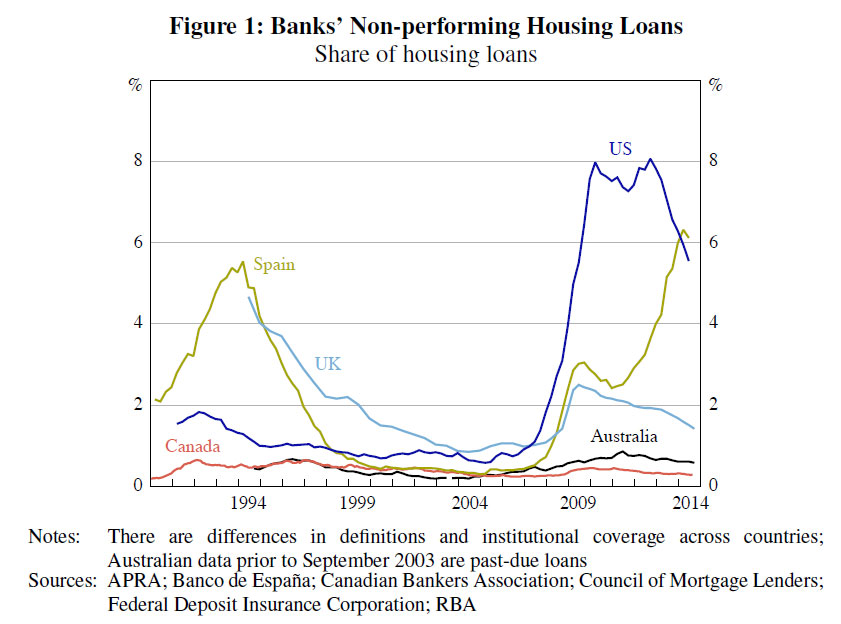
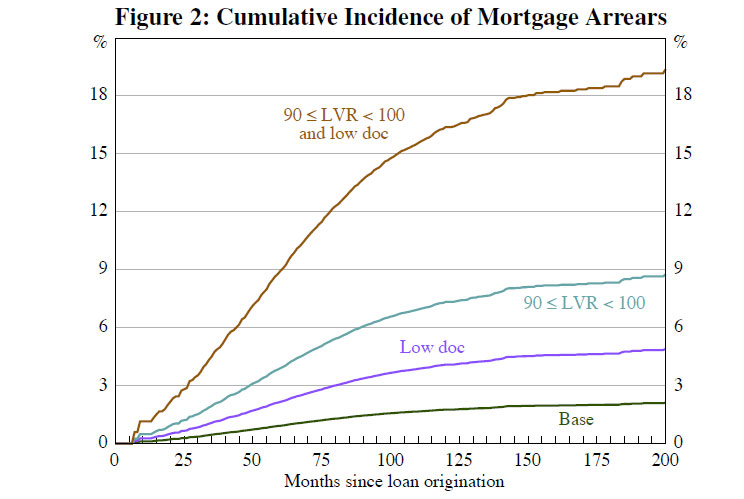
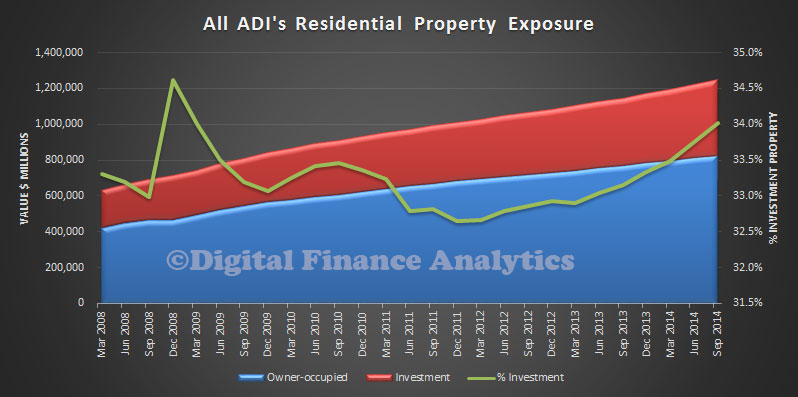
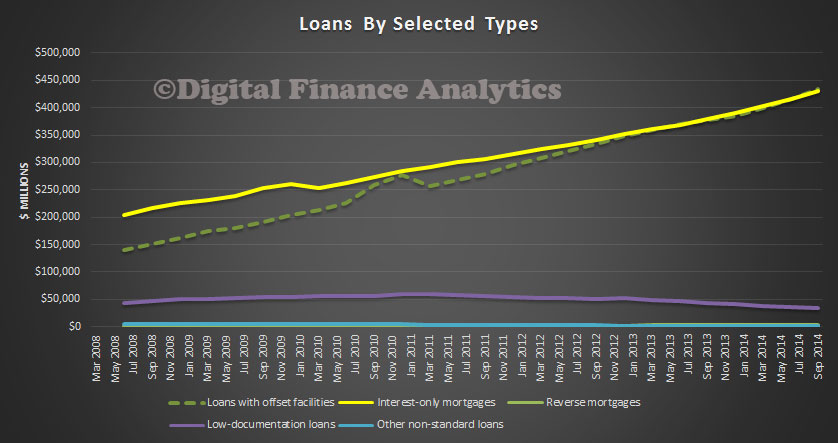
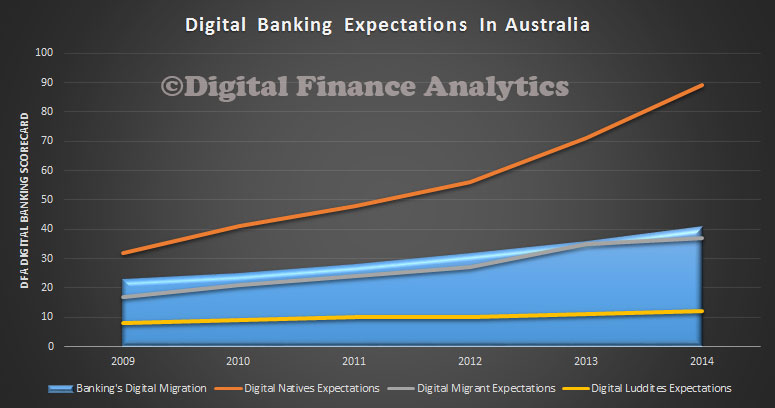
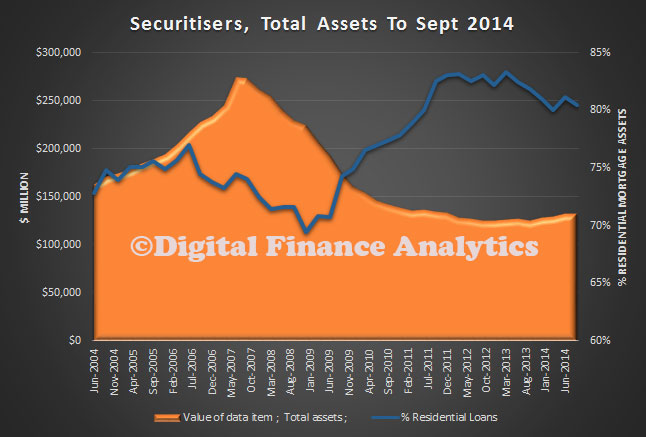
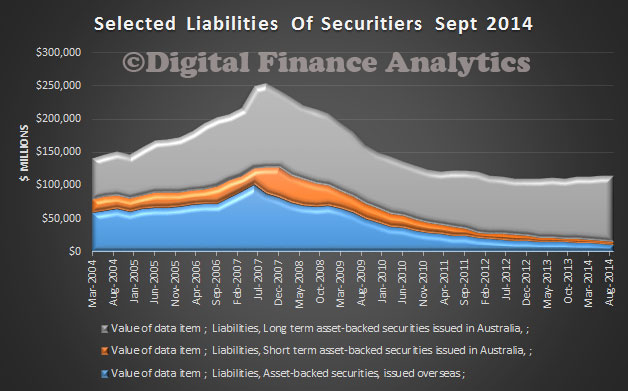
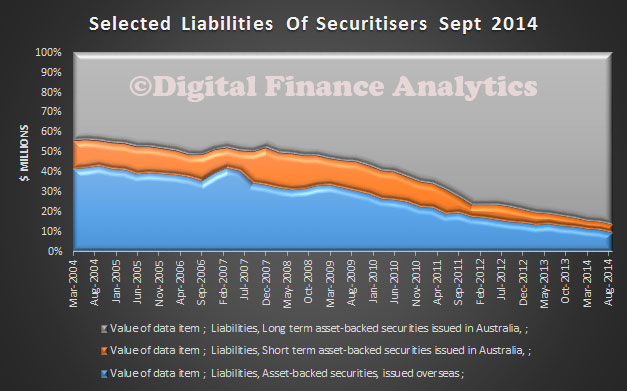
The RBA today published a paper on “Mortgage-related Financial Difficulties: Evidence from Australian Micro-level Data.” Although default rates in Australia are lower than in many other countries,
their research paper delved into the different types of mortgage lending, using loan-level pool data provided by MARQ Services and concluded that higher LVR lending, and interest only loans were more risky than average.
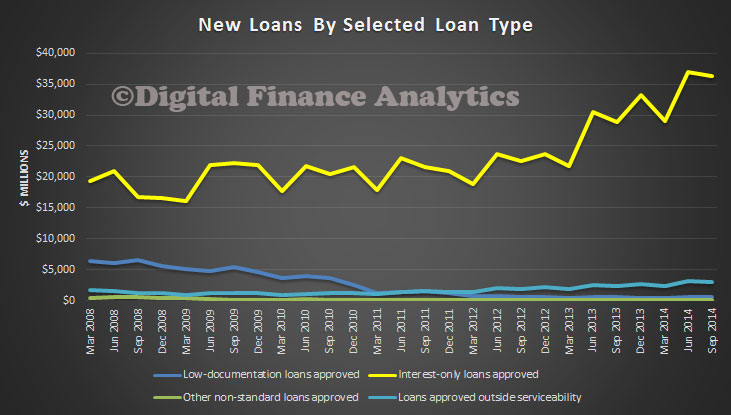
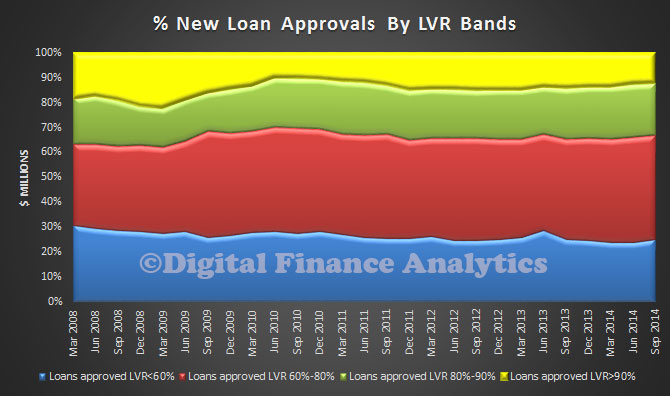
Our loan-level analysis suggests that loans with high loan-to-valuation ratios (above 90 per cent) are more likely to enter arrears, while loans that are repaid relatively quickly are less likely to enter arrears. Together, these results reinforce the importance of supervisors carefully monitoring changes in lending standards that affect the loan-to-valuation ratio of loans at origination and rates of principal repayment thereafter. Although interest-only and fixed-rate loans appear less likely to enter arrears, the fact that these loans tend to be repaid relatively slowly (particularly interest-only loans) means that increases in these types of lending can represent an increase in risk. Additionally, low-doc loans appear more likely to enter arrears than other types of loans, even after controlling for whether the borrower was self-employed. This suggests that lenders should maintain sound income documentation and verification policies, and that supervisors should continue to monitor developments in the low-doc lending space.
Borrowers with relatively high mortgage interest rates have a higher probability of entering arrears, even after controlling for the estimated minimum mortgage repayment, which is consistent with riskier borrowers being charged higher interest rates to compensate for their higher risk. We caution, however, that the loan-level results are affected by data limitations, such as a lack of information on borrower income, wealth and labour force status, and a relatively small sample of banks.
Complementary analysis using household-level data suggests that having a high debt-servicing ratio (above 50 per cent) significantly increases the probability of missing a mortgage payment. This highlights the importance of borrowers not overextending themselves by taking out loans of a size that will be difficult to comfortably service. Additionally, it reinforces the importance of lenders maintaining sound debt-serviceability and income-verification policies.
Having previously missed a mortgage payment is also found to be a significant predictor of subsequently missing another mortgage payment. This highlights the heightened risk associated with lending to borrowers with a history of missing payments, and supports the practice of lenders using information on previous debt payment behaviour (such as credit scores) in their credit assessment processes.Overall, our results reinforce the importance of supervisors carefully monitoring changes in lending standards, as well as the importance of borrowers exercising prudence when taking on mortgage debt.
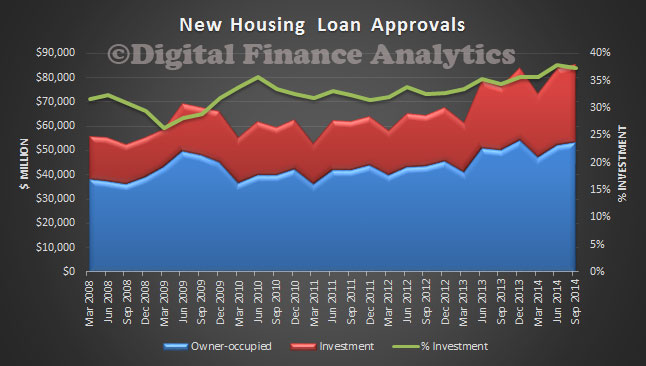
This is a significant and important contribution to the current debate about how risky the mortgage loan portfolio are. It also chimes with DFA mortgage stress analysis. Today we highlighted the APRA data which showed that both high LVR loans and interest only loans made up a significant element in the current new business mix. This research paper adds further weight to the argument that capital rules needs to be changed to reflect the true risks of mortgage lending.