The latest edition of our finance and property news digest with a distinctively Australian flavour.
Tag: Federal Reserve
What The F (ed)? – The DFA Daily 19th April 2020 [Podcast]
The latest edition of our finance and property news digest with a distinctively Australian flavour.

What The F (ed)? – The DFA Daily 19th April 2020
The latest edition of our finance and property news digest with a distinctively Australian flavour.
Fed Announces Extensive New Measures To Support The Economy
More Ammo from the Federal Reserve.
The Federal Reserve is committed to using its full range of tools to support households, businesses, and the U.S. economy overall in this challenging time. The coronavirus pandemic is causing tremendous hardship across the United States and around the world. Our nation’s first priority is to care for those afflicted and to limit the further spread of the virus. While great uncertainty remains, it has become clear that our economy will face severe disruptions. Aggressive efforts must be taken across the public and private sectors to limit the losses to jobs and incomes and to promote a swift recovery once the disruptions abate.

The Federal Reserve’s role is guided by its mandate from Congress to promote maximum employment and stable prices, along with its responsibilities to promote the stability of the financial system. In support of these goals, the Federal Reserve is using its full range of authorities to provide powerful support for the flow of credit to American families and businesses. These actions include:
- Support for critical market functioning. The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) will purchase Treasury securities and agency mortgage-backed securities in the amounts needed to support smooth market functioning and effective transmission of monetary policy to broader financial conditions and the economy. The FOMC had previously announced it would purchase at least $500 billion of Treasury securities and at least $200 billion of mortgage-backed securities. In addition, the FOMC will include purchases of agency commercial mortgage-backed securities in its agency mortgage-backed security purchases.
- Supporting the flow of credit to employers, consumers, and businesses by establishing new programs that, taken together, will provide up to $300 billion in new financing. The Department of the Treasury, using the Exchange Stabilization Fund (ESF), will provide $30 billion in equity to these facilities.
- Establishment of two facilities to support credit to large employers – the Primary Market Corporate Credit Facility (PMCCF) for new bond and loan issuance and the Secondary Market Corporate Credit Facility (SMCCF) to provide liquidity for outstanding corporate bonds.
- Establishment of a third facility, the Term Asset-Backed Securities Loan Facility (TALF), to support the flow of credit to consumers and businesses. The TALF will enable the issuance of asset-backed securities (ABS) backed by student loans, auto loans, credit card loans, loans guaranteed by the Small Business Administration (SBA), and certain other assets.
- Facilitating the flow of credit to municipalities by expanding the Money Market Mutual Fund Liquidity Facility (MMLF) to include a wider range of securities, including municipal variable rate demand notes (VRDNs) and bank certificates of deposit.
- Facilitating the flow of credit to municipalities by expanding the Commercial Paper Funding Facility (CPFF) to include high-quality, tax-exempt commercial paper as eligible securities. In addition, the pricing of the facility has been reduced.
In addition to the steps above, the Federal Reserve expects to announce soon the establishment of a Main Street Business Lending Program to support lending to eligible small-and-medium sized businesses, complementing efforts by the SBA.
The PMCCF will allow companies access to credit so that they are better able to maintain business operations and capacity during the period of dislocations related to the pandemic. This facility is open to investment grade companies and will provide bridge financing of four years. Borrowers may elect to defer interest and principal payments during the first six months of the loan, extendable at the Federal Reserve’s discretion, in order to have additional cash on hand that can be used to pay employees and suppliers. The Federal Reserve will finance a special purpose vehicle (SPV) to make loans from the PMCCF to companies. The Treasury, using the ESF, will make an equity investment in the SPV.
The SMCCF will purchase in the secondary market corporate bonds issued by investment grade U.S. companies and U.S.-listed exchange-traded funds whose investment objective is to provide broad exposure to the market for U.S. investment grade corporate bonds. Treasury, using the ESF, will make an equity investment in the SPV established by the Federal Reserve for this facility.
Under the TALF, the Federal Reserve will lend on a non-recourse basis to holders of certain AAA-rated ABS backed by newly and recently originated consumer and small business loans. The Federal Reserve will lend an amount equal to the market value of the ABS less a haircut and will be secured at all times by the ABS. Treasury, using the ESF, will also make an equity investment in the SPV established by the Federal Reserve for this facility. The TALF, PMCCF and SMCCF are established by the Federal Reserve under the authority of Section 13(3) of the Federal Reserve Act, with approval of the Treasury Secretary.
These actions augment the measures taken by the Federal Reserve over the past week to support the flow of credit to households and businesses. These include:
- The establishment of the CPFF, the MMLF, and the Primary Dealer Credit Facility;
- The expansion of central bank liquidity swap lines;
- Steps to enhance the availability and ease terms for borrowing at the discount window;
- The elimination of reserve requirements;
- Guidance encouraging banks to be flexible with customers experiencing financial challenges related to the coronavirus and to utilize their liquidity and capital buffers in doing so;
- Statements encouraging the use of daylight credit at the Federal Reserve.
Taken together, these actions will provide support to a wide range of markets and institutions, thereby supporting the flow of credit in the economy.
The Federal Reserve will continue to use its full range of tools to support the flow of credit to households and businesses and thereby promote its maximum employment and price stability goals.
Mortgage Bond Sales Flood Market
The financial crisis is now in full swing, and credit markets are at the epicentre of current events, as owners of mortgage bonds and other asset-backed securities try to sell billions of dollars in assets, amid reports that there are significant investor withdrawals from these funds.

Bloomberg reported that Funds who buy up bonds of all kinds — from debt of America’s largest corporations to securities backed by mortgages — have struggled with record investor withdrawals amid choppy trading conditions in fixed-income markets. The rush to unload mortgage-backed securities signals that a credit meltdown that began with corporate bonds is spreading to other corners of the market.
Further Federal Reserve support, and other Central bank support is being sought. Raises the question, who should be supporting who, and should financial speculators really be bailed out?
Amid the selling, the Structured Finance Association, an industry group for the asset-backed securities market, asked government leaders on Sunday to step in and help boost liquidity in the market.
In a letter to U.S. Treasury Secretary Steven Mnuchin and Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell, the industry group said that “the future path of the pandemic has significantly disrupted the normal functioning of credit markets.”
The group asked them to “immediately enact a new version of the Term Asset-Backed Securities Loan Facility,” a financial crisis-era program that helped support the issuance of securities backed by consumer and small-business loans. Such a measure, the group said, would help enhance the liquidity and functioning of crucial credit markets.
“The overwhelming supply of securities for sale to meet redemptions has put significant downward pressure on almost all segments of the bond market,” Szilagyi said in the statement.
The sales included at least $1.25 billion of securities being listed by the AlphaCentric Income Opportunities Fund. It sought buyers for a swath of bonds backed primarily by private-label mortgages as it sought to raise cash, said the people, who asked not to be identified discussing the private offerings.
“The coronavirus has resulted in severe market dislocations and liquidity issues for most segments of the bond market,” AlphaCentric’s Jerry Szilagyi said in an emailed statement on Sunday. “The Fund is not immune to these dislocations” and “like many other funds, is moving expeditiously to address the unprecedented market conditions.”
The best way to obtain favorable prices is to offer a wider range of securities for bid he said, declining to discuss the amount of securities the fund put up for sale.
The AlphaCentric fund plunged 17% on Friday, bringing its total decline for the week to 31%.
“We can most likely expect a continuation of price volatility across the bond market spectrum until the panic selling and market uncertainty subsides or government agencies intervene to support the broader fixed-income market,” Szilagyi said
Fed Supports Liquidity Of US State and Municipal Money Markets
The Federal Reserve Board on Friday expanded its program of support for the flow of credit to the economy by taking steps to enhance the liquidity and functioning of crucial state and municipal money markets. Through the Money Market Mutual Fund Liquidity Facility, or MMLF, the Federal Reserve Bank of Boston will now be able to make loans available to eligible financial institutions secured by certain high-quality assets purchased from single state and other tax-exempt municipal money market mutual funds.

All U.S. depository institutions, U.S. bank holding companies (parent companies incorporated in the United States or their U.S. broker-dealer subsidiaries), or U.S. branches and agencies of foreign banks are eligible to borrow under the Facility.
Collateral that is eligible for pledge under the Facility must be one of the following types:
- U.S. Treasuries & Fully Guaranteed Agencies;
- Securities issued by U.S. Government Sponsored Entities;
- Asset-backed commercial paper that is issued by a U.S. issuer, is rated at the time purchased from the Fund or pledged to the Reserve Bank not lower than A1, F1, or P1 by at least two major rating agencies or, if rated by only one major rating agency, is rated within the top rating category by that agency;
- Unsecured commercial paper that is issued by a U.S. issuer, is rated at the time purchased from the Fund or pledged to the Reserve Bank not lower than A1, F1, or P1 by at least two major rating agencies or, if rated by only one major rating agency, is rated within the top rating category by that agency; or
- U.S. municipal short-term debt that: i.Has a maturity that does not exceed 12 months; and ii.At the time purchased from the Fund or pledged to the Reserve Bank: 1.If rated in the short-term rating category, is rated in the top short-term rating category (e.g.,rated SP1, MIG1, or F1, as applicable) by at least two major rating agencies or if rated by only one major rating agency, is rated within the top rating category by that agency; or 2.If not rated in the short-term rating category, is rated in the top long-term rating category (e.g., AA or above) by at least two major rating agencies or if rated by only one major rating agency, is rated within the top rating category by that agency.
- In addition, the facility may accept receivables from certain repurchase agreements. The facility at this time will not take variable rate demand notes or tender option bonds, but the feasibility of adding these and other asset classes to the facility will be considered in the future.Rate: Advances made under the Facility that are secured by U.S. Treasuries & Fully Guaranteed Agencies or Securities issued by U.S. Government Sponsored Entities will be made at a rate equal to the primary credit rate in effect at the Reserve Bank that is offered to depository institutions at the time the advance is made.
Advances made under the Facility that are secured by U.S. municipal short-term debt will be made at a rate equal to the primary credit rate in effect at the Reserve Bank that is offered to depository institutions at the time the advance is made plus 25 bps.
Fed Extends USD Swap Lines To Nine Additional Countries
The US Federal Reserve has opened the taps for central banks in nine additional countries to access dollars in response to the current unstable financial system.

US Dollars have been in huge demand – and tight supply – in markets outside US borders as banks, companies and governments scramble to secure them to service the dollar-denominated debts many have accumulated. That has sent dollar-funding costs spiraling and has led to a historic run-up in the dollar’s value against other currencies.
The new facilities total $60 billion for central banks in Australia, Brazil, South Korea, Mexico, Singapore, and Sweden, and $30 billion each for Denmark, Norway, and New Zealand. The swap lines will be in place for at least six months.
This is a combined total of $US450 billion, money to ensure the world’s dollar-dependent financial system continues to function.
Those countries were given swap lines during the 2007 to 2009 crisis, and the Fed has permanent swap arrangements with the Bank of Canada, the Bank of England, the Bank of Japan, the European Central Bank, and the Swiss National Bank.
The Fed said the new swap lines “like those already established between the Federal Reserve and other central banks, are designed to help lessen strains in global US dollar funding markets, thereby mitigating the effects of these strains on the supply of credit to households and businesses, both domestically and abroad”.
US dollar credit to non-bank borrowers outside the United States grew by 4 per cent year-on-year at end-June 2019 to reach $US11.9 trillion, according to the BIS.
This helps to underscore the status of the US dollar as a reserve currency.
Making dollars available to foreign nations — even if it didn’t cost the Fed — became a point of contention for some in the U.S. Congress, says Bloomberg.
The central bank had to repeatedly defend the action and explain to lawmakers that U.S. taxpayers were not lending foreign nations money and that because these were swaps — not loans — there was no risk of default.
Fed Cuts To Zero, As Part Of Global Coordinated Action
The Fed has just cut rates to 0- 1/4 percent.
In addition the Federal Reserve on Sunday announced it would purchases $700 billion in bonds and securities to stabilize financial markets and support the economy.
The emergency rate cut and push to flood the Treasury bond market with liquidity comes as the coronavirus pandemic forces businesses across the U.S. and world to shutter, likely plunging the global economy into a recession.
This is part of a coordinated global response, the Fed says.
The Bank of Canada, the Bank of England, the Bank of Japan, the European Central Bank, the Federal Reserve, and the Swiss National Bank are today announcing a coordinated action to enhance the provision of liquidity via the standing U.S. dollar liquidity swap line arrangements.
These central banks have agreed to lower the pricing on the standing U.S. dollar liquidity swap arrangements by 25 basis points, so that the new rate will be the U.S. dollar overnight index swap (OIS) rate plus 25 basis points. To increase the swap lines’ effectiveness in providing term liquidity, the foreign central banks with regular U.S. dollar liquidity operations have also agreed to begin offering U.S. dollars weekly in each jurisdiction with an 84-day maturity, in addition to the 1-week maturity operations currently offered. These changes will take effect with the next scheduled operations during the week of March 16.1 The new pricing and maturity offerings will remain in place as long as appropriate to support the smooth functioning of U.S. dollar funding markets.
The swap lines are available standing facilities and serve as an important liquidity backstop to ease strains in global funding markets, thereby helping to mitigate the effects of such strains on the supply of credit to households and businesses, both domestically and abroad.

The coronavirus outbreak has harmed communities and disrupted economic activity in many countries, including the United States. Global financial conditions have also been significantly affected. Available economic data show that the U.S. economy came into this challenging period on a strong footing. Information received since the Federal Open Market Committee met in January indicates that the labor market remained strong through February and economic activity rose at a moderate rate. Job gains have been solid, on average, in recent months, and the unemployment rate has remained low. Although household spending rose at a moderate pace, business fixed investment and exports remained weak. More recently, the energy sector has come under stress. On a 12‑month basis, overall inflation and inflation for items other than food and energy are running below 2 percent. Market-based measures of inflation compensation have declined; survey-based measures of longer-term inflation expectations are little changed.
Consistent with its statutory mandate, the Committee seeks to foster maximum employment and price stability. The effects of the coronavirus will weigh on economic activity in the near term and pose risks to the economic outlook. In light of these developments, the Committee decided to lower the target range for the federal funds rate to 0 to 1/4 percent. The Committee expects to maintain this target range until it is confident that the economy has weathered recent events and is on track to achieve its maximum employment and price stability goals. This action will help support economic activity, strong labor market conditions, and inflation returning to the Committee’s symmetric 2 percent objective.
The Committee will continue to monitor the implications of incoming information for the economic outlook, including information related to public health, as well as global developments and muted inflation pressures, and will use its tools and act as appropriate to support the economy. In determining the timing and size of future adjustments to the stance of monetary policy, the Committee will assess realized and expected economic conditions relative to its maximum employment objective and its symmetric 2 percent inflation objective. This assessment will take into account a wide range of information, including measures of labor market conditions, indicators of inflation pressures and inflation expectations, and readings on financial and international developments.
The Federal Reserve is prepared to use its full range of tools to support the flow of credit to households and businesses and thereby promote its maximum employment and price stability goals. To support the smooth functioning of markets for Treasury securities and agency mortgage-backed securities that are central to the flow of credit to households and businesses, over coming months the Committee will increase its holdings of Treasury securities by at least $500 billion and its holdings of agency mortgage-backed securities by at least $200 billion. The Committee will also reinvest all principal payments from the Federal Reserve’s holdings of agency debt and agency mortgage-backed securities in agency mortgage-backed securities. In addition, the Open Market Desk has recently expanded its overnight and term repurchase agreement operations. The Committee will continue to closely monitor market conditions and is prepared to adjust its plans as appropriate.
Voting for the monetary policy action were Jerome H. Powell, Chair; John C. Williams, Vice Chair; Michelle W. Bowman; Lael Brainard; Richard H. Clarida; Patrick Harker; Robert S. Kaplan; Neel Kashkari; and Randal K. Quarles. Voting against this action was Loretta J. Mester, who was fully supportive of all of the actions taken to promote the smooth functioning of markets and the flow of credit to households and businesses but preferred to reduce the target range for the federal funds rate to 1/2 to 3/4 percent at this meeting.
In a related set of actions to support the credit needs of households and businesses, the Federal Reserve announced measures related to the discount window, intraday credit, bank capital and liquidity buffers, reserve requirements, and—in coordination with other central banks—the U.S. dollar liquidity swap line arrangements. More information can be found on the Federal Reserve Board’s website.
Markets Crash And Fed’s $1.5 Trillion Repo Purchases Escalate Dramatically
The Dow plunged to its biggest-one day percentage loss since October 1987 as fears the spread of the novel coronavirus will pick up pace and usher in a global recession overshadowed the Federal Reserve’s bold new stimulus measures to calm funding markets.
The Dow Jones Industrial Average fell nearly 10%, or 2,352 points, it worst one-day percentage drop since Black Monday when it lost 22.6%. It was the fourth-largest percentage drop for the blue chip index in history, rivaling those seen in 1929.
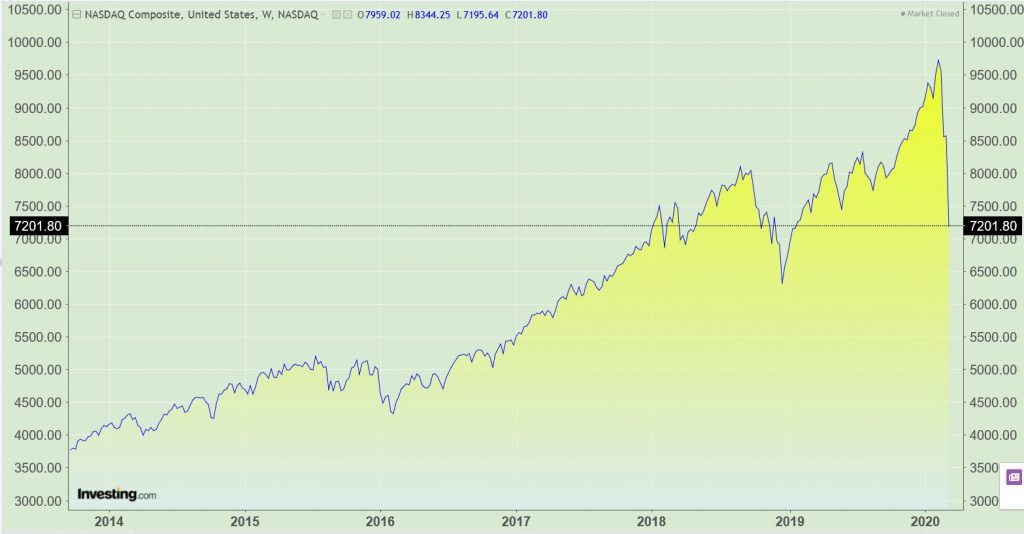
The S&P 500 plunged 9.5% and the Nasdaq Composite slumped 9.4%.
The rout on Wall Street for the second-straight day comes as investors upped their bearish bets on stocks despite the Federal Reserve unveiling $1.5 trillion in fresh liquidity to combat “temporary disruptions” in funding markets.
The short-term pause in selling following the Fed announcement proved short-lived as investor sentiment on stocks continued to be swayed by the latest updates on the spread of Covid-19, which has killed nearly 5,000 people, with infections topping 133,000 worldwide.
In the U.S., where infections are feared to increase in the coming weeks, state-wide bans on large gatherings to limit the virus impact continued, with New York announcing announce a ban on gatherings of 500 or more people.
The Fed’s announcement was unprecedented:
The Open Market Trading Desk (the Desk) at the Federal Reserve Bank of New York has released a new monthly schedule of Treasury securities operations and has updated the current monthly schedule of repurchase agreement (repo) operations. Pursuant to instruction from the Chair in consultation with the FOMC, adjustments have been made to these schedules to address temporary disruptions in Treasury financing markets. The Treasury securities operation schedule includes a change in the maturity composition of purchases to support functioning in the market for U.S. Treasury securities. Term repo operations in large size have been added to enhance functioning of secured U.S. dollar funding markets.
- As a part of its $60 billion reserve management purchases for the monthly period beginning March 13, 2020 and continuing through April 13, 2020, the Desk will conduct purchases across a range of maturities to roughly match the maturity composition of Treasury securities outstanding. Specifically, the Desk plans to distribute reserve management purchases across eleven sectors, including nominal coupons, bills, Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities, and Floating Rate Notes. The distribution of purchases across sectors will be the same distribution as the Desk uses to reinvest principal payments from the Federal Reserve’s holdings of agency debt and agency MBS in Treasury securities. The first such purchases will begin tomorrow, March 13, 2020.
- Today, March 12, 2020, the Desk will offer $500 billion in a three-month repo operation at 1:30 pm ET that will settle on March 13, 2020. Tomorrow, the Desk will further offer $500 billion in a three-month repo operation and $500 billion in a one-month repo operation for same day settlement. Three-month and one-month repo operations for $500 billion will be offered on a weekly basis for the remainder of the monthly schedule. The Desk will continue to offer at least $175 billion in daily overnight repo operations and at least $45 billion in two-week term repo operations twice per week over this period.
These changes are being made to address highly unusual disruptions in Treasury financing markets associated with the coronavirus outbreak. Reserve management purchases into the second quarter will continue to be conducted with this maturity allocation. The terms of operations will be adjusted as needed to foster smooth Treasury market functioning and efficient and effective policy implementation.
Detailed information on the schedule of Treasury purchases is provided on the Treasury Securities Operational Details page. Detailed information on the schedule and parameters of term and overnight repo operations are provided on the Repurchase Agreement Operational Details page.
Fed Ups The Repo Ante
The Open Market Trading Desk (the Desk) at the Federal Reserve Bank of New York has released the repurchase agreement (repo) operational schedule for the upcoming period.
Beginning Thursday, March 12, 2020 and continuing through Monday, April 13, 2020, the Desk will offer at least $175 billion in daily overnight repo operations and at least $45 billion in two-week term repo operations twice per week over this period. In addition, the Desk will also offer three one-month term repo operations, with the first operation occurring on Thursday, March 12, 2020. The amount offered for each of these three operations will be at least $50 billion.
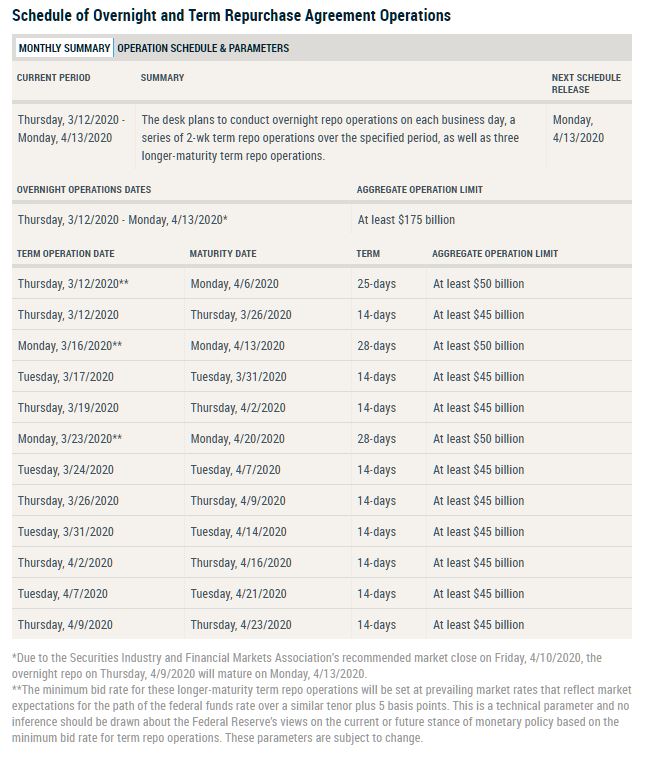
Consistent with the FOMC directive to the Desk, these operations are intended to ensure that the supply of reserves remains ample and to mitigate the risk of money market pressures that could adversely affect policy implementation. They should help support smooth functioning of funding markets as market participants implement business resiliency plans in response to the coronavirus. The Desk will continue to adjust repo operations as needed to foster efficient and effective policy implementation consistent with the FOMC directive.
Detailed information on the schedule and parameters of term and overnight repo operations are provided on the Repurchase Agreement Operational Details page.
We are headed to $800 billion extra liquidity, which clearly is more than a temporary problem in the banking system. John Adams and I discussed this in a recent post.
