Having summarised the main observations from the 460 page Financial System Inquiry (FSI) interim report yesterday, today we start to delve more deeply into some of most important issues raised. In a number of areas, we believe the work to date could be sharpened.
Lender’s Mortgage Insurance. The report rightly highlights that for banks with advanced capital models, there is now no benefit to underwriting risks to an LMI entity, as they already receive a 20% weighting, whether or not they are LMI insured. Therefore, LMI may become sidelined, and be used by smaller banks only, reducing volumes and increasing underlying portfolio risks.
However, whilst the report recognises that about 25% of new loans are underwritten by LMI, and the borrower pays, it does not reflect on the fact that the insurance is not portable, so consumers forfeit the premium they pay if they move later; that consumers are confused by the cover provided (protects the banks, not the household) and LMI encourages higher LVR lending. We think the role of LMI should be considered more broadly.
Industry Concentration. The report comments “Some submissions argue that the increasing concentration and integration of the major banks is harming competition. They submit the major banks can cross-subsidise products to drive out competitors in some markets. Submissions also argue that the major banks’ market power has led to oligopolistic competition and higher prices for consumers. The major banks have market power across a range of markets. However, it is not clear they are abusing this power. The ACCC has taken relatively little action against the major banks in recent years. The Inquiry would welcome views on the level and exercise of market power across the various markets in which the major banks operate.”
The major banks have become financial services conglomerates, extending their reach across retail, business and commercial banks, as well as wealth management, wealth management platforms and insurance. In addition, they have become more vertically integrated, with the accumulation of mortgage brokers, financial planners and other advisors businesses, and are extending services into online channels as well as branch networks. There are important implications, first consumers often find the brand they transact with does not clearly indicate its relationship with the parent bank. Second, as players control more of the value chain there is more opportunity for price control and reduced competition. For example, a mortgage broker working for one of the large players may recommend an in-house mortgage, so long as it is not unsuitable.
The report says “Vertical integration of mortgage broking may create conflicts of interest, which could hamper competition. Mortgage brokers can improve competition by enabling smaller players to access a broader range of consumers than their standard distribution networks would allow. However, vertical integration may have the potential to distort the way in which mortgage brokers direct borrowers to lenders. The extent of this issue is not clear. The Inquiry welcomes views on this issue.”
More broadly there is a case for greater transparency in the proportion of industry segments which players occupy. No consolidated data is provided by the regulators, across business streams. In addition, ACCC tends to look at specific transactions, not necessarily setting them in the broader cross segment context. We need an overall industry concentration metric, and regular reporting.
The Implications of Four Pillars. The report noted that “The ‘four pillars’ policy, which prevents mergers between the big four banks, has been in place, with some modifications, since 1990. Allowing a merger between the large banks would likely reduce competition, and this may offset any advantages that flow from larger scale. No submissions supported removing this policy.”
“The Inquiry views this as appropriate and does not plan to recommend changes. The banking sector is already concentrated; further significant concentration has the potential to limit competitive pressure in the market and reduce the choices available to Australian individuals and firms. Although general competition law may prevent a merger between the major banks, the Inquiry sees merit in retaining the four pillars policy.”
Now, I agree that further consolidation in the industry amongst the major banks should be resisted, however, the unintended consequence of this policy is that the banks can complete quite happily on the basis of inefficient processes and systems. This in turn flows on to higher fees and charges. So, with competition dampened by four pillars, what mechanisms should be established to ensure that Australia Inc. does not pay more than it should for banking and financial services products? At very least, we need an objective cost benchmark, against players in analogous markets overseas, to ensure that the four pillars does not artificially support higher margins and fees.
Innovation in Financial Services. The report recognises that innovation, often enabled by new technology is significant and important. “Government and regulators face challenges from the expected pace of change in technological developments. By its nature, regulation lags market developments. Consequently, Government and regulators need effective mechanisms for monitoring emerging trends, a flexible approach, and the ability to adapt and design regulation in a changing environment. Where new, technology-enabled business models, products and delivery mechanisms emerge, regulators need to consider whether and how to regulate such developments. They may also need to be flexible in how they apply existing frameworks.”
The latency between developing new business models, and regulation needs to be reduced. For example, Peer-To-Peer lending, is now on ASIC’s radar, and regulatory mechanisms are being developed.
So the report is considering “Developing a comprehensive Government strategy, in consultation with industry, to ensure the regulatory framework supports technological innovation, while managing risks.” One option mooted is to “Establish a central mechanism or body for monitoring and advising Government on technology and innovation. Consider, for example, a public–private sector collaborative body or changing the mandate of an existing body to include technology and innovation”.
Our recent experience is that the currently constituted bodies are populated predominantly with people who live within the current mode of operation in financial services. There is the need to break the mould, and inject innovation into the heart of the financial services environment. This would indeed require a different model of engagement. In addition, the pace of change, as individuals adopt new devices, and smart mobile becomes the norm, this is important, and urgent.
Next time, we will look at some of the other important area.
Author: Martin North
July RBA Minutes Flags Property Slow Down
In the minutes for the July Reserve Bank Board Meeting, released today, there are interesting comments on the property sector. They said “Dwelling investment increased noticeably in the March quarter and, over the six months to March, was running at close to the fastest pace seen in around a decade. Residential building approvals had declined somewhat in recent months, but they remained at relatively high levels and both work yet to be done and loan approvals for new dwellings pointed to further strong growth in dwelling investment in coming quarters. At the same time, there had been signs of a tempering in conditions in the established housing market. Members observed that, looking through the monthly volatility, housing price inflation had slowed over recent months, auction clearance rates had fallen from the high levels seen late last year, and loan approvals had been little changed over the past six months.”
This is consistent with our view that momentum in the property market is changing.
Coles Raises Its Banking Game
As reported in Fairfax outlets today, Coles has announced plans to offer personal loans by teaming up with GE Capital and will split the cost 50/50. The new service planned is planned for launch mid-2015. It will need regulatory approval, but Coles will not need a banking licence. 400,000 Coles MasterCard customer accounts form part of the venture which is targetting a lending book of $800 million in its first year. Coles already announced plans to launch its “mobile wallet” using a credit card chip embedded in a sticker that can be applied to the case of a smart phone. The sticker also contains a barcode linking purchases to flybuys rewards. A smartphone application will provide assess to transaction data and a flybuys statement.
Financial System Inquiry – Interim Report
The draft report was released today. In a layered document, it sets out a series of 28 observations, and possible options for ongoing consideration. The main observations are set out below:
• The banking sector is competitive, albeit concentrated. The application of capital requirements is not competitively neutral. Banks that use internal ratings-based (IRB) risk weights have lower risk weights for mortgage lending than smaller authorised deposit-taking institutions (ADIs) that use standardised risk weights, giving the IRB banks a cost advantage.
• Regulation of credit card and debit card payment schemes is required for competition to lead to more efficient outcomes. However, differences in the structure of payment systems have resulted in systems that perform similar functions being regulated differently, which may not be competitively neutral.
• Ongoing access to foreign funding has enabled Australia to sustain higher growth than otherwise would have been the case. The risks associated with Australia’s use of foreign funding can be mitigated by having a prudent supervisory and regulatory regime and sound public sector finances.
• There are structural impediments for small- and medium-sized enterprises to access finance. These impediments include information asymmetries, regulation and taxation.
• Australia has an established domestic bond market, although a range of regulatory and tax factors have limited its development.
• There is little evidence of strong fee-based competition in the superannuation sector, and operating costs and fees appear high by international standards. This indicates there is scope for greater efficiencies in the superannuation system.
• If allowed to continue, growth in direct leverage by superannuation funds, although embryonic, may create vulnerabilities for the superannuation and financial systems.
• Superannuation policy settings lack stability, which adds to costs and reduces long-term confidence and trust in the system.
• During the GFC, significant government actions in a number of countries, including Australia, entrenched perceptions that some institutions are too-big-to-fail. These perceptions can be reduced in Australia by making it more credible to resolve these institutions without Government support.
• A number of jurisdictions have implemented new macroprudential toolkits to assist with managing systemic risks. The effectiveness of these for a country like Australia is not yet well established, and there are significant practical difficulties in using such tools.
• Australia has implemented some aspects of global prudential frameworks earlier than a number of jurisdictions. It has also used national discretion in defining capital ratios. When combined with other aspects of the prudential framework and calculated on a consistent basis, Australian banks’ capital ratios (common equity tier 1) are around the middle of the range relative to other countries. However, differences such as those in definitions of capital do limit international comparability.
• To contribute to the effectiveness of the financial system, sound corporate governance requires clarity of the responsibilities and authority of boards and management. There are differences in the duties and requirements of governing bodies for different types of financial institutions and, within institutions, substantial regulator focus on boards has confused the delineation between the role of the board and that of management.
• The current disclosure regime produces complex and lengthy documents that often do not enhance consumer understanding of financial products and services, and impose significant costs on industry participants.
• Affordable, quality financial advice can bring significant benefits for consumers. Improving standards of adviser competence and removing the impact of conflicted remuneration can improve the quality of advice. Comprehensive financial advice can be costly, and there is consumer demand for lower-cost scaled advice.
• Technological developments have the potential to reduce insurance pooling. This will reduce premiums for some consumers; however, others will face increased premiums, or be excluded from access to insurance. Underinsurance may occur for a number of reasons, including: personal choice, behavioural biases, affordability, and lack of adequate information or advice on the level of insurance needed.
• The regulatory perimeters could be re-examined in a number of areas to ensure each is targeted appropriately and can capture emerging risks.
• Australia generally has strong, well-regarded regulators, but some areas of possible improvement have been identified to increase independence and accountability.
• During the GFC and beyond, Australia’s regulatory coordination mechanisms have been strong, although there may be room to enhance transparency.
• Regulators’ mandates and powers are generally well defined and clear; however, more could be done to emphasise competition matters. In addition, ASIC has a broad mandate, and the civil and administrative penalties available to it are comparatively low in relation to comparable peers internationally.
• To be able to perform their roles effectively in accordance with their legislative mandate, regulators need to be able to attract and retain suitably skilled and experienced staff.
• The retirement phase of superannuation is underdeveloped and does not meet the risk management needs of many retirees.
• There are regulatory and other policy impediments to developing income products with risk management features that could benefit retirees.
• Technological innovation is a major driver of efficiency in the financial system and can benefit consumers. Government and regulators need to balance these benefits against the risks, as they seek to manage the flexibility of regulatory frameworks and the regulatory perimeter. Government is also well-positioned to facilitate innovation through coordinated action, regulatory flexibility and forward-looking mechanisms.
• Access to growing amounts of customer information and new ways of using it have the potential to improve efficiency and competition, and present opportunities to empower consumers. However, evidence indicates these trends heighten privacy and data security risks.
• The financial system’s shift to an increasingly online environment heightens cyber security risks and the need to improve digital identity solutions. Government has the ability to facilitate industry coordination and innovation in these areas.
• Although elements of Australia’s financial system are internationally integrated, a number of potential impediments have been identified. Financial system developments in the region will require continuing Government engagement to facilitate integration with Asia.
• Government efforts to promote Australia’s policy interests on international standard setting bodies have been successful. Domestic regulatory processes could be improved to better consider international standards and foreign regulation, including processes for collaboration and consultation about international standard implementation, and mutual recognition and equivalence assessment processes.
• Coordination of Australia’s international financial integration could be improved.
A number of important areas are highlighted, but at this stage its too early to read the potential impact. We are pleased to note that macroprudential measures and lending to smaller businesses are highlighted, as well as the impact of technology. Further consultation is to follow. According to the media release, the closing date for second round submissions is 26 August 2014.
Focus On Lenders Mortgage Insurance
The ABC TV News and The Business featured a piece in Lenders Mortgage Insurance (LMI). The segment included data from the DFA household survey, data which can be found in our post Is Lenders Mortgage Insurance a Good Thing? We concluded:
“Overall, whilst LMI may allow some to access the property markets sooner, and protects the banks from risk of loss, borrowers are paying for this insurance, and if borrowing more than 80% they will have no choice as this has become industry practice.
There are systemic risks to LMI, and there is some consumer confusion about the role of LMI. The fact LMI is generally not portable is problematic.
In my view LMI is at least partly responsible for the lofty property prices in Australia, and it lifts the cost of entry into the market and if capitalised increases loan amounts on which interest is paid. It is a barrier to switching. Therefore the role of LMI should be reviewed as part of any wider property or banking inquiry”.
We note that the Financial Systems Inquiry interim report, published Tuesday, did not cover this issue.
No Housing Bubble In Australia – RBA
The RBA today published a discussion paper entitled Is Housing Overvalued?
This is an important question, given The Economist (2013) and the OECD (2013) report that Australian house prices are 24 per cent and 21 per cent ‘overvalued’, respectively. The report makes the point cost to income ratios are meaningless unless you know the cost of the alternative!
Their approach is to examine whether it is more expensive to own a house or to rent. They assess houses as ‘overvalued’ if home buyers pay too much, in the sense that they would be better off renting than buying. This involves comparing the financial cost of renting a home with the cost of owning a similar dwelling, where the latter depends on the purchase price, interest rates, repairs, council rates and so on.
They conclude that real house prices have increased at an average annual rate of slightly less than 2½ per cent since 1955. If this rate of appreciation is expected to continue then houses are fairly valued. Many observers have suggested that future house price growth is likely to be somewhat less than this historic average. In that case, at current prices, rents, interest rates and so on, the average household is probably financially better off renting than buying.
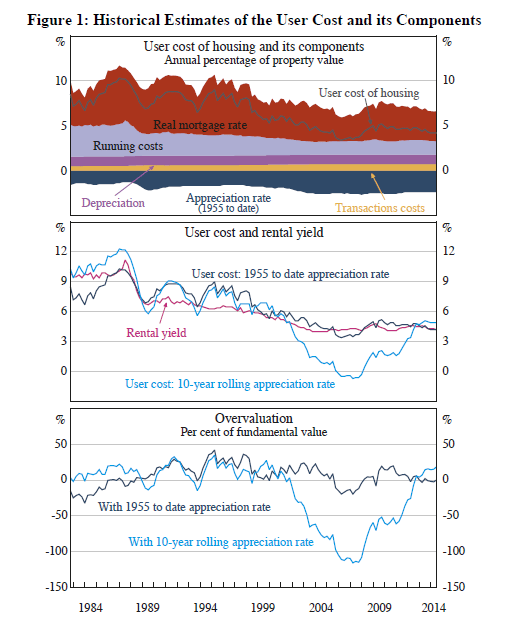 Interestingly, there is no direct discussion in the paper on housing bubbles, though there is a throw away line in the abstract “Recent data do not show signs of a bubble”.
Interestingly, there is no direct discussion in the paper on housing bubbles, though there is a throw away line in the abstract “Recent data do not show signs of a bubble”.
Now, we agree that there is not a housing bubble in Australia, rather thanks to macroeconomic policies over a long period, poor land release, and freely available credit, house prices are out of kilter, based on loan to income, loan to value, and on other metrics. In fact, the best approach is to use a range of measures to baseline the position of house prices, across countries. The weakness in the RBA analysis is that house prices and rental costs are connected, so they will tend to move together. Therefore, relatively speaking the fact that rents are tracking prices are not a good indicator of whether house prices are over valued. It is a closed system, and self fulfilling.
Lending Finance Slips In May – ABS
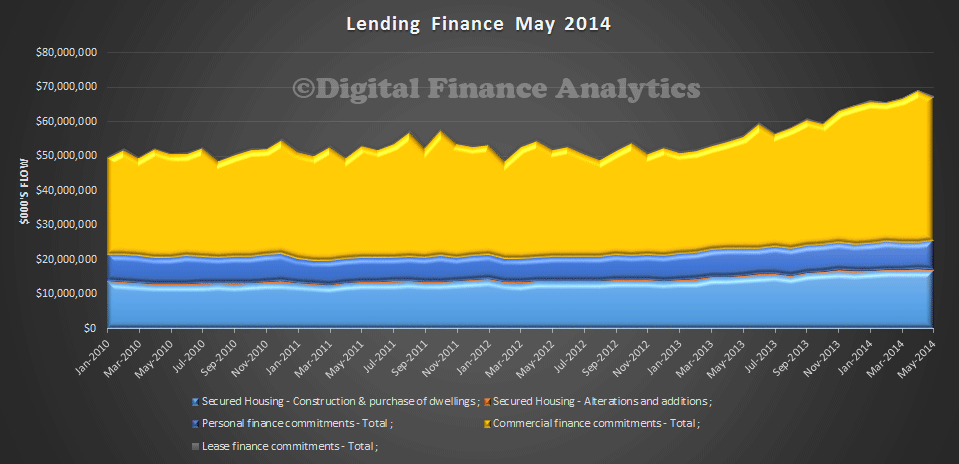
The ABS today published their data series on Lending Finance in Australia to May 2014. The seasonably adjusted value for owner occupation fell 0.7% compared with April, whilst overall commercial lending fell 6.0% month on month. There were increases in personal finance and leasing, but overall lending fell. We start with a chart showing the trend growth in seasonally adjusted terms from January 2010. Remember that commercial lending includes investment housing.
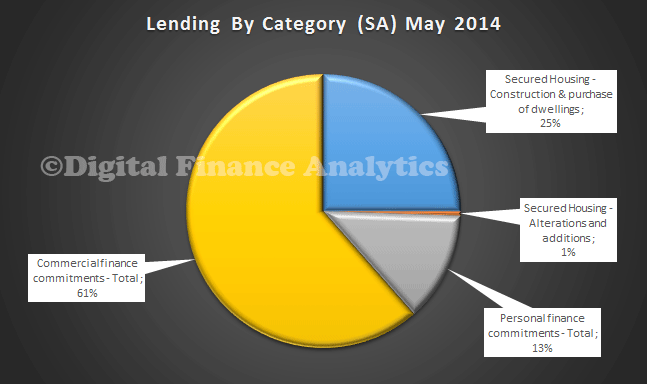
 25% of loans were for housing owner occupation, 13% were for personal finance (both revolving and fixed term loans), and 61% were commercial loans.
25% of loans were for housing owner occupation, 13% were for personal finance (both revolving and fixed term loans), and 61% were commercial loans.
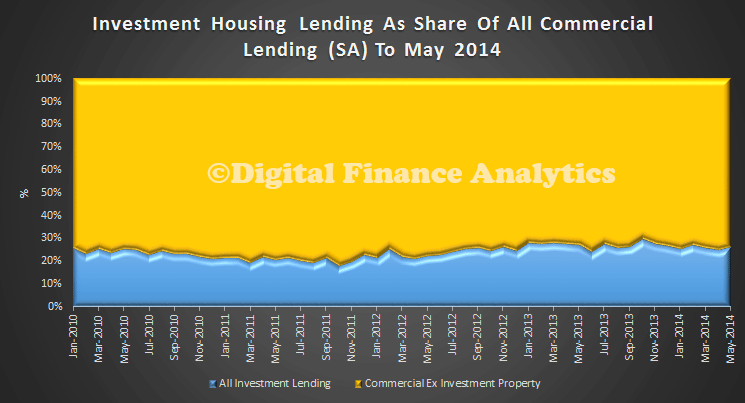
 So now we separate out the share of investment loans from commercial lending, and we see the growth has stalled.
So now we separate out the share of investment loans from commercial lending, and we see the growth has stalled.
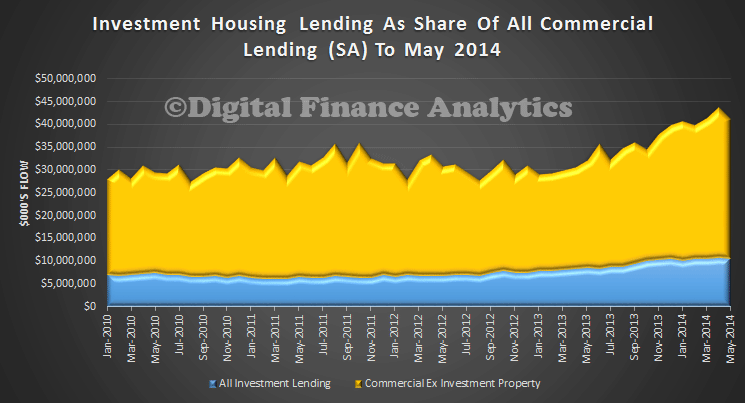 This is more striking when we look at the percentage splits. About 25% of all commercial lending is for investment housing purposes.
This is more striking when we look at the percentage splits. About 25% of all commercial lending is for investment housing purposes.
 Turning to housing lending, we see that this has also stalled in May. The growth in the “others” category, includes self-managed superannuation investors, though it is still a relatively small proportion of all lending.
Turning to housing lending, we see that this has also stalled in May. The growth in the “others” category, includes self-managed superannuation investors, though it is still a relatively small proportion of all lending.
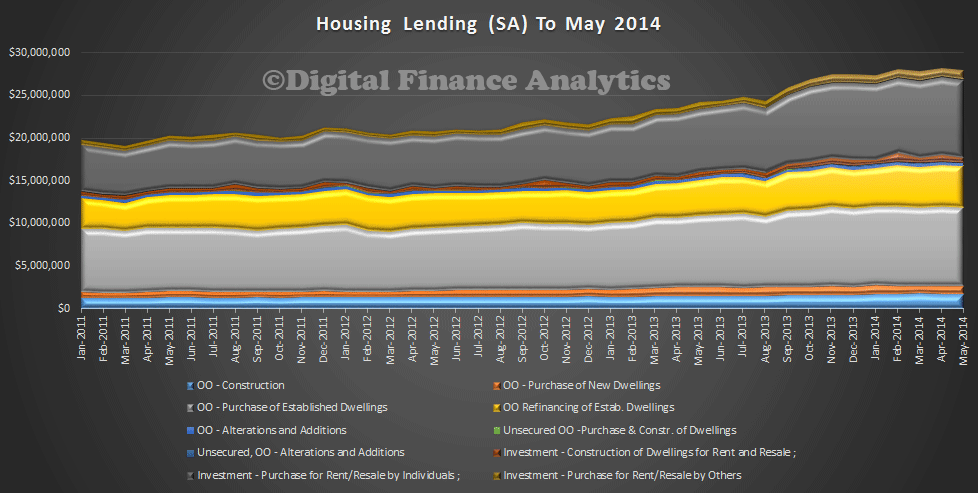
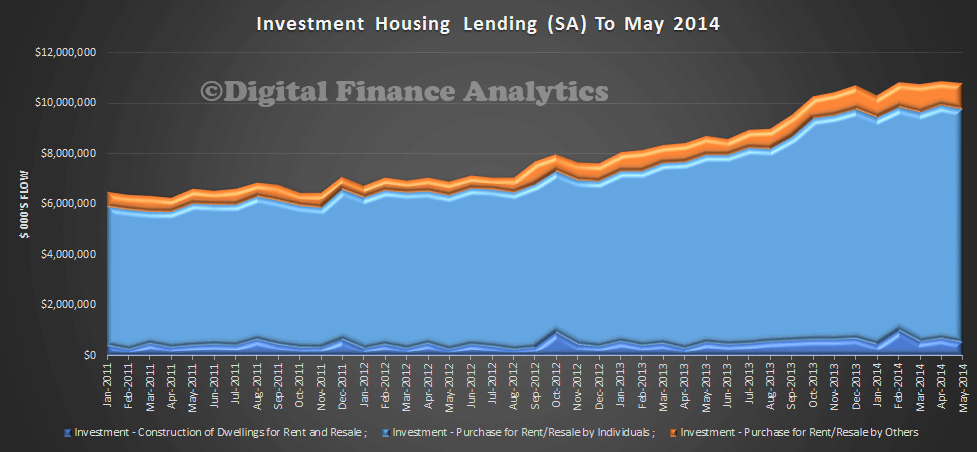
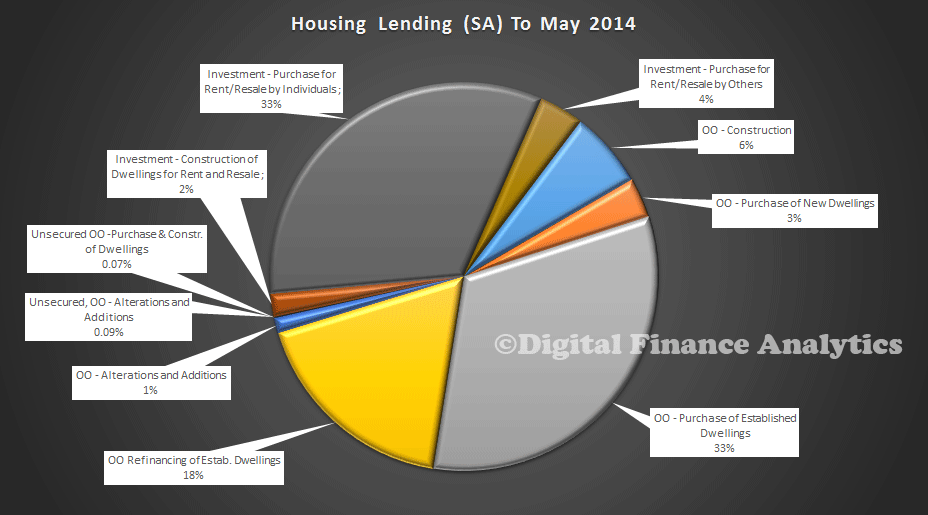
Looking at the splits, investment housing accounted for 39% of loans, 4% of which are for other entities, including SMSF’s. Refinancing accounted for 18% of lending, and 33% was for the purchase of established dwellings.
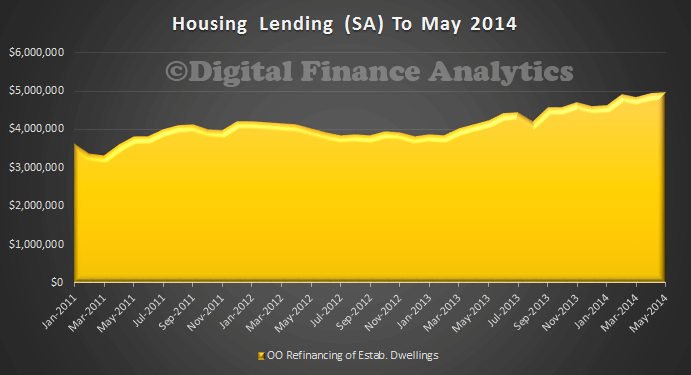
 Finally, it is worth noting the trend growth in refinancing, households are still looking to lock in the current low rates, and to reduce their monthly repayments where possible.
Finally, it is worth noting the trend growth in refinancing, households are still looking to lock in the current low rates, and to reduce their monthly repayments where possible.
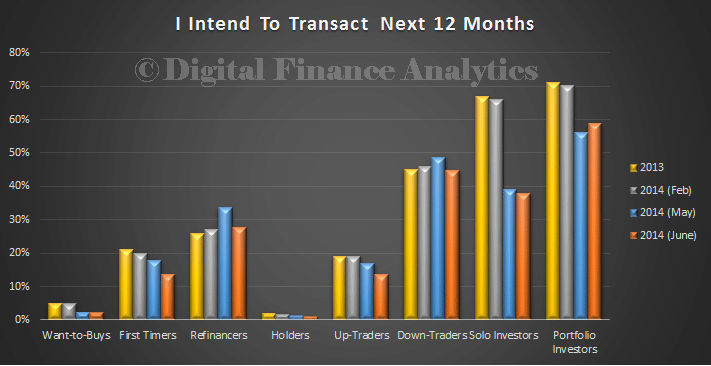
 We hold to our view that momentum is shifting, as we reported recently.
We hold to our view that momentum is shifting, as we reported recently.
Housing Sector Likely To Stall
Reflecting on the ABS data released today, and already covered here, and putting that into context of our household surveys, we think momentum is changing and the housing sector could stall in coming months. Demand for new finance fell 0.8% in May. Whilst refinancing remains quite buoyant, thanks to low rates, investors appear to be slowing, as already foreshadowed in our surveys.
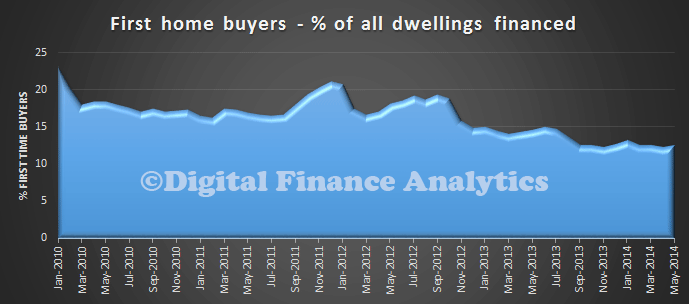
 First time buyers are still at low levels,
First time buyers are still at low levels,
 and they are still priced out of the market.
and they are still priced out of the market.
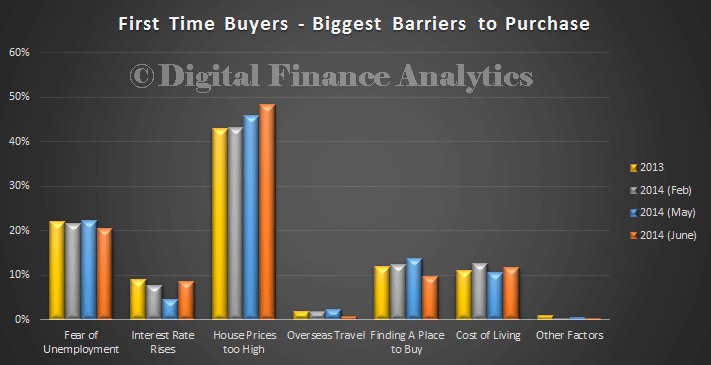 The current low interest rates and rising prices have together encouraged households to transact sooner than they might otherwise would, pulling transactions forwards, but this won’t last.
The current low interest rates and rising prices have together encouraged households to transact sooner than they might otherwise would, pulling transactions forwards, but this won’t last.
So, if future demand is not coming from first time buyers and investors, where will demand come from? Well, we know there are many households who would like to enter the market, but cannot because prices are too high, these property inactives won’t change their tune anytime soon. Will foreign investors keep the property ship afloat? The problem here is there is little good data on overseas investors, and in any case, is this sensible policy? The contribution which SMSF investors might make will hardly move the dial.
We also know that unemployment is up, and likely to continue to trend this way, which directly impacts households and mortgage stress. In addition consumer confidence is not that flash.
We think interest rates may be taken down by the RBA later in the year, but lower rates wont bring more households out of the woodwork because the banks won’t relax their serviceability buffers any further.
Putting all this together, it is likely we are at the top, and both house prices and lending will probably reverse later in the year. This creates a massive problem for the RBA who were banking on housing being the economic bridge between the end of the mining boom and the return to growth from other commercial sectors.
We should have implemented policies to stimulate the commercial sector earlier, rather than inflating house prices and the banks balance sheets with unproductive lending. Lending to business returns growth to the economy, flowing funds to inflated housing does not.
Housing Finance Up To $1.3 Trillion In May – ABS
The ABS released their latest housing statistics today. Total ADI lending now tops $1.3 trillion. Investment lending has reached a new high at 33.8% of all loans. The trend estimate for the total value of dwelling finance commitments excluding alterations and additions rose 0.2%. Investment housing commitments rose 0.3% and owner occupied housing commitments rose 0.2%. However, In seasonally adjusted terms, the total value of dwelling finance commitments excluding alterations and additions fell 0.8%.
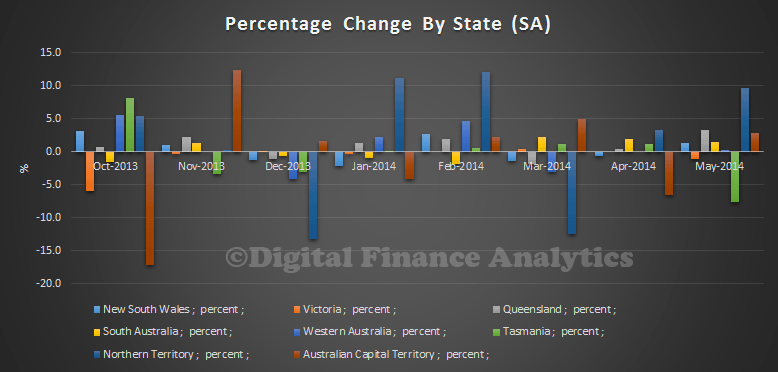
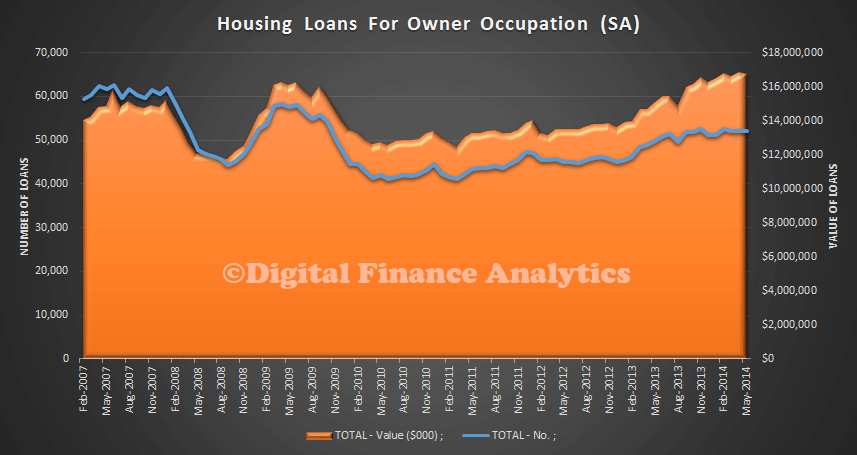 There were some state variations in owner occupation loans, but in percentage terms there is more noise in the data from the smaller states. NSW, QLD and SA were up from the previous month, whilst VIC and TAS fell month on month.
There were some state variations in owner occupation loans, but in percentage terms there is more noise in the data from the smaller states. NSW, QLD and SA were up from the previous month, whilst VIC and TAS fell month on month.
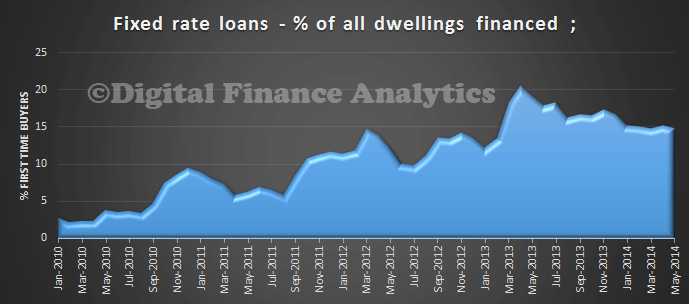
The proportion of fixed rate loans remain elevated, but off its 20% high in 2013.
 First time buyers were slightly higher in May, but still lower than average and close to all time lows.
First time buyers were slightly higher in May, but still lower than average and close to all time lows.
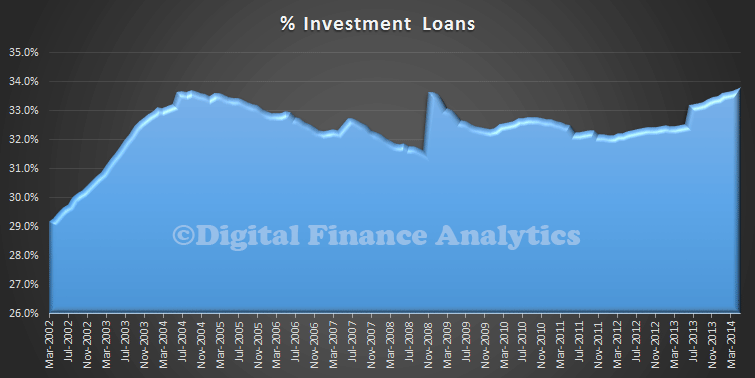
 Investment lending is still a significant factor, with close of 33.8% of lending for investment purposes. This is an all time record for investment lending.
Investment lending is still a significant factor, with close of 33.8% of lending for investment purposes. This is an all time record for investment lending.
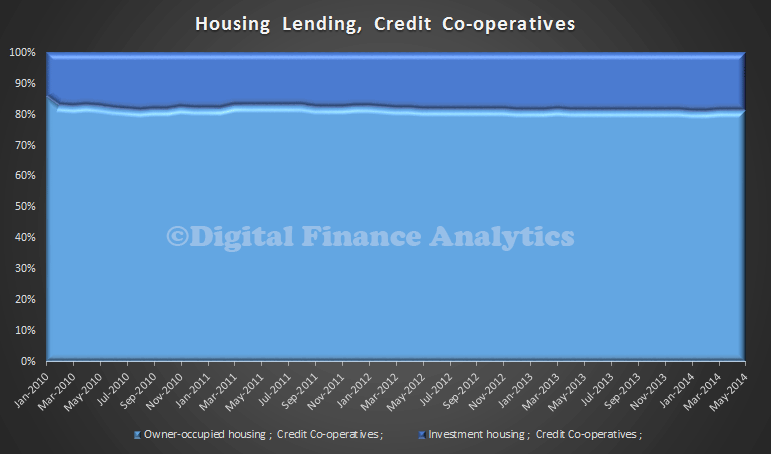
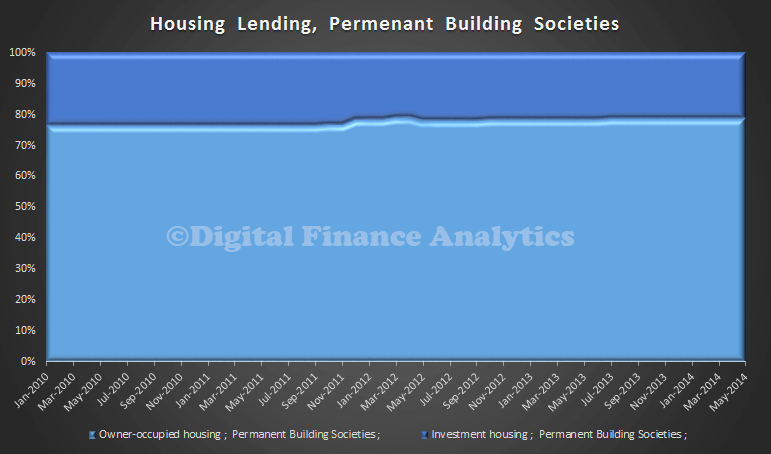
 The banks have a greater proportion of investment lending …
The banks have a greater proportion of investment lending …
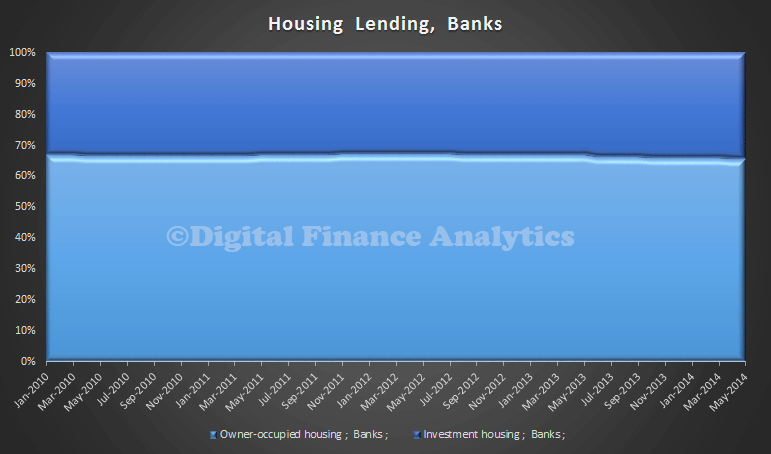 compared with credit unions or building societies.
compared with credit unions or building societies.
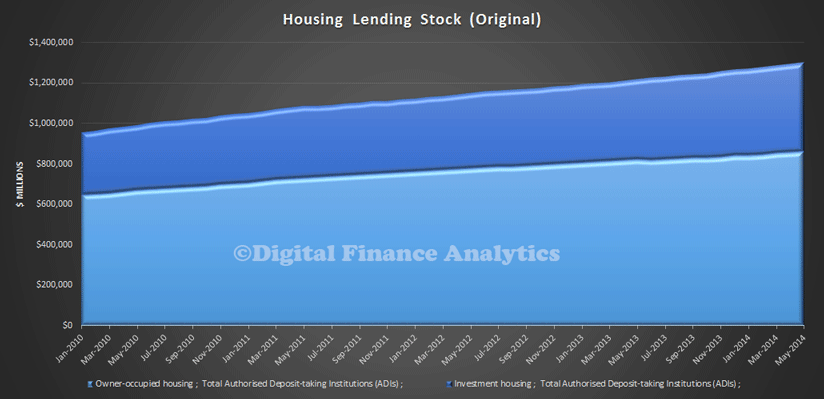
 The stock of total ADI housing lending is now above $1.3 trillion in original terms.
The stock of total ADI housing lending is now above $1.3 trillion in original terms.
 Finally, note there is an investigation into the first time buyer data. The ABS advise that in collecting this information, lenders are asked to report all loans to first home buyers. Concerns have been raised that under-reporting could occur if some lenders were only able to accurately report on those buyers receiving a first home buyer grant. Most data on first home buyers are collected by the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA) under the Financial Sector (Collection of Data) Act 2001. APRA is contacting lenders on behalf of the ABS to investigate whether lenders experience any difficulties reporting on loans to first home buyers. The outcomes from the investigation will be published on the ABS website.
Finally, note there is an investigation into the first time buyer data. The ABS advise that in collecting this information, lenders are asked to report all loans to first home buyers. Concerns have been raised that under-reporting could occur if some lenders were only able to accurately report on those buyers receiving a first home buyer grant. Most data on first home buyers are collected by the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA) under the Financial Sector (Collection of Data) Act 2001. APRA is contacting lenders on behalf of the ABS to investigate whether lenders experience any difficulties reporting on loans to first home buyers. The outcomes from the investigation will be published on the ABS website.
UK Rates Kept at 0.5%; QE Continues
Today the Bank of England announced that it would maintain Bank Rate at 0.5% and the size of the Asset Purchase Programme at £375 billion.
The previous change in Bank Rate was a reduction of 0.5 percentage points to 0.5% on 5 March 2009. A programme of asset purchases financed by the issuance of central bank reserves was initiated on 5 March 2009. The previous change in the size of that programme was an increase of £50 billion to a total of £375 billion on 5 July 2012.
In March 2009, the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) announced that it would reduce Bank Rate to 0.5%. The Committee also judged that Bank Rate could not practically be reduced below that level, and in order to give a further monetary stimulus to the economy, it decided to undertake a series of asset purchases.
Quantitative Easing Explained
Between March and November 2009, the MPC authorised the purchase of £200 billion worth of assets, mostly UK Government debt or “gilts”. The MPC voted to begin further purchases of £75 billion in October 2011 and, subsequently, at its meeting in February 2012 the Committee decided to buy an additional £50 bn. In July the MPC announced the purchase of a further £50bn to bring total assets purchases to £375 bn. The purpose of the purchases was and is to inject money directly into the economy in order to boost nominal demand. Despite this different means of implementing monetary policy, the objective remained unchanged – to meet the inflation target of 2 per cent on the CPI measure of consumer prices. Without that extra spending in the economy, the MPC thought that inflation would be more likely in the medium term to undershoot the target.
This policy of asset purchases is often known as ‘Quantitative Easing’. It does not involve printing more banknotes. Furthermore, the asset purchase programme is not about giving money to banks. Rather, the policy is designed to circumvent the banking system. The Bank of England electronically creates new money and uses it to purchase gilts from private investors such as pension funds and insurance companies. These investors typically do not want to hold on to this money, because it yields a low return. So they tend to use it to purchase other assets, such as corporate bonds and shares. That lowers longer-term borrowing costs and encourages the issuance of new equities and bonds to stimulate spending and keep inflation on track to meet the government’s target.
The Bank will continue to offer to purchase high-quality private sector assets on behalf of the Treasury, financed by the issue of Treasury bills.