Recent events have the potential to create a revolution in Australian Finance. We explore the 72 hours that changed banking forever.
 Welcome to the Property Imperative Weekly to 10th February 2018.Watch the video or read the transcript.
Welcome to the Property Imperative Weekly to 10th February 2018.Watch the video or read the transcript.
In our latest weekly digest, we start with the batch of new reports, all initiated by the current Australian Government – and which combined have the potential to shake up the Financial Services sector, and reduce the excessive market power which the four major incumbents have enjoyed for years.
On Wednesday, the Productivity Commission, Australian Government’s independent research and advisory body released its draft report into Competition in the Australian Financial System. It’s a Doozy, and if the final report, after consultation takes a similar track it could fundamentally change the landscape in Australia. They leave no stone unturned, and yes, customers are at a significant disadvantage. Big Banks, Regulators and Government all cop it, and rightly so. They say, Australia’s financial system is without a champion among the existing regulators — no agency is tasked with overseeing and promoting competition in the financial system. It has also found that competition is weakest in markets for small business credit, lenders’ mortgage insurance, consumer credit insurance and pet insurance. The report demonstrates the inter-linkages between difference financial entities, and their links to the four majors. They criticised mortgage brokers and financial advisers for poor advice (influenced by commission and ownership structures) and the regulatory environment, where the shadowy Council of Finance Regulators (RBA, ASIC, APRA and Treasury) do not even release minutes of the meetings which set policy direction. You can watch our separate video blog on this.
On Thursday, the Treasurer released draft legislation to require the big four banks to participate fully in the credit reporting system by 1 July 2018. They say this measure will give lenders access to a deeper, richer set of data enabling them to better assess a borrower’s true credit position and their ability to pay a loan. This removes the current strategic advantage which the majors have thanks to the credit data asymmetry, and the current negative reporting. We note that there is no explicit consumer protection in this bill, relating to potential inaccuracies of data going into a credit record. This is, in our view a significant gap, especially as the proposed bulk uploading will require large volumes of data to be transferred. It does however smaller lenders to access information which up to now they could not, so creating a more level playing field. Consumers may benefit, but they should also beware of the implications of the proposals.
On Friday, Treasurer Morrison released the report by King & Wood Mallesons partner Scott Farrell in to open banking which aims to give consumers greater access to, and control over, their data and which mirrors developments in the UK. This “open banking” regime mean that customers, including small businesses, can opt to instruct their bank to send data to a competitor, so it can be used to price or offer an alternative product or service. Great news for smaller players and fintechs, and possibly for customers too. Bad news for the major players. The report recommends that the open banking regime should apply to all banks, though with the major banks to join it first. For non-banks and fintechs, the report wants a “graduated, risk-based accreditation standard”. Superannuation funds and insurers are not included for now. In terms of implementation, data holders should be required to allow customers to share information with eligible parties via a dedicated application programming interface, not screen scraping. A period of approximately 12 months between the announcement of a final Government decision on Open Banking and the Commencement Date should be allowed for implementation. From the Commencement Date, the four major Australian banks should be obliged to comply with a direction to share data under Open Banking. The remaining Authorised Deposit-taking Institutions should be obliged to share data from 12 months after the Commencement Date, unless the ACCC determines that a later date is more appropriate.
Then of course the Royal Commission in Financial Services starts this coming week. We discussed this on ABC The Business on Thursday. Lending Practice is on the agenda, highly relevant given the new UBS research (they of liar loans) suggesting that incomes of many more affluent households are significantly overstated on mortgage application forms. And The BEAR – the bank executive behaviour regime legalisation – passed the Senate, and as a result of amendments, Small and medium banking institutions have until 1 July 2019 to prepare for the BEAR while it will commence for the major banks on 1 July 2018.
APRA Chairman Wayne Byers spoke at the A50 Australian Economic Forum, Sydney. Significantly, he says the temporary measures taken to address too-free mortgage lending will morph into the more permanent focus on among other things, further strengthening of borrower serviceability assessments by lenders, strengthened capital requirements for mortgage lending, and the comprehensive credit reporting being mandated by the Government.
Adelaide Bank is ahead of the curve, as it introducing an alert system that will monitor property borrowers that are struggling with their repayments. The bank and its subsidiaries and affiliates will compare monthly mortgage repayments with borrowers’ income ratios. In addition, extra scrutiny will be applied where the loan-to-income ratio exceeds five times or monthly mortgage repayments exceed 35% of a borrower’s income.
But combined, data sharing, positive credit and banking competition and regulation are all up in the air, or are already coming into force and in each case it appears the big four incumbents are the losers, as they are forced to share customer data, and competition begins to put their excessive profitability under pressure. It highlights the dominance which our big banks have had in recent years, and the range of reforms which are in train. The face of Australian Banking is set to change, and we think customers will benefit. But wait for the rear-guard actions and heavy lobbying which will take place ahead.
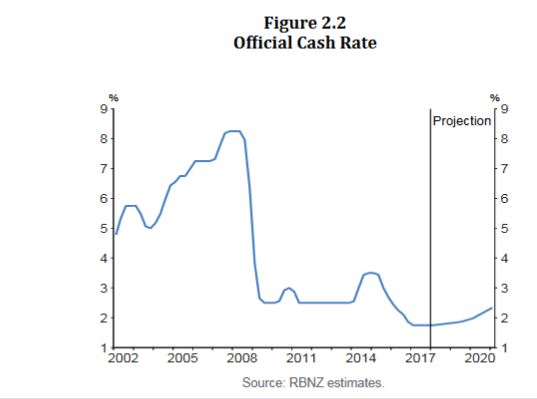
Of course the RBA left the cash rate on hold this week, and signalled the next move will likely be up, but not for some time. Retail turnover for December fell 0.5% according to the ABS seasonally adjusted. This is the headline which will get all the coverage, but the trend estimate rose 0.2 per cent in December 2017 following a rise of 0.2 per cent in November 2017. Compared to December 2016 the trend estimate rose 2.0 per cent. This is in line with average income growth, but not good news for retailers.
The latest Housing Finance Data from the ABS shows a fall in flows in December. In trend terms, the total value of dwelling finance commitments excluding alterations and additions fell 0.1% or $31 million. Owner occupied housing commitments rose 0.1% while investment housing commitments fell 0.5%. Owner occupied flows were worth $14.8 billion, and down 0.3% last month, while owner occupied refinancing was $6.2 billion, up 1.2% or $73 million. Investment flows were worth 11.9 billion, and fell 0.5% or $62 million. The percentage of loans for investment, excluding refinancing was 45%, down from 49% in Dec 2016. Refinancing was 29.5% of OO transactions, up from 29.2% last month. Momentum fell in NSW and VIC, the two major states. In original terms, the number of first home buyer commitments as a percentage of total owner occupied housing finance commitments fell to 17.9% in December 2017 from 18.0% in November 2017 – the number of transactions fell by 1,300 compared with last month. But the ABS warns that the First Time Buyer data may be revised and users should take care when interpreting recent ABS first home buyer statistics. The ABS plans to release a new publication which will see Housing Finance, Australia (5609.0) and Lending Finance, Australia (5671.0) combined into a single, simpler publication called Lending to Households and Businesses, Australia (5601.0).
We continue to have data issues with mortgage lending, with the RBA in their new Statement on Monetary Policy saying it now appears unnecessary to adjust the published growth rates to undo the effect of regular switching flows between owner occupied and investment loans as they have been doing for the past couple of years. So now investor loan growth on a 6-month basis has been restated to just 2%. More fluff in the numbers! Additionally, the RBA will publish data on aggregate switching flows to assist with the understanding of this switching behaviour.
More data this week highlighting the pressures on households. National Australia Bank’s latest Consumer Behaviour Survey, shows the degree of anxiety being caused by not only cost of living pressures but also health, job security, retirement funding as well as Australian politics. Of all the things bothering Australian households in early 2018, nothing surpasses cost of living pressures. Over 50% of low income earners reported some form of hardship, with almost one in two 18 to 49-year-olds being effected.
Despite improved job conditions and households reporting healthier financial buffers, the overall financial comfort of Australians is not advancing, according to ME’s latest Household Financial Comfort Report. In its latest survey, ME’s Household Financial Comfort Index remained stuck at 5.49 out of 10, with improvements in some measures of financial comfort linked to better employment conditions – e.g. a greater ability to maintain a lifestyle if income was lost for three months – offset by a fall in comfort with living expenses.
We released the January 2018 update of our Household Financial Confidence Index, using data from our rolling 52,000 household surveys. The news is not good, with a further fall in the composite index to 95.1, compared with 95.7 last month. This is below the neutral setting, and is the eighth consecutive monthly fall below 100. Costs of living pressures are very real, with 73% of households recording a rise, up 1.5% from last month, and only 3% a fall in their living costs. A litany of costs, from school fees, child care, fuel, electricity and rates all hit home. You can watch our separate video on this.
We also published updated data on net rental yields this week, using data from our household surveys. Gross yield is the actual rental stream to property value, net rental is rental payments less the costs of funding the mortgage, management fees and other expenses. This is calculated before any tax offsets or rebates. The latest results were featured in an AFR article. The results are pretty stark, and shows that many property investors are underwater in cash flow terms – not good when capital values are also sliding in some places. Looking at rental returns by states – Hobart and Darwin are the winners; Melbourne, and the rest of Victoria, then Sydney and the rest of NSW the losers. The returns vary between units and houses, with units doing somewhat better, and we find some significant variations at a post code level. But we found that more affluent households are doing significantly better in terms of net rental returns, compared with those in more financially pressured household groups. Batting Urban households, those who live in the urban fringe on the edge of our cities are doing the worst. This is explained by the types of properties people are buying, and their ability to select the right proposition. Running an investment property well takes skill and experience, especially in the current rising interest rate and low capital growth environment. Another reason why prospective property investors need to be careful just now.
Finally, we saw market volatility surge, as markets around the world gyrated following the “good news” on US Jobs last week, which signalled higher interest rates. In our recent video blog we discussed whether this is a blip, or something more substantive. We believe it points to structural issues which will take time to play out, so expect more uncertainly, on top of the correction which we have already had. This will put more upward pressure on interest rates, and also on bank funding here.
Overall then, a week which underscores the uncertainly across the finance sector, and households. This will not abate anytime soon, so brace for a bumpy ride. And those managing our large banks will need to adapt to a fundamentally different, more competitive landscape, so they are in for some sleepless nights.
If you found this useful, do like the post, add a comment and subscribe to receive future updates. Many thanks for taking the time to watch.