households (those with the top 10 per cent of debt) debt is 5.4 times household income in New South Wales, but Western Australia leads the way with debt levels at 6.1 times household income
• Highly leveraged households in the combined territories carry debt levels 5.7 times annual income and for Queensland households debt comes in at 5.5 times income.
Regions with the highest typical debt repayment burden are found in the outer ring suburbs of major capital cities
• Looking at households with typical repayments in each region, households in northern Perth are the most burdened with interest repayments at $15,100 per year or 14 per cent of disposable income. A 2.5 percentage point increase would push up repayments by $6,400 a year.
AMP publishes these reports to help the community make informed financial and lifestyle decisions and to contribute to important social and economic policy debate.