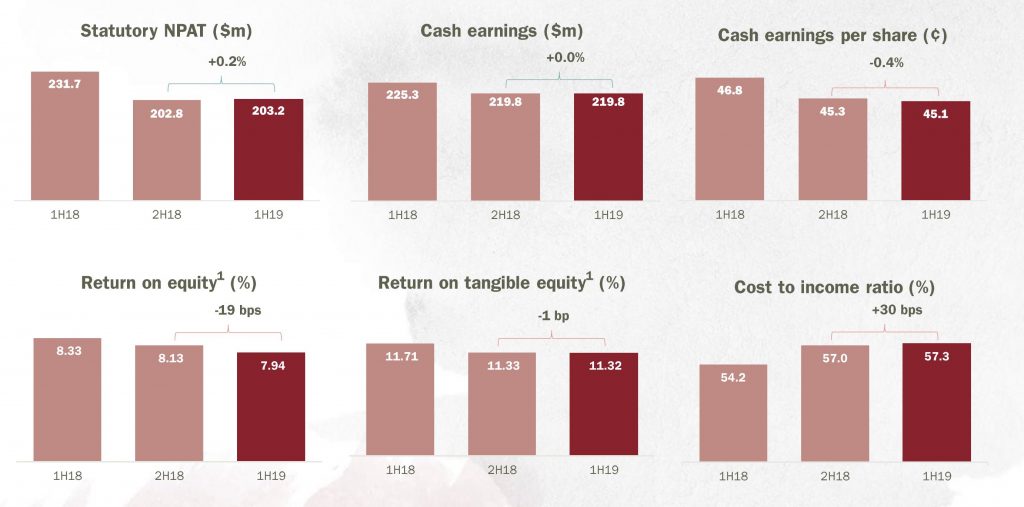
Yesterday Bendigo and Adelaide Bank released their results for the half year to December 2018. The after tax statutory profit was $203.2 million up 0.2% on the prior half, but significantly lower than the $231.7 million in 1H18. The cash earnings was flat at $219.8 million, but again lower than $225.3 million in 1H18. The earnings per share was 45.1 cents, down 0.2 cents and the fully franked dividend was 35 cents per share. The return on equity fell 19 basis point half on half.
They are positioning as “Australia’s fifth largest retail bank” and they saw a rise of 18% in new customers joining and according to research are the 9th most trusted brand in Australia. Have no doubt the franchise and “local” approach is attractive to some customers, but the question is, can the current formula work in the current tight margin, highly competitive market at a time when home loan momentum is falling. One signal is cost to income, which is rising – a reflection of the high touch model.
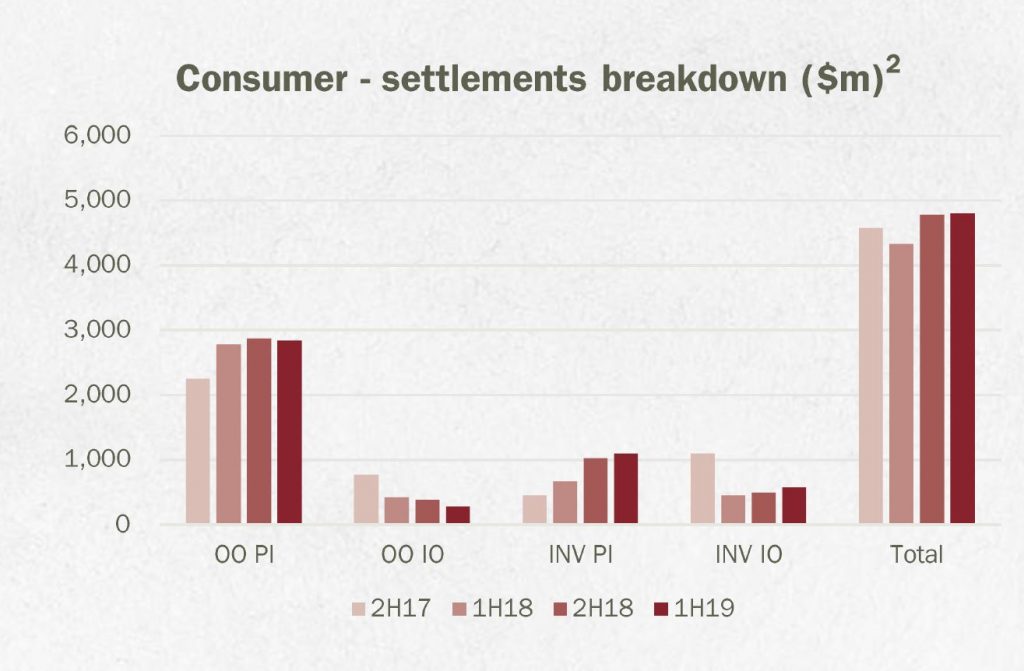
Mortgage book growth was 2.7%, compared with system growth of 3.3% with a portfolio of $23.1 billion. They saw more growth in investor loans than owner occupied loans.
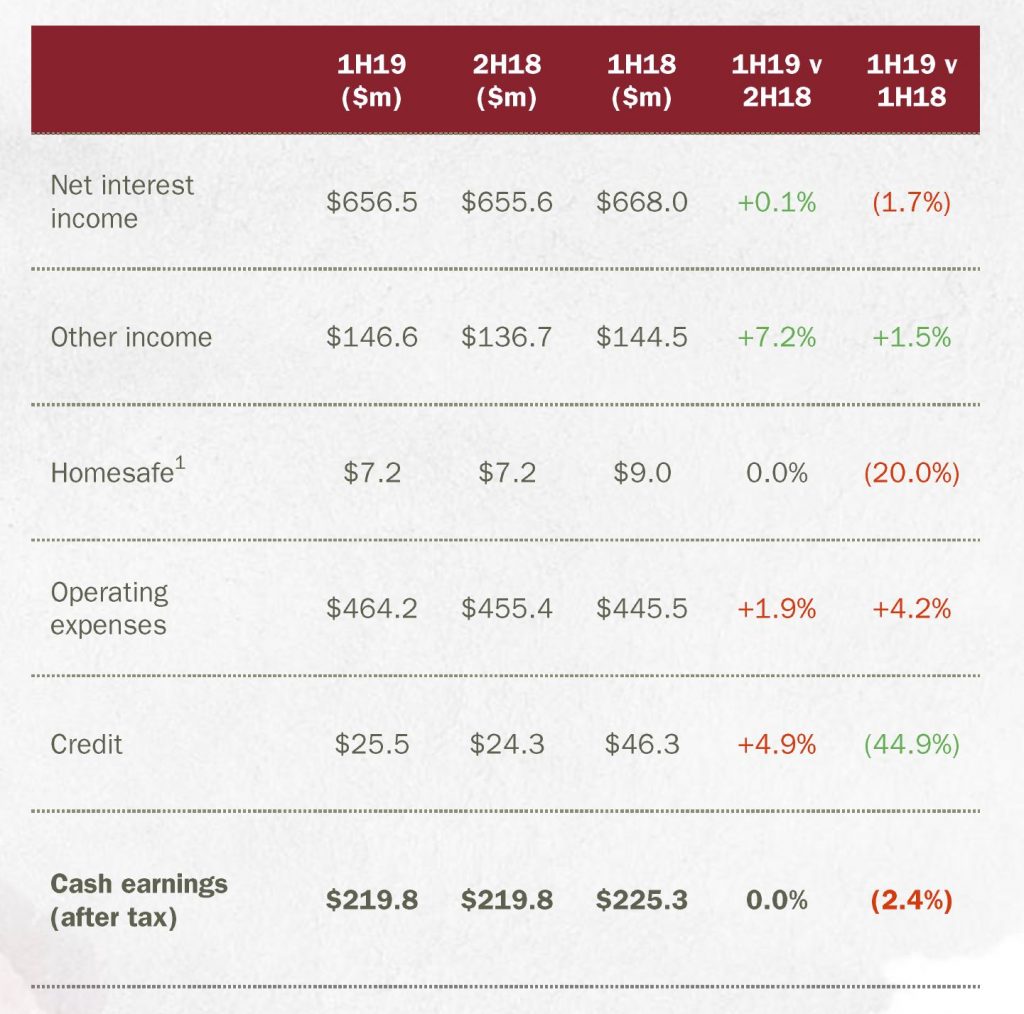
Earnings were support by other income (card activity and commissions on managed funds plus FX transactions), but net interest income was flat and Homesafe reflects changes to its accounting treatment.
Net interest margin was down 2 basis points reflecting discounting for new loans, higher funding costs and deposit repricing.
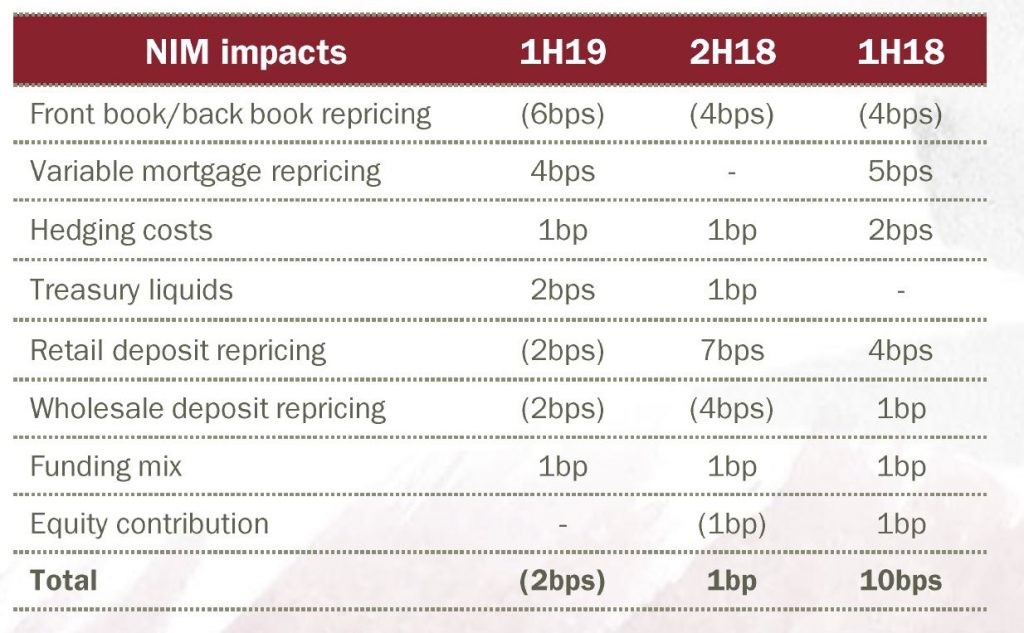
The exit margin was 2.34% and will remain under pressure ahead.
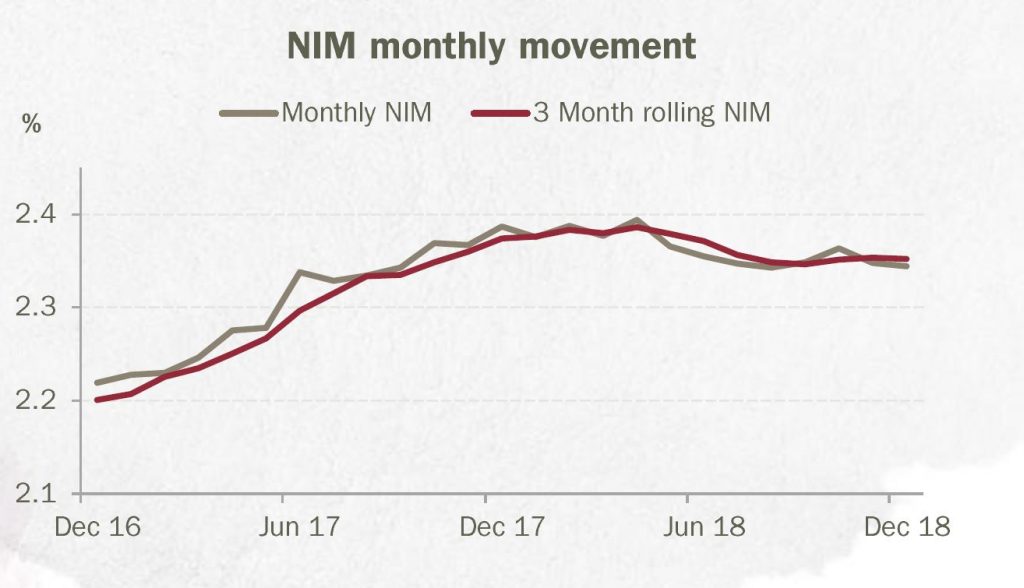
Homesafe contribution was subject to a review of their portfolio valuation methodology, as a result they removed the overlay and revised down valuation growth rates to 0% in year 1, 3% year 2 and 4% year 3 and beyond. The result was a $1.9m change to the valuation. Essentially, they tweaked the property valuations lower (from 6% growth) but then changed the discount rate to mask the effect. A little sneaky! We said last year their home price projections were heroic… but there is still more downside risk here in our view.
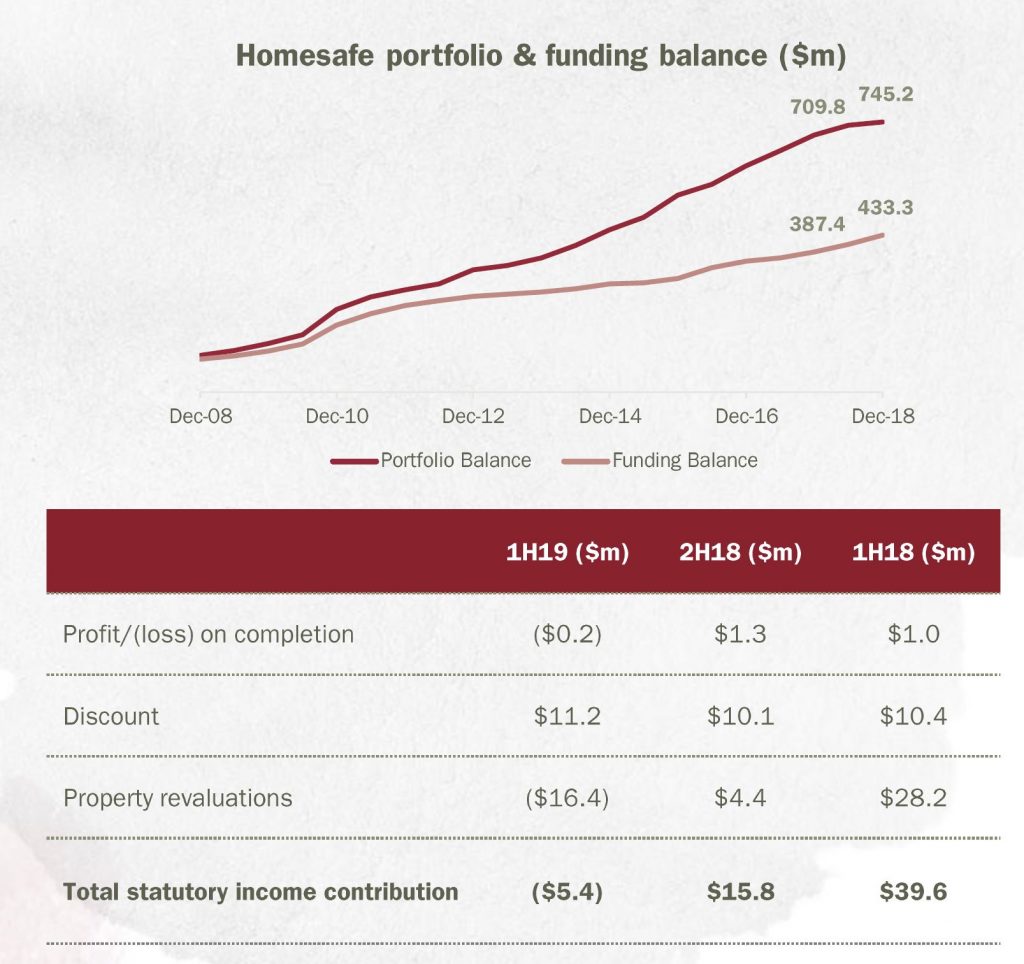
Their costs were higher, up 30 basis points to a cost income ratio of 57.3%, including higher staff costs, technology and legal and compliance.
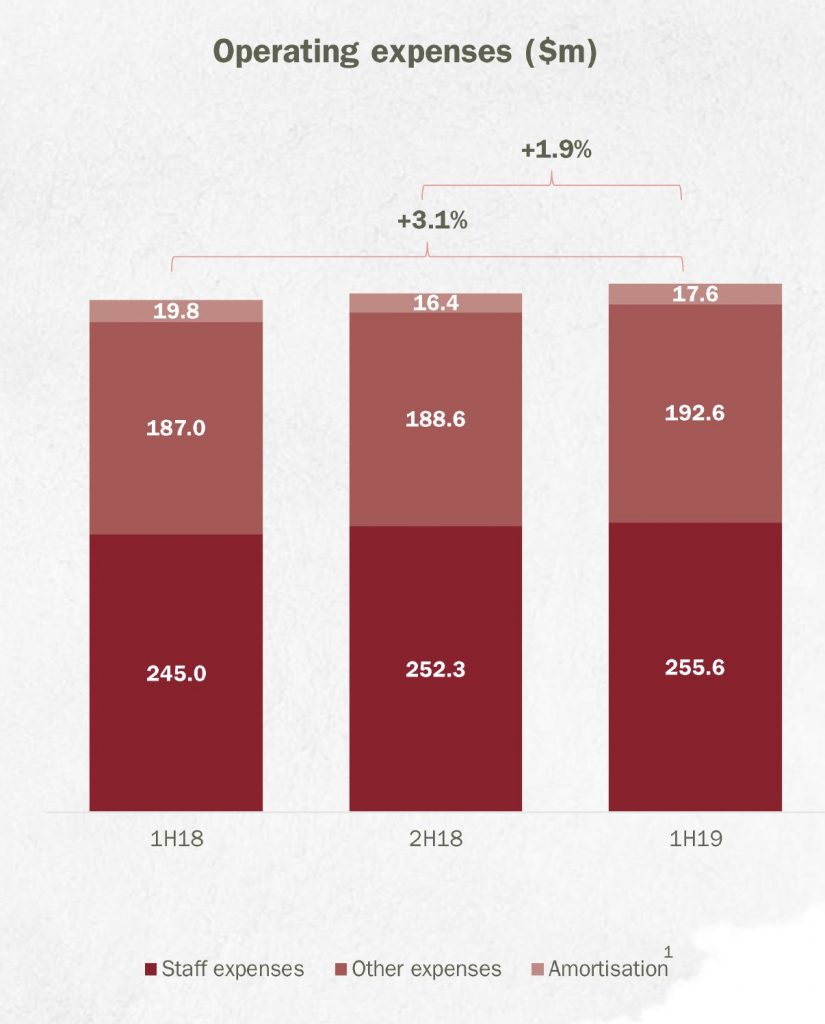
Along with the other banks, they continue to adjust their provisions to AASB9 which has lifted the collective provisions. It stands at 8 basis points, below the long term average.
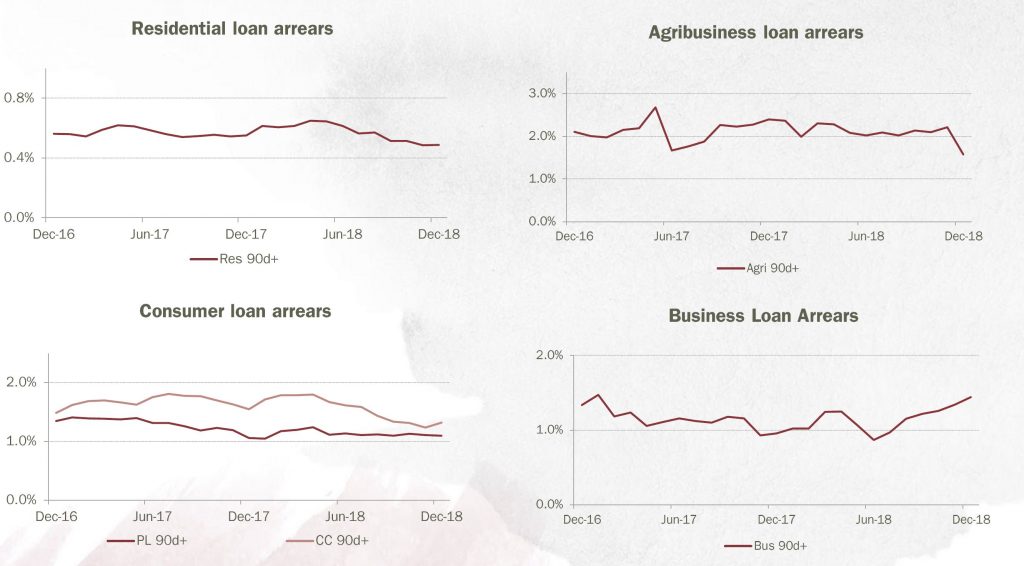
Arrears appears well contained at the moment. There was a small spike in 90 days plus credit card arrears, and business loans. Note though these figures EXCLUDE impaired loans over 90 days.
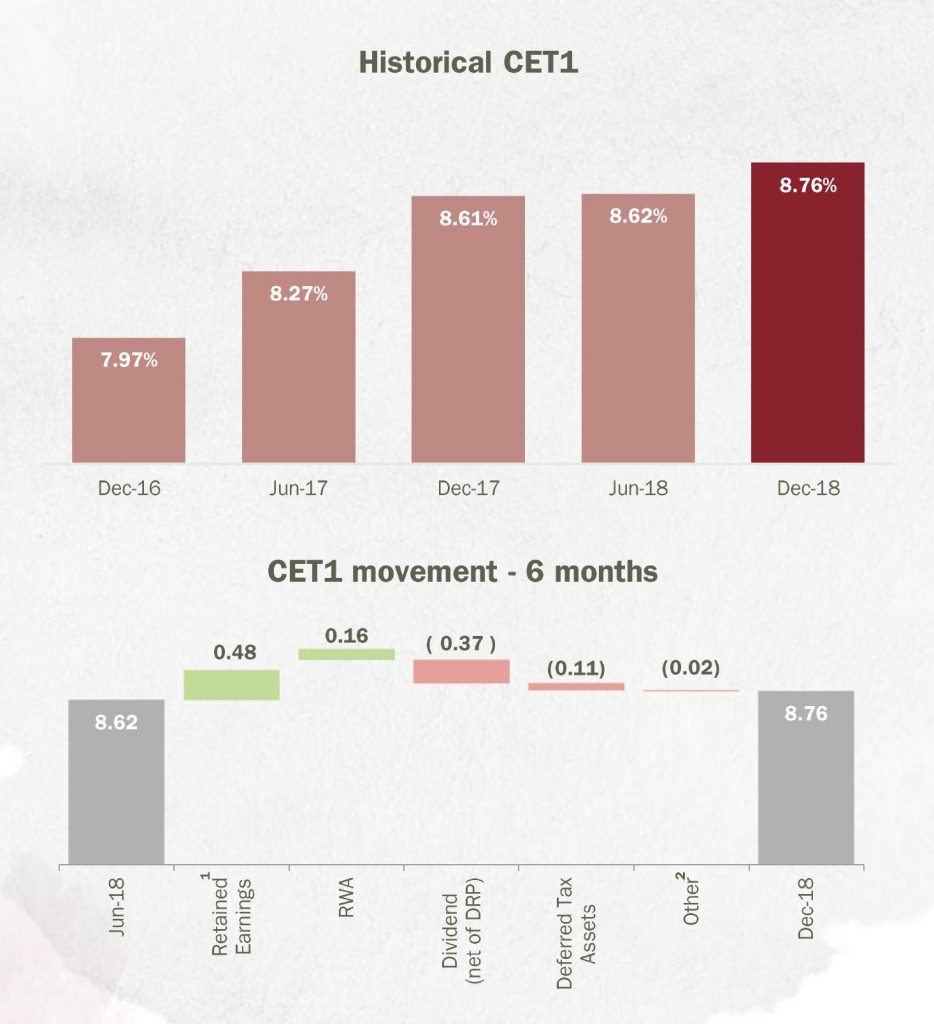
Capital position is 8.76% CET1, up 14 basis points. They are still working on advanced APRA accreditation (though the benefit looks increasing questionable in my view given APRA’s moves to lift the advanced ratios, relative to standard approaches.
Funding from deposits increased to 82.4% but they noted that higher BBSW impacted the cost of wholesale and securitisation funding.
So to conclude, we wonder about ongoing margin compression and the slowing housing sector and mortgage growth. Their cost base appears to contain significant fixed elements, which means they may have ongoing cost ratio issues. The benefit of advanced capital accreditation may be lower as APRA turns the screws. A tricky time for a player which gets the consumer, but has difficulty in competing in the current environment.
