On 1 July, legislation in Denmark took effect that will trigger the inaugural issuance of Danish public housing covered bonds (almene realkreditobligationer) as a new asset class, says Moody’s.
These new covered bonds will be issued out of newly established capital centres with the sole purpose of funding mortgage loans granted to public housing companies (almen boligforening). As is the practice in the Danish covered bond market, assets serving as security for covered bonds must be segregated into independent cover pools, referred to as capital centres in mortgage banks. The Danish government guarantees in full the mortgage loans as well as the public housing covered bonds.
The law is credit positive for potential investors in public housing covered bonds because their credit risk will be lower than in existing mortgage covered bonds. Although investors in both types of covered bonds benefit from recourse to the issuing mortgage bank and a pool of good quality mortgage assets, only public housing covered bonds benefit from a state guarantee in case the issuer fails to fulfil its obligations.
Today, public housing loans benefit from a municipality’s partial guarantee of the loan, but under the new framework such loans will benefit from the federal government’s guarantee covering the full loan amount. In 2017, Danish municipalities guaranteed on average the most risky 62% of mortgage loans. Under the new model, the government will charge a guarantee commission from the mortgage banks. The mortgage banks, owing to the government’s full guarantee, will have lower capital requirements and lower over- collateralisation requirements for the covered bonds that are set in Denmark at 8% of risk-weighted assets.
Denmark’s public housing covered bonds will be issued by mortgage banks via frequently held auctions and tap sales. For the issuance of public housing covered bonds, banks shall obtain bids for purchases from Denmark’s central bank on behalf of the Danish government before the bonds are sold to others, which reduces funding execution risk for the public housing companies and the mortgage banks. According to the Danish central bank, the government will purchase DKK42.5 billion of public-sector covered bonds in 2018, corresponding to the total of new loans and refinancings of existing loans. The government will bid at a rate corresponding to the yield on government bonds.
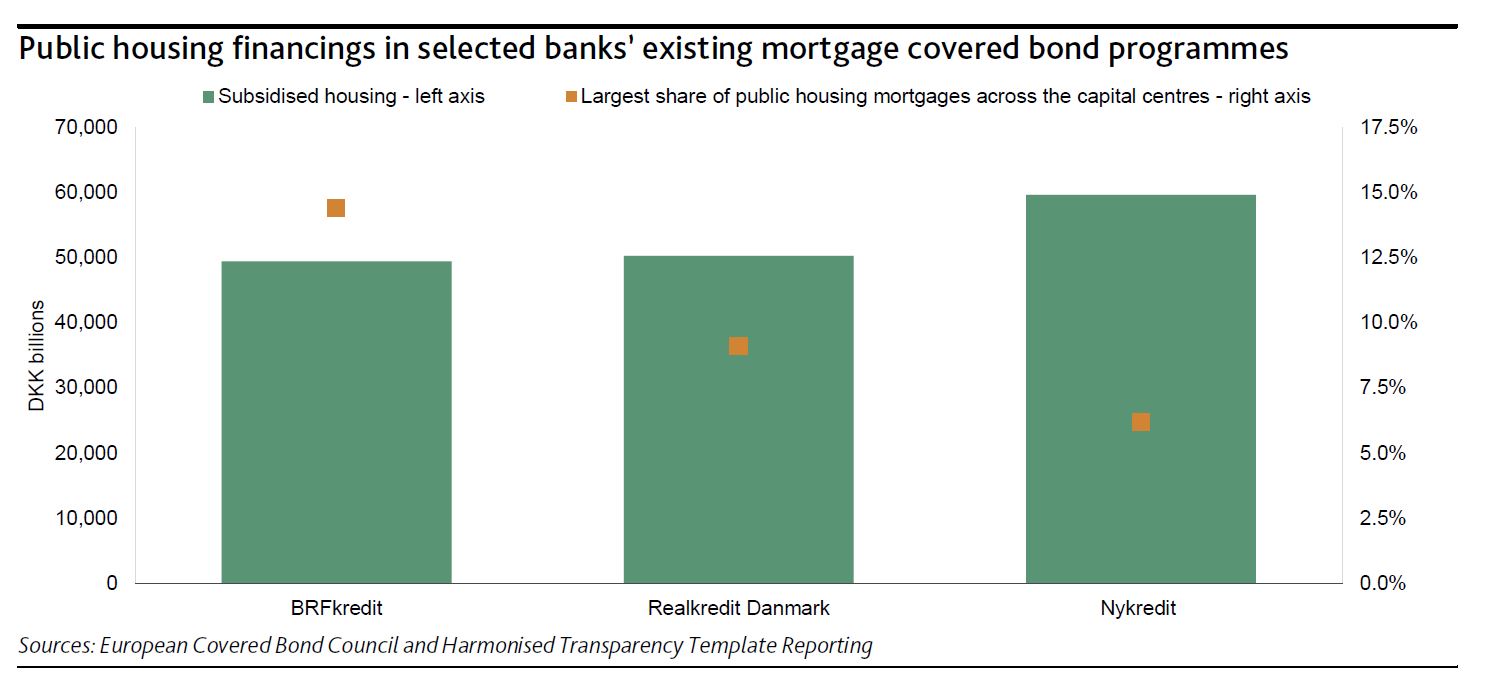
We expect a quick migration of public housing loans to the newly established capital centres in order to benefit from the government guarantees. This will lead to an increased level of prepayments and refinancings in the existing capital centres. The public housing sector has subsidised loans totalling around DKK180 billion that are largely financed by existing capital centres that issue mortgage covered bonds.
Nykredit Realkredit A/S, Realkredit Danmark A/S (part of Danske Bank) and BRFkredit A/S (part of Jyske Bank) are active lenders in this sector, each currently lending DKK50-DKK60 billion to the public housing sector. Despite the public housing loans being refinanced into the new capital centres, the risk characteristics of the capital centres will not change materially because the share of public housing loans is often small and in active capital centres does not exceed 15% as shown in the exhibit.