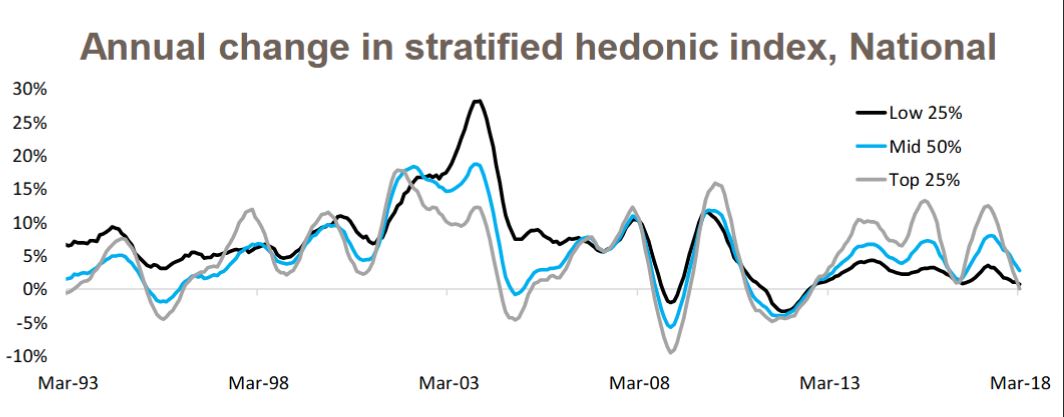
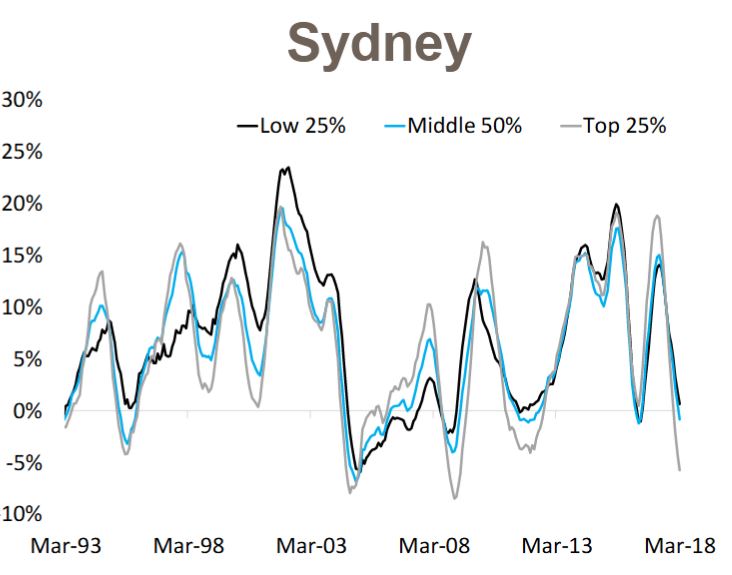
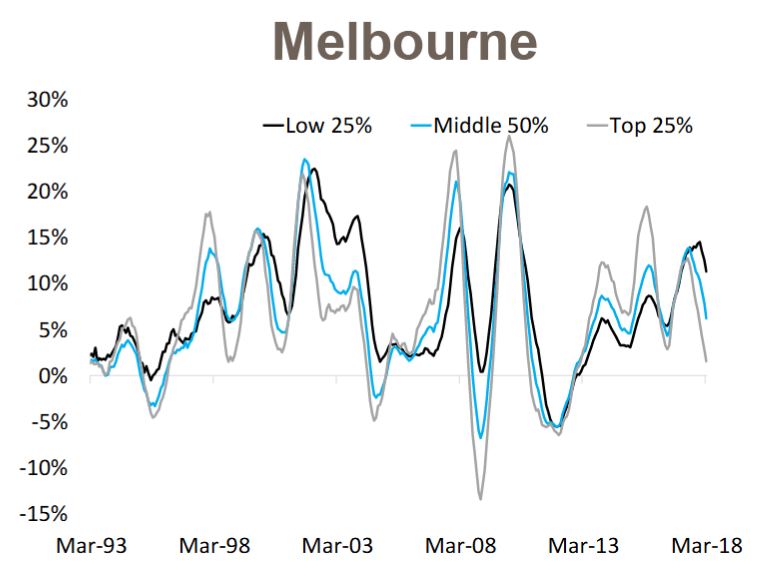
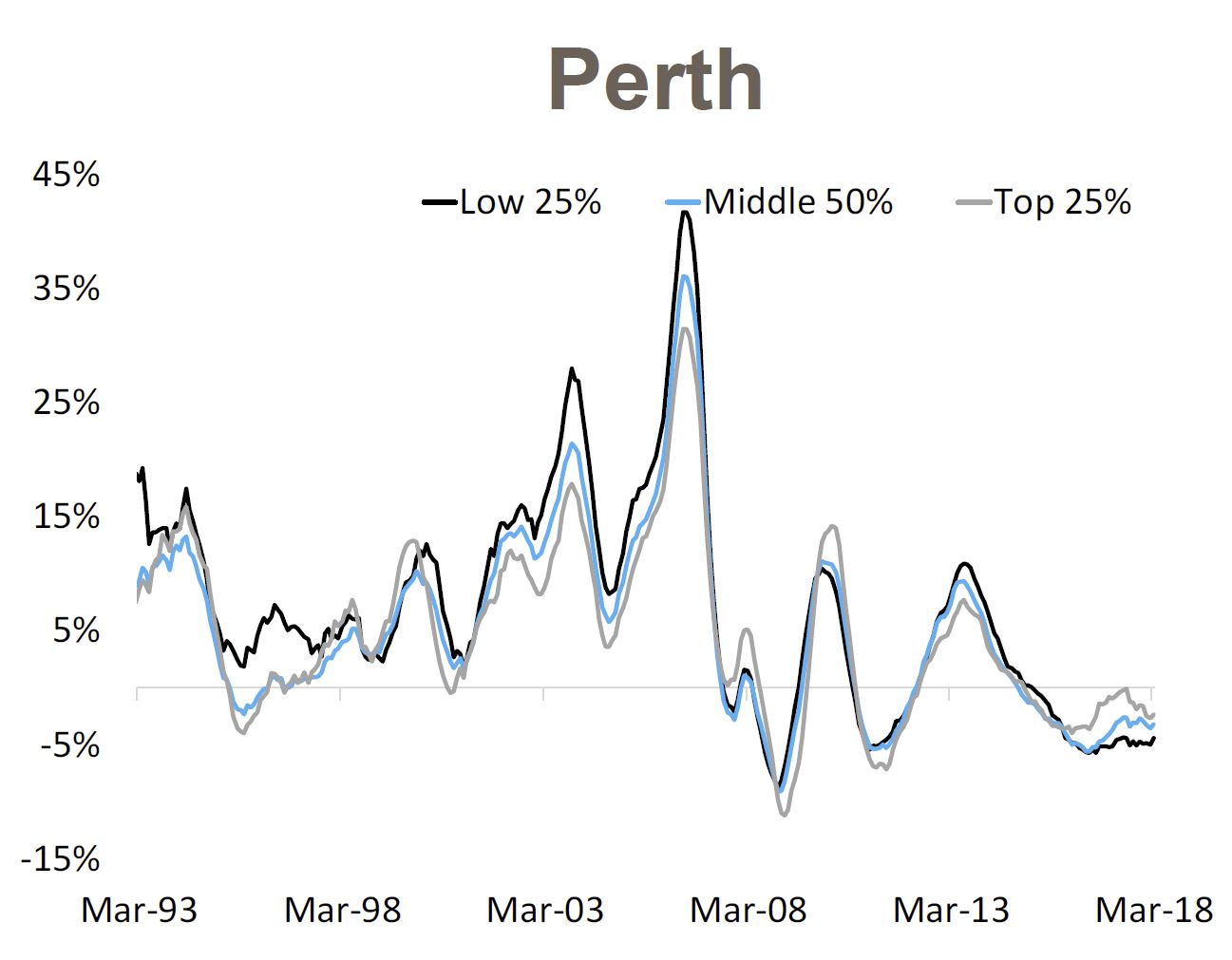
The finance sector unmentionable hits the proverbial fan. Welcome to the Property Imperative Weekly to 21st April 2018.
 We start this week’s review of the latest finance and property news with the latest from the Royal Commission into Financial Services Misconduct.
We start this week’s review of the latest finance and property news with the latest from the Royal Commission into Financial Services Misconduct.
After the shameful disclosures relating to poor lending practices, bad advice, misaligned incentives and poor regulation last time; now they have been looking to the nether regions of financial planning and advice. And guess what, the same behaviours are evident again, in spades. Bearing in mind 48% of the $4.6 billion annual revenue from wealth management goes to the big four banks and AMP, they were forced to admit their mistakes in public. You can watch our separate video on the detailed findings “More Cultural Badness from The Finance Sector”. But here are a few highlights.
AMP apologised unreservedly for the misconduct and failures in regulatory disclosures in the advice business as revealed in the Royal Commission and Chief Executive Officer, Craig Meller will step down from his role with immediate effect.
The Australian Bankers Association admitted that the issues raised have been unacceptable and do not meet the high standards the community rightly expects of banks. And the Treasurer announced significant increases in penalties ASIC can impose. The government will increase penalties under the Corporations Act to: “For individuals: 10 years’ imprisonment; and/or the larger of $945,000 OR three times the benefits; For corporations: the larger of $9.45 million OR three times benefits OR 10% of annual turnover. “The Government will expand the range of contraventions subject to civil penalties, and also increase the maximum civil penalty amounts that can be imposed by courts, to the maximum of: the greater of $1.05 million (for individuals, from $200,000) and $10.5 million (for corporations, from $1 million); or three times the benefit gained or loss avoided; or 10% of the annual turnover (for corporations). “In addition, ASIC will be able to seek additional remedies to strip wrongdoers of profits illegally obtained, or losses avoided from contraventions resulting in civil penalty proceedings.”
These increases are right, as before the financial impact of poor behaviour was very low. However, do not be misled, changing penalties will not address the fundamental cultural, structural and economic issues which have combined to deliver a finance sector which is simply not fit for purpose.
We need to remove incentives from the advice sector (mortgage brokers included). Actually we need unified regulation across credit and wealth sectors (the current two regimes are an accident of history).
We need structural separate and disaggregation of our financial conglomerates. We need a realignment of interests to focus on the customer – which by the way is not at odds with shareholder returns, as customer focus builds franchise value and returns in the long term.
We need cultural reform and new values from our finance sector leaders. And Executive Pay should come under the spot light.
We need a reform of the regulatory structure in Australia, because they are captured at the moment at least by group think, and their interests are aligned too closely to the finance sector. This must include ASIC, APRA, RBA and ACCC. All have bits of the finance puzzle, but no one is seriously accountable.
But there is a more fundamental issue. We have relied on overblown credit, and superannuation sectors, as a proxy for high quality economic growth. This inflated housing and lifted household debt and GDP. We need a fundamental economic reset, because reforming financial services alone won’t solve our underlying issues.
The Government, who resisted the Royal Commission, has now also indicated they are receptive to expanding the scope and term of the inquiry, which in my view should include regulation of the sector, and the macroprudential settings in place. So write to the Commissioner, and your MP advocating a broader scope.
Finally, on this, it is worth noting that former deputy prime minister Barnaby Joyce went with a full-monty confession. “In the past I argued against a Royal Commission into banking. I was wrong. What I have heard … so far is beyond disturbing”, he tweeted. Joyce is now a backbencher, and free with his opinions. It’s another story with current ministers. They continue trying to score political points over Labor, which had been agitating for a royal commission long before it was set up.
My suggestion is this financial sector mess is so significant, that both sides of politics should set aside party differences and focus on the main game. Because what happens next will fundamentally determine the future economic success of the country, no less. If we continue with the current sets of assumptions we will run the country into the ground as the debt burden becomes unbearable, and savings for retirement are devalued and destroyed. It’s that serious.
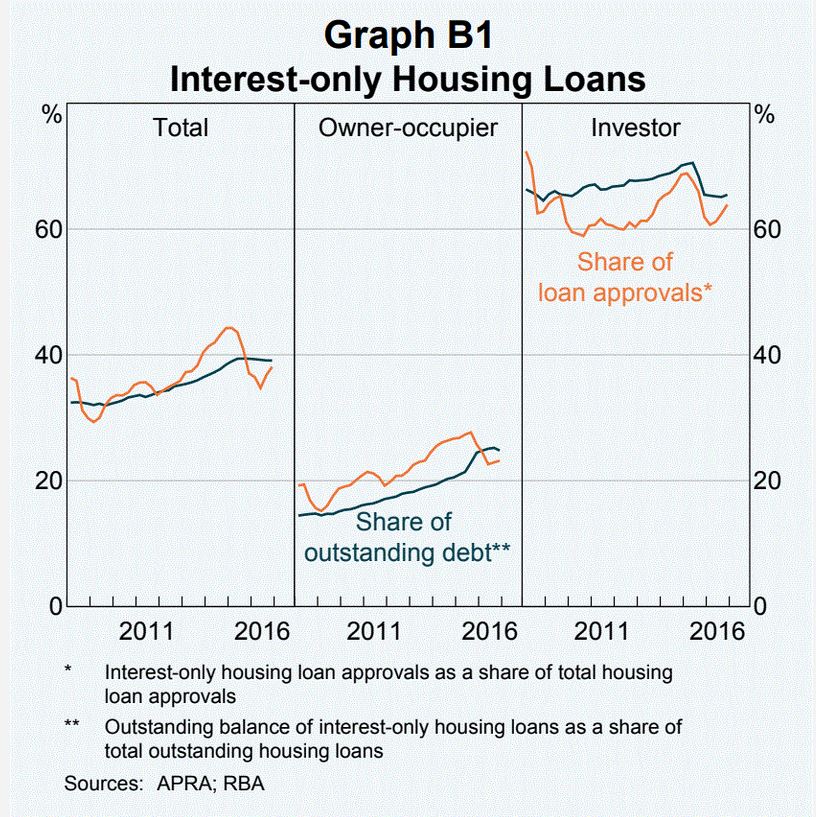
Turning now to more immediate economic news, the latest lending stats from the ABS underscores that the “Great Credit Binge Is Ending”. You can watch our recent video where we discuss the results in full. To start at the end of the story, we see significant falls across most states in investment lending flows, with the most significant falls in the Sydney market. The share of investment flows continues to drift lower, to around 35%. But that is still substantial investment lending! Finally, the percentage of investment lending of all lending flows is below 20%, and shows a small fall. But we also see a fall in business lending to around 55%, excluding investment property lending.
The ABS also released their March 2018 unemployment statistics. It was not good with the trend unemployment rate increasing slightly to 5.6 per cent though the trend participation rate increased to a record high of 65.7 per cent. WA has the highest rate of unemployment at 6.4% and is still rising, whilst rates in NSW and ACT also rose.
The HIA released their latest Housing Affordability report, claiming that affordability improved in most of Australia’s capital cities during the first three months of 2018 as house price pressures eased. But this is largely spin, as their calculations do not necessarily take account of the now tighter, and becoming even tighter lending standards now in play. And in any case, in most centres, affordability is still well below the long term averages. But of course, they are advocates for the property sector, so there should be no surprise.
There was important evidence of the rising costs of funds this week as ME Bank says it has lifted its standard variable rate on existing owner-occupier principal and interest mortgages, effective April 2018. ME’s standard variable rate for existing owner-occupier principal-and-interest borrowers with an LVR of 80% or less, will increase by 6 basis points to 5.09% p.a. Variable rates for existing investor principal-and-interest borrowers will increase by 11 basis points, while rates for existing interest-only borrowers will increase by 16 basis points. ME CEO Mr Jamie McPhee said the changes are in response to increasing funding costs and increased compliance costs. More hikes will follow, across the industry together with reductions in rates paid on deposits as the fallout of the Royal Commission and higher international funding costs take their toll.
For example, the 10-year US Bond rate is moving higher again, following some slight fall earlier in April. Have no doubt, funding cost pressure will continue to rise. We discussed the whole question of debt and the potential trigger for a recession in a recent video blog, “Global Debt and the Upcoming Recession”. The outlook looks more and more like our Armageddon scenario, as we discussed in detail in an earlier programme “Four Scenarios (None Good)”. Worse, regulators in the USA and China are both weakening banking regulation, at this time of high risk, high debt.
Oh, and by the way, we think it quite possible the RBA will need to do its own form of quantitative easing down the track, and that they will most likely buy pools of residential mortgages (yes including those with breached lending standards) to assist the banks in their liquidity, to assist home prices to rise, and allowing the debt bomb to tick for longer. Sound of can being kicked firmly down the road! But that would be the time to buy Australian equities, and even property. Maybe we need a scenario 5!
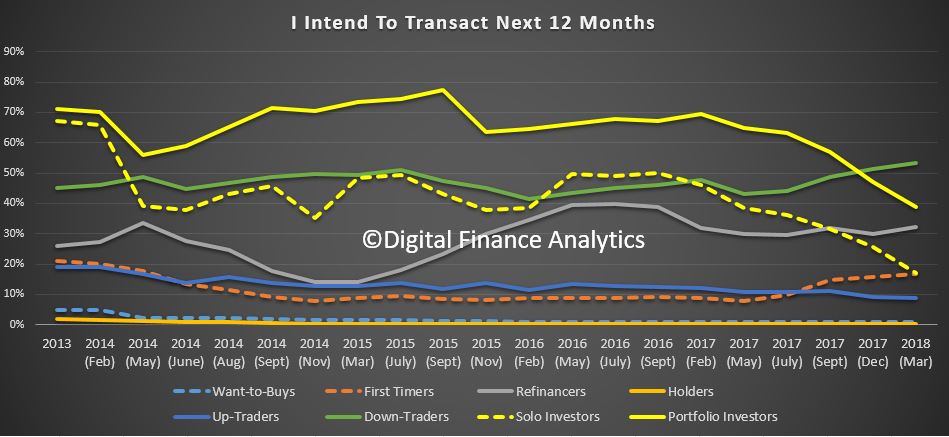
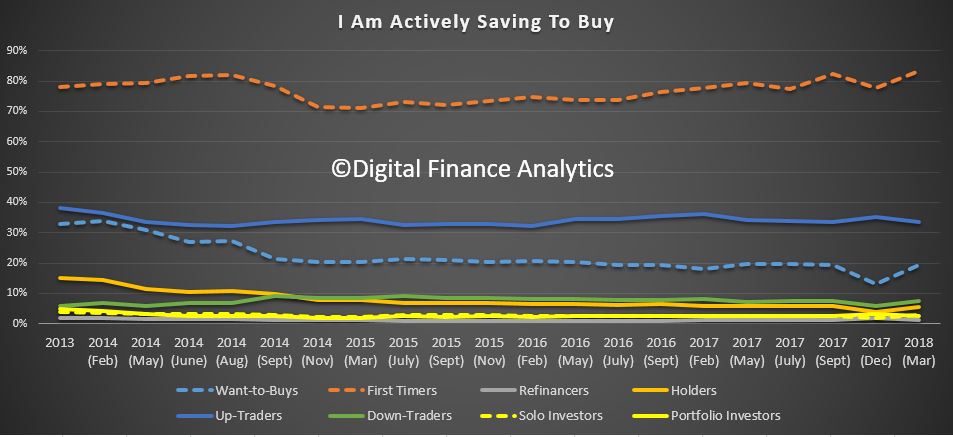
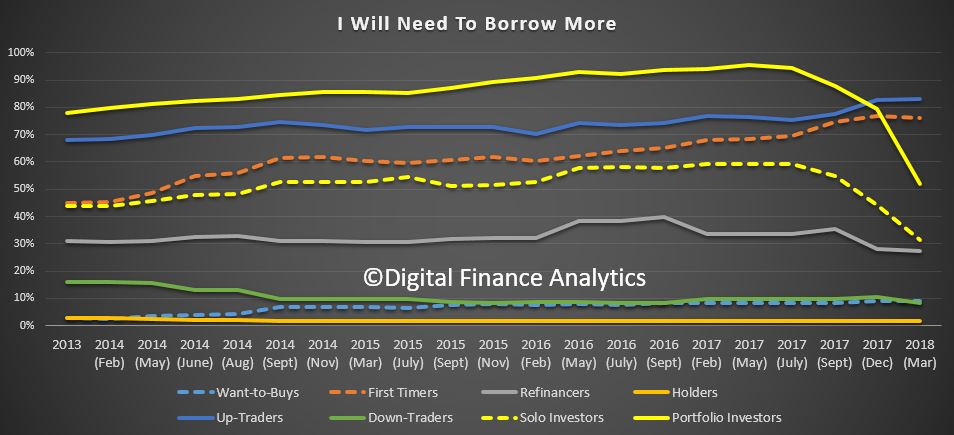
We released the latest Digital Finance Analytics Household Finance Confidence Index for March 2018 shows a further slide in confidence compared with the previous month. The current score is 92.3, down from 94. 6 in February, and it has continued to drop since October 2016. The trend is firmly lower and below the neutral setting. You can watch our separate video on this “Why Household Finance Confidence Fell Again”. But in summary, across the states, confidence is continuing to fall in NSW and VIC, was little changes in SA and QLD, but rose in WA. There were there were falls in all age groups. Turning to the property-based segmentation, owner occupied householders remain the most confident, while property investors continue to become more concerned about the market. Those who are property inactive – renting, or living with parents or friends remain the least confident. Nevertheless, those who are property owners remain more confident relative to property inactive households. Based on the latest results, we see little on the horizon to suggest that household financial confidence will improve. We expect wages growth to remain contained, and home prices to slide, while costs of living pressures continue to grow. There will also be more pressure on mortgage interest rates as funding costs rise, and lower rates on deposits as banks trim these rates to protect their net margins.
Finally, we turn to CoreLogics’s auctions data. They suggest that fewer auctions will take place this week, with a total of 1,592 properties scheduled, compared with last week’s final result of1,915 auctions held. This is also lower than a year ago when 1,751 auctions were held across the capital city markets. Sydney is set to see the most significant drop in activity this week. Victoria’s Reservoir and Surfers Paradise in Queensland both top the busiest suburb list this week, each with 19 properties scheduled to go to auction. Following with 14 scheduled auctions each is Burwood and Point Cook both in Victoria.
Turning to last week’s final results the clearance rate was a 61.7 per cent success rate which was lower than the week prior when 62.8 per cent. Melbourne’s final auction clearance rate fell to 62.4 per cent last week across a slightly higher volume of auctions week-on-week with 873 held, up on the 723 over the week prior when a higher 68.2 per cent cleared. In Sydney, the final clearance rate fell to 61.5 per cent, down on the 62.9 per cent the previous week, with volumes across the city remaining steady over the week with a total of 795 held. Clearance rates improved across all of the remaining auction markets last week, with the exception Tasmania which remained unchanged. Geelong recorded the highest clearance rate of the non-capital city regions, with 77.1 per cent of 54 auctions clearing.
You might want to watch my video on “Auction Results Under The Microscope”, where we discuss how the results are collated and whether we can trust them.
So overall, there is little evidence to suggest the property market is recovering (despite more from the Industry claiming that this was the case, this week). And we have yet to see the impact of tighter lending standards flowing through. Our survey data indicates that more households are finding it tougher to meet the income and expenditure hurdles now, and as a result we expect credit and therefore home prices to continue to fall. And if anything, that fall will likely accelerate, unless we get unusual measures in the budget, which by the way we think are quite likely.