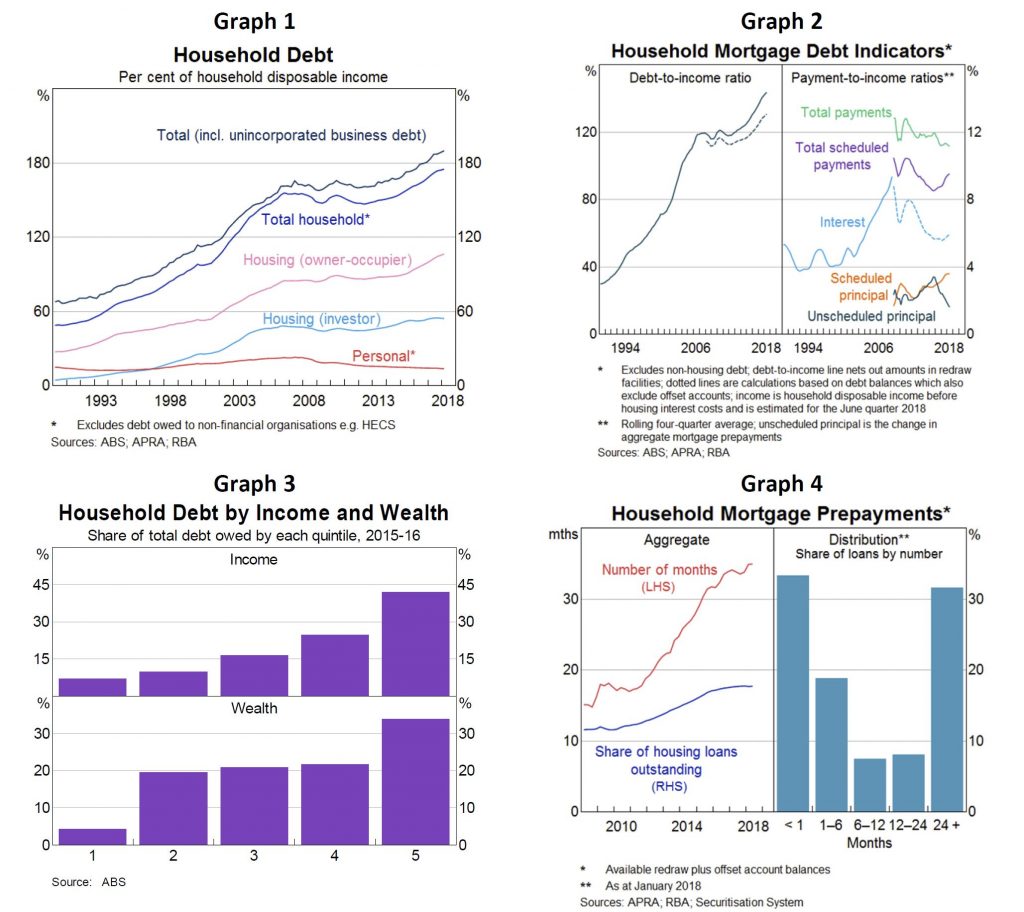
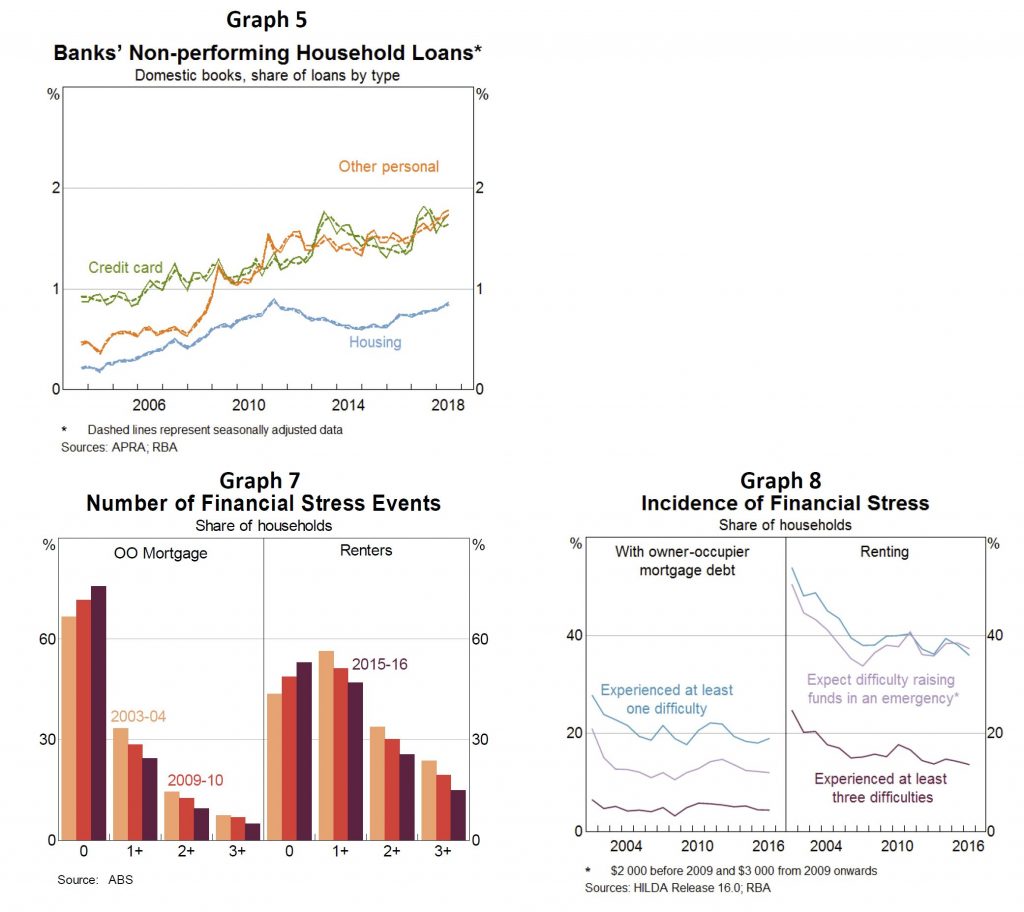
Credit rating agency Fitch Ratings has changed its outlook on Westpac and ANZ from “stable” to “negative”, following APRA’s update of its capital requirements for the major banks. Via InvestorDaily.

While the additional operational capital requirements should remain manageable for the banks, Fitch said the main driver for the changes were driven by a concern for governance and culture in the institutions.
Westpac recently released its self-assessment on governance, accountability and culture, admitting significant shortcomings.
The big four evaluated themselves last year when APRA chair Wayne Byres wrote to the country’s banks, insurers and super licensees after the CBA prudential inquiry. He asked them to determine whether weaknesses uncovered at CBA existed in their companies.
The result of the self-assessments led APRA last week to increase the minimum capital requirements by $500 million and prompted Westpac to release publicly its self-assessment.
ANZ is the only bank of the big four which has yet to publish its self-assessment.
“The additional capital requirements should remain manageable and not impair the bank’s ability to meet APRA’s ‘unquestionably strong’ targets starting in 2020, but it indicates material shortcomings in operational risk management, which were not aligned to what Fitch had previously incorporated into its ratings,” Fitch said in its update on Westpac.
“This has resulted in a downward revision to our score for management and strategy and weaker outlook on earnings and profitability.”
The rating agency made a similar note on ANZ, saying APRA’s findings indicated deficiencies within both companies’ management of operational and compliance risks, culture and governance.
However, Westpac said Fitch’s affirmation of its rating at AA- meant despite the challenges the bank faces, the credit agency expects it to “maintain its strong company profile in the short term, which in turn supports its strong financial profile.”
Likewise, ANZ was reaffirmed at AA- for both its banking group and New Zealand company. Fitch stated the group “continues to have robust risk and reporting controls around other risks, including credit, market and liquidity risk, as reflected by its conservative underwriting standards and very high degree of asset quality stability.”
Separately, on 9 July S&P Global Ratings affirmed the AA- long-term and A-1+ short-term issuer credit ratings and revised its outlook on the major Australian banks to “stable” from “negative.”
Westpac commented: “This outlook change reflects S&P’s view that the Australian government remains highly supportive of Australia’s systemically important banks based on APRA’s release on loss absorbing capacity.”